Xiphinema bakeri
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.210165 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6171864 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B47487DD-8031-8142-F9F1-FC40FEC01E97 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Xiphinema bakeri |
| status |
|
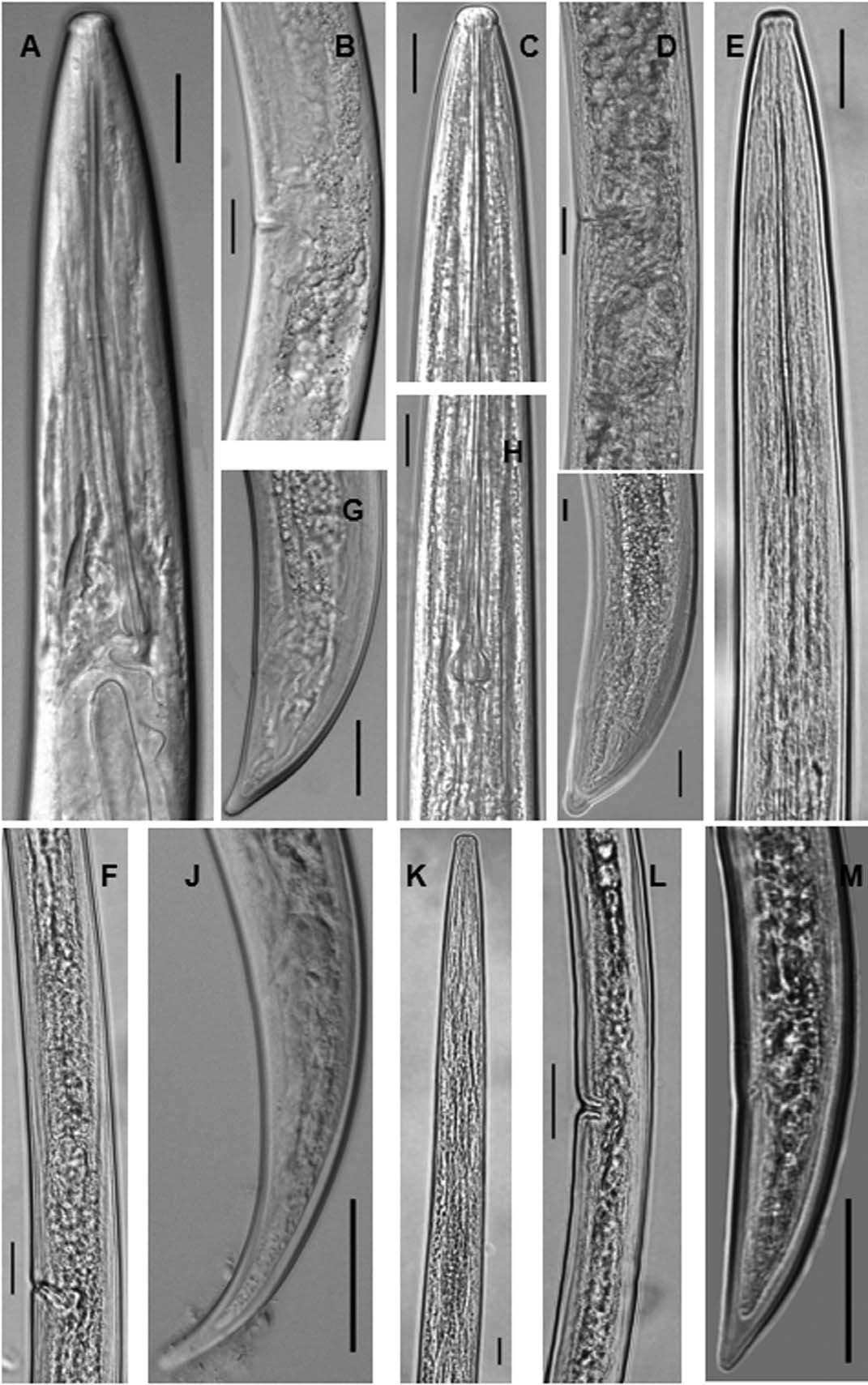
( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 C, D, H, I)
Measurements. See Table 15 View TABLE 15 .
Remarks. Xiphinema bakeri was first described form British Columbia, Canada by Williams (1961). It has been reported from Arkansas ( Ye & Robbins 2010), Iowa ( Norton et al. 1982), Florida ( Tarjan 1974), California, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Oregon, Tennessee, Washington ( Norton et al. 1984; Tarjan 1964b), Korea ( Lee & Han 1976) and Japan ( Yokoo 1970). Xiphinema bakeri was considered to be the primary pathogen in corky root etiology ( Sutherland 1977) and acquired and transmitted arabis mosaic nepovirus in laboratory experiments ( Iwaki & Komuro 1974). In this study, X. bakeri was found in golf course fairways established with bermudagrass in Lee County, NC. The morphological characteristics differed from those described by Williams (1961) in body length and a value in females. This is the first record of X. bakeri from turfgrasses in NC.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Diphtherophorina |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |