Sinopoda subcampanacea, Zhang & Zhang & Zhang, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5244.2.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3DD5186D-20EF-4CFF-8B97-09540B5E74E4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7656190 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/BE1FEA58-9071-FF30-E1A5-BB82FCBE809E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sinopoda subcampanacea |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Sinopoda subcampanacea sp. n.
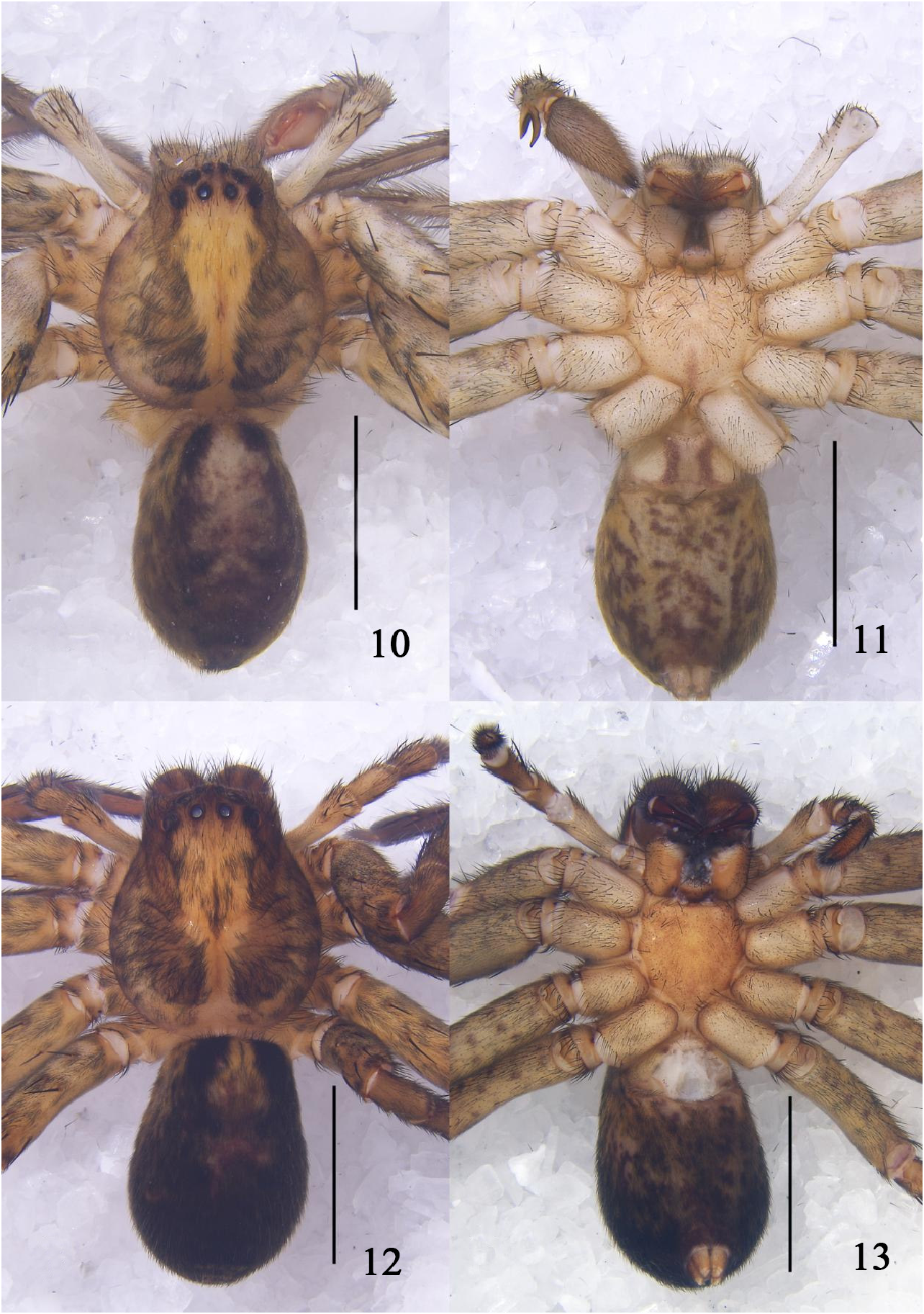
Figs 10–19 View FIGURES 10–13 View FIGURES 14–19
Type material. Holotype male (MHBU-ARA-2021-382-1): CHINA: Gansu Province: Hui County, Jialing Town, Xiaolongshan National Nature Reserve , 34°8′8″N, 106°31′56″E, 1347 m, 15 August 2021, Zhaoyi Li & Rui Zhang leg. GoogleMaps Paratype: 1♀ (MHBU-ARA-2021-382-2), with same data as holotype GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The specific name is an adjective, referring to the similarity to S. campanacea Wang, 1990 ; adjective.
Diagnosis. Males of S. subcampanacea sp. n. differ from other Sinopoda species in having a short, slender embolus, except for S. campanacea ( Wang, 1990: figs 1–5) and S. serrata ( Wang, 1990: figs 17–19). From these species it can be distinguished by the following characters: (1) vRTA with slender distal tip (flat distal tip in S. campancea and absent in S. serrata ); (2) dRTA slender, dorsally bending (thick and ventrally bending in S. campancea and S. serrata ). The female of S. subcampanacea sp. n. is similar to S. campanacea ( Wang, 1990: figs 1–5) in having the narrow lateral lobes and anteriorly situated lobal septum, but can be distinguished by the following combination of characters: (1) the U-shaped anterior margins of the lateral lobes (vs. C-shape in S. campanacea ); (2) short glandular appendages (vs. long in S. campanacea ).
Description. Male (holotype): total length 7.20; prosoma 3.38 long, 3.54 wide; opisthosoma 3.82 long, 2.69 wide. Eye diameters and interdistances: AME 0.18, ALE 0.24, PME 0.18, PLE 0.28; AME–AME 0.14, AME–ALE 0.05, PME–PME 0.33, PME–PLE 0.23. MOA 0.52 long, anterior width 0.50, posterior width 0.69. Endite 0.88 long, 0.60 wide. Leg measurements (mm): I 11.17 (3.12, 1.20, 2.19, 3.36, 1.30), II 13.59 (3.21, 1.52, 3.99, 3.31, 1.56), III 10.00 (3.13, 0.81, 2.24, 2.90, 0.92), IV 10.97 (2.69, 1.22, 2.51, 3.34, 1.21). Leg formula: 2143. Spination: Palp: 131, 101, 2021; Fe: I–IV 323; Pa: I–IV 101; Ti: I–II 1318, III–IV 2328; Mt: I–II 1014, III–IV 2026. Chelicerae with three promarginal and four retromarginal teeth, and with ca. 20 denticles between them.
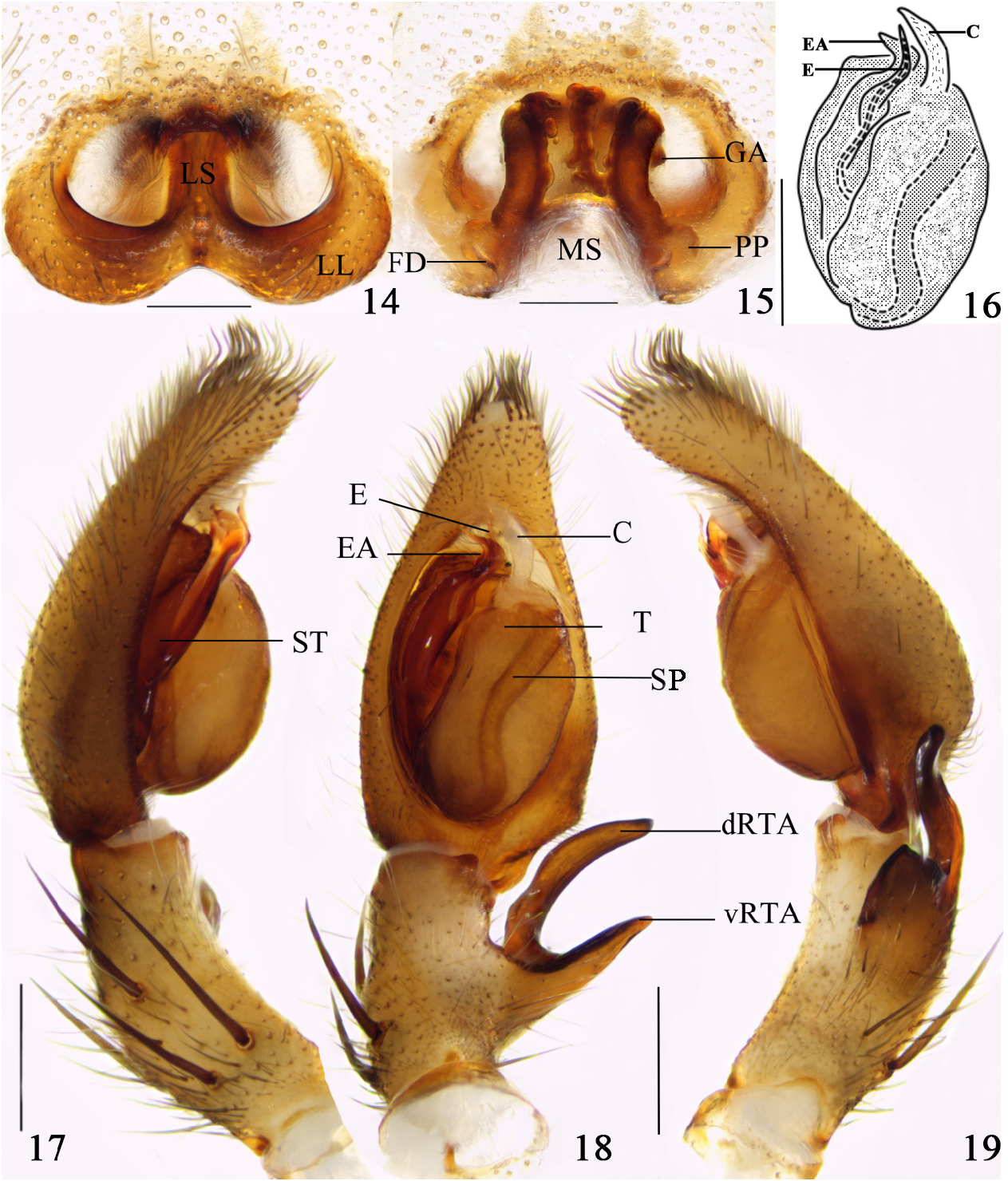
Coloration in ethanol ( Figs 10, 11 View FIGURES 10–13 ): carapace dorsally pale yellowish with two distinct dark lateral bands, posterior part distinctly serrated. Radial furrows and dorsal carapace margins with black hairs. Fovea and radial furrows distinctly marked. Labium pale yellowish, distal parts of labium brighter. Endite longer than wide. Sternum pale yellowish, with black hairs. Legs pale yellowish with dark spots. Dorsal opisthosoma brown, covered by black hairs laterally. Ventral opisthosoma yellowish brown with dark brown spots.
Palp ( Figs 16–19 View FIGURES 14–19 ) as in diagnosis. Embolus arising from tegulum at 8 to 9-o’clock-position (left palp in ventral view), broad at base. Spermophor bent in the middle of the tegulum. dRTA digitiform, dorso-distad in retrolateral view, vRTA broad in retrolateral, acute in ventral view.
Female (paratype): total length 8.54; prosoma 4.15 long, 3.60 wide; opisthosoma 4.39 long, 3.03 wide. Darker in body color than male. Shape, color and markings of body as in male ( Figs 10–13 View FIGURES 10–13 ). Endite 1.05 long, 0.60 wide. Eye diameters and interdistances: AME 0.14, ALE 0.27, PME 0.21, PLE 0.24; AME–AME 0.22, AME–ALE 0.11, PME–PME 0.31, PME–PLE 0.38. MOA 0.45 long, anterior width 0.51, posterior width 0.79. Leg measurements: I 10.48 (3.32, 1.63, 1.90, 2.65, 0.98), II 11.26 (3.31, 1.44, 2.90, 2.66, 0.95), III 9.18 (3.13, 1.35, 1.79, 2.01, 0.90), IV 9.39 (3.46, 1.32, 2.04, 1.86, 0.71). Leg formula: 2143. Spination: Palp: 131, 101, 2021; Fe: I–IV 323; Pa: I–IV 101; Ti: I–II 1318, III–IV 2328; Mt: I–II 1014, III–IV 2026. Chelicerae with three promarginal and four retromarginal teeth, and with ca. 18 denticles between them.
Epigyne with anterior margins of lateral lobes almost parallel to posterior margins; glandular appendages short, bent, posterior-laterad. Posterior part of the internal duct system as wide as the anterior part. Longitudinal fusion bubbles situated between the fertilization ducts ( Figs 14, 15 View FIGURES 14–19 ).
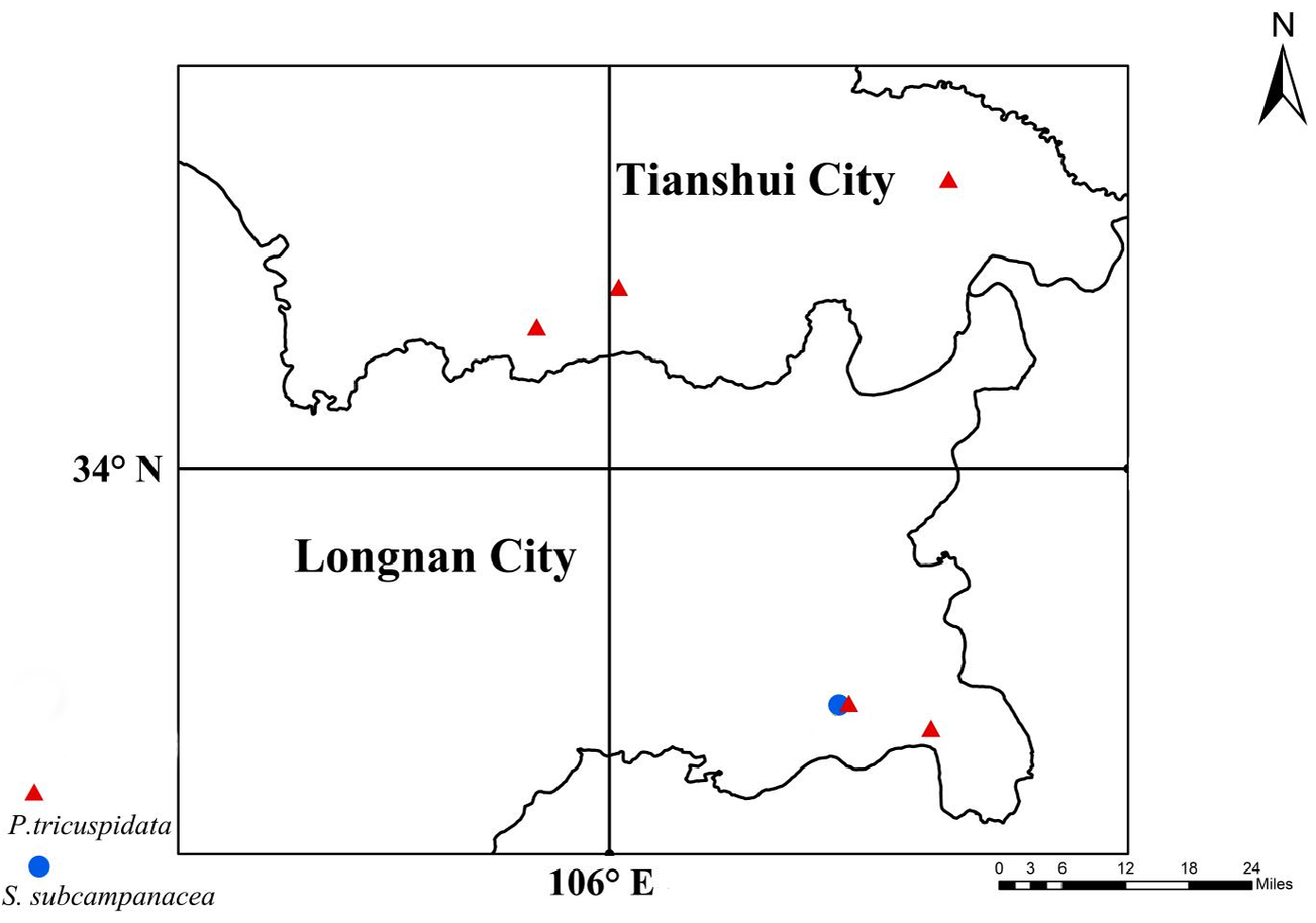
Distribution. Known only from the type locality ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Heteropodinae |
|
Genus |