Simulium (Simulium) thailandicum Takaoka & Suzuki, 1984
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.571608 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C097C43E-D522-46C4-9D64-76D3CD4BAD86 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4927591 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7E4B87AF-B143-A27E-FF2B-FDFAFB5BFAEA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Simulium (Simulium) thailandicum Takaoka & Suzuki, 1984 |
| status |
|
Simulium (Simulium) thailandicum Takaoka & Suzuki, 1984 View in CoL
Simulium (Simulium) thailandicum Takaoka & Suzuki, 1984: 37 View in CoL –38 (Male and pupa).
Distribution. China (Yunnan), Thailand, and Vietnam (Bac Giang, Ha Tay, Lang Son and Yen Bai). Remarks. Simulium (S.) thailandicum was originally described from Thailand ( Takaoka and Suzuki 1984). It was recorded from four provinces in Vietnam by Pham (1998, 1999).
Simulium (Simulium) tavanense Takaoka & Sofian-Azirun sp. nov.
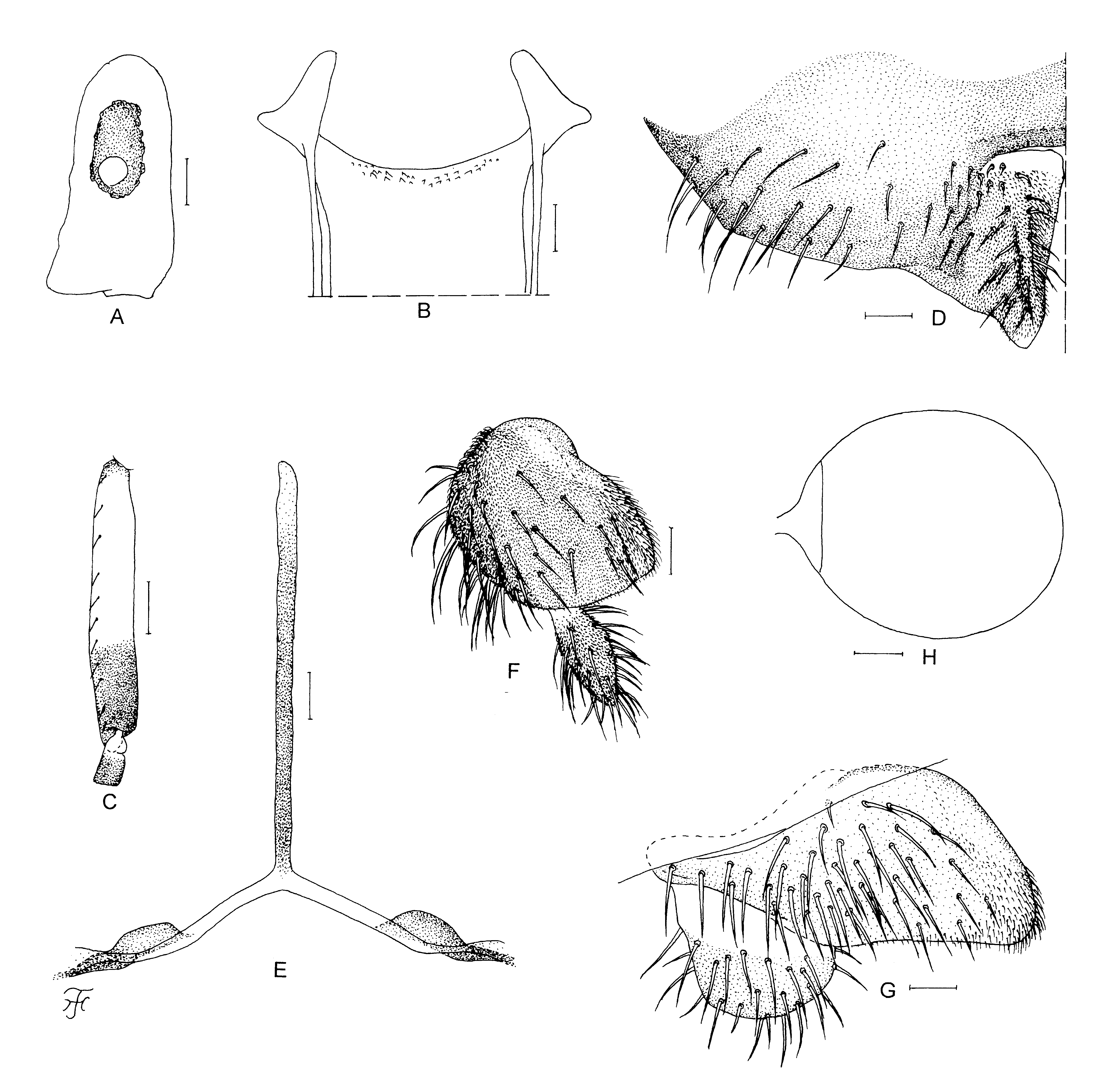
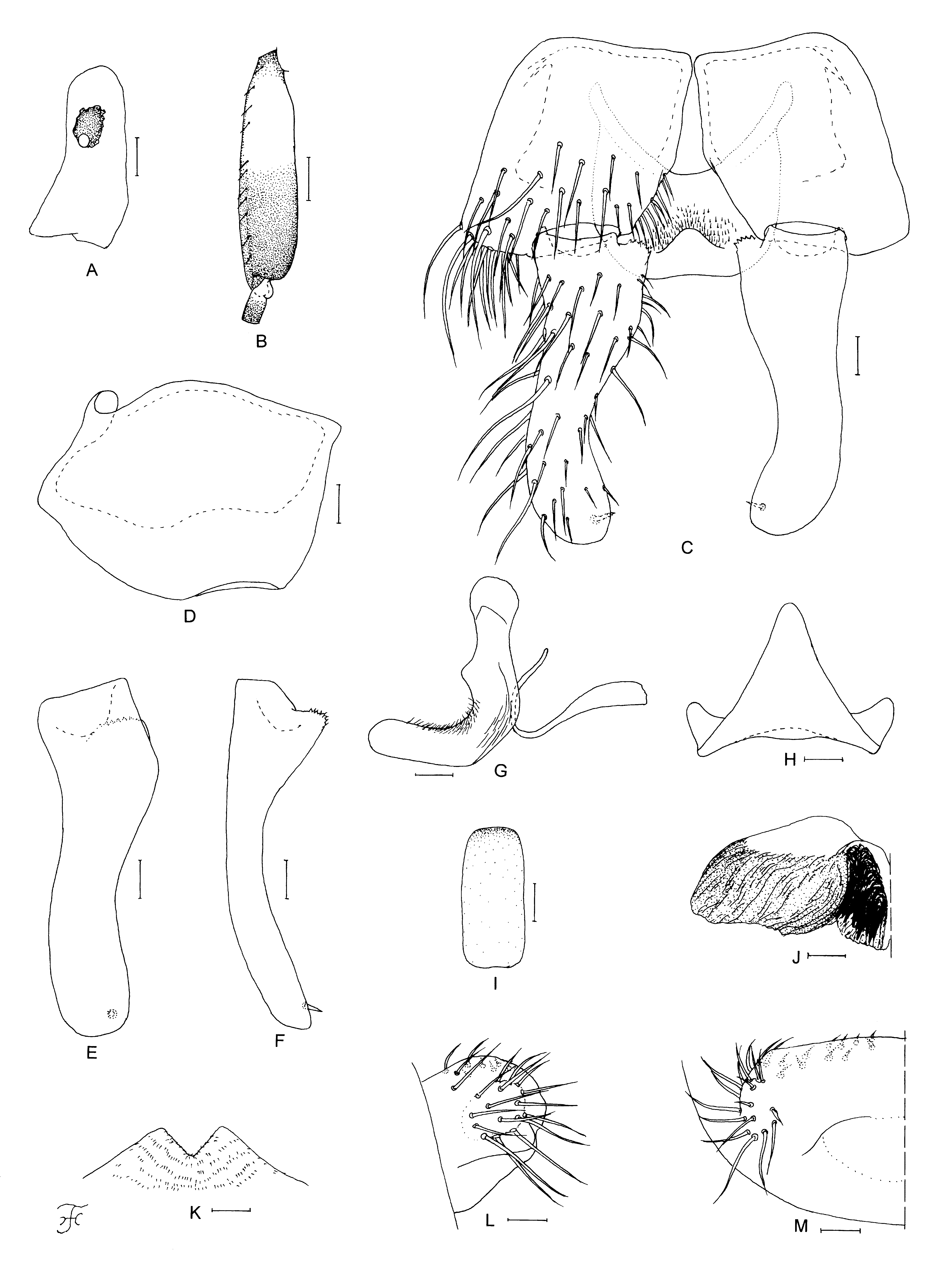
Female. Body length 2.2–2.4 mm. Head. Slightly narrower than thorax. Frons black, shiny with bluish reflection when illuminated at certain angles, with several dark stout hairs along lateral margins and several hairs just above lower margin; frontal ratio 1.4:1.0:1.2; frons:head ratio 1.0:3.6. Fronto-ocular area well developed, short, directed laterally, and rounded apically. Clypeus brownish-black, slightly shiny and gray pruinose when illuminated at certain angles, moderately covered with dark-brown medium-long hairs (though mediolongitudinal portion of upper half widely bare). Labrum 0.7 times length of clypeus. Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, medium to dark brown except scape, pedicel, and first and second flagellomeres yellow when viewed anteriorly (medium brown to dark brown except scape, pedicel and base of first flagellomere yellow when viewed posteriorly). Maxillary palp with five segments, medium brown except first and second segments ochreous or light brown, and third segment dark brown; proportional lengths of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.0:1.0:2.5; third segment ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 A) of normal size, with medium-sized ellipsoidal sensory vesicle (0.42 times length of third segment) having opening of moderate size. Maxillary lacinia with 12 inner and 13 or 14 outer teeth. Mandible with 23 inner and 13 outer teeth. Cibarium ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 B) with 31 minute processes near posterodorsal margin. Thorax. Scutum black, shiny, densely covered with whitish-yellow to yellow recumbent short hairs and sparsely with several dark-brown long upright hairs on prescutellar area; scutum gray pruinose with five non-pruinose longitudinal vittae (one medial, two submedial, and two lateral), medial and submedial vittae well defined from anterior margin to posterior portion and submedial and lateral vittae united widely near anterior margin), all vittae united with transverse non-pruinose band on prescutellar area, when illuminated in front and viewed dorsally; scutum gray pruinose except four non-pruinose longitudinal vittae, when illuminated posteriorly and viewed dorsally. Scutellum medium brown, covered with dark-brown upright long hairs and yellow short hairs. Postnotum brownish black, shiny, white pruinose when illuminated at certain angles, and bare. Pleural membrane bare. Katepisternum brownish black, longer than deep, shiny, white pruinose when illuminated at certain angles, and bare. Legs. Foreleg: coxa and trochanter yellowish white; femur light brown except inner surface of basal portion widely whitish yellow, and apical tip medium brown; tibia dark brown to brownish black; tarsus black, with moderate dorsal hair crest; basitarsus greatly dilated, 5.3–5.9 times as long as its greatest width. Midleg: coxa brownish black; trochanter light brown except base whitish; femur medium brown except apical cap dark brown; tibia light to medium brown with apical cap dark brown and base whitish, and with whitish sheen widely on posterior surface when illuminated at certain angles; tarsus light to medium brown except basal five-sixths of basitarsus and base of second tarsomere whitish. Hind leg: coxa brownish black; trochanter yellowish white; femur dark brown to brownish black except base whitish yellow; tibia dark brown except base yellowish white and with whitish sheen on basal half or more of posterior surface when illuminated at certain angles; tarsus medium brown except basal two-thirds of basitarsus and basal half of second tarsomere yellowish white; basitarsus ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 C) nearly parallel-sided, 6.3 times as long as wide, and 0.7 and 0.6–0.7 times as wide as greatest widths of hind tibia and femur, respectively; calcipala ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 C) moderately developed, slightly shorter than wide, and 0.4 times as wide as greatest width of basitarsus; pedisulcus ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 C) well developed. Claw simple, without tooth. Wing. Length 2.2 mm. Costa with dark spinules and hairs; subcosta haired except near apex bare; basal section of radius with four or five hairs on apical half or little more; R1 with dark brown spinules and hairs; R2 with dark-brown hairs; hair tuft on base of radius dark brown; basal cell absent. Halter . White except base darkened. Abdomen. Basal scale dark brown, with fringe of pale hairs. Dorsal surface of abdomen medium brown to brownish black, with light to dark-brown short hairs; tergite 2 shiny and silvery iridescent when illuminated at certain angles and tergites 6–9 shiny. Ventral surface of seventh segment with pair of weakly sclerotized submedian sternal plates. Terminalia . Sternite 8 ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 D) with posterior margin concave medially in form of reversed-U shape, bare medially, with 15–20 dark-brown medium-long to long stout hairs and 9–11 yellow short to medium-long hairs on each lateral surface. Ovipositor valve ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 D) triangular, with ventrally produced lobe near inner margin, membranous except narrow area along inner margin slightly sclerotized, covered with 23–26 short yellow hairs and numerous microsetae; inner margins slightly sinuous, somewhat separated from each other. Genital fork ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 E) of inverted-Y form, with narrow well-sclerotized stem; arms of moderate width, each with moderately sclerotized lateral portion. Paraproct in ventral view ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 F) rounded, subequal in length to greatest width, strongly pigmented on anterior surface, with 41–44 yellow and dark short to medium-long hairs on lateral and ventral surfaces, and with six to eight short sensilla on anteromedial surface; paraproct in lateral view ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 G) nearly 0.5 times as long as wide, and much protruding ventrally beyond ventral margin of cercus. Cercus in lateral view ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 G) short, 0.5 times as long as wide, with numerous medium-long hairs, and rounded posteriorly. Spermatheca ( Fig. 52 View FIGURE 52 H) nearly ovoid, 1.2 times as long as greatest width, well sclerotized except portion of junction with duct widely unsclerotized, without definite reticulate patterns on its surface; internal setae present; accessory ducts subequal in thickness to each other, and slightly thicker than major duct.
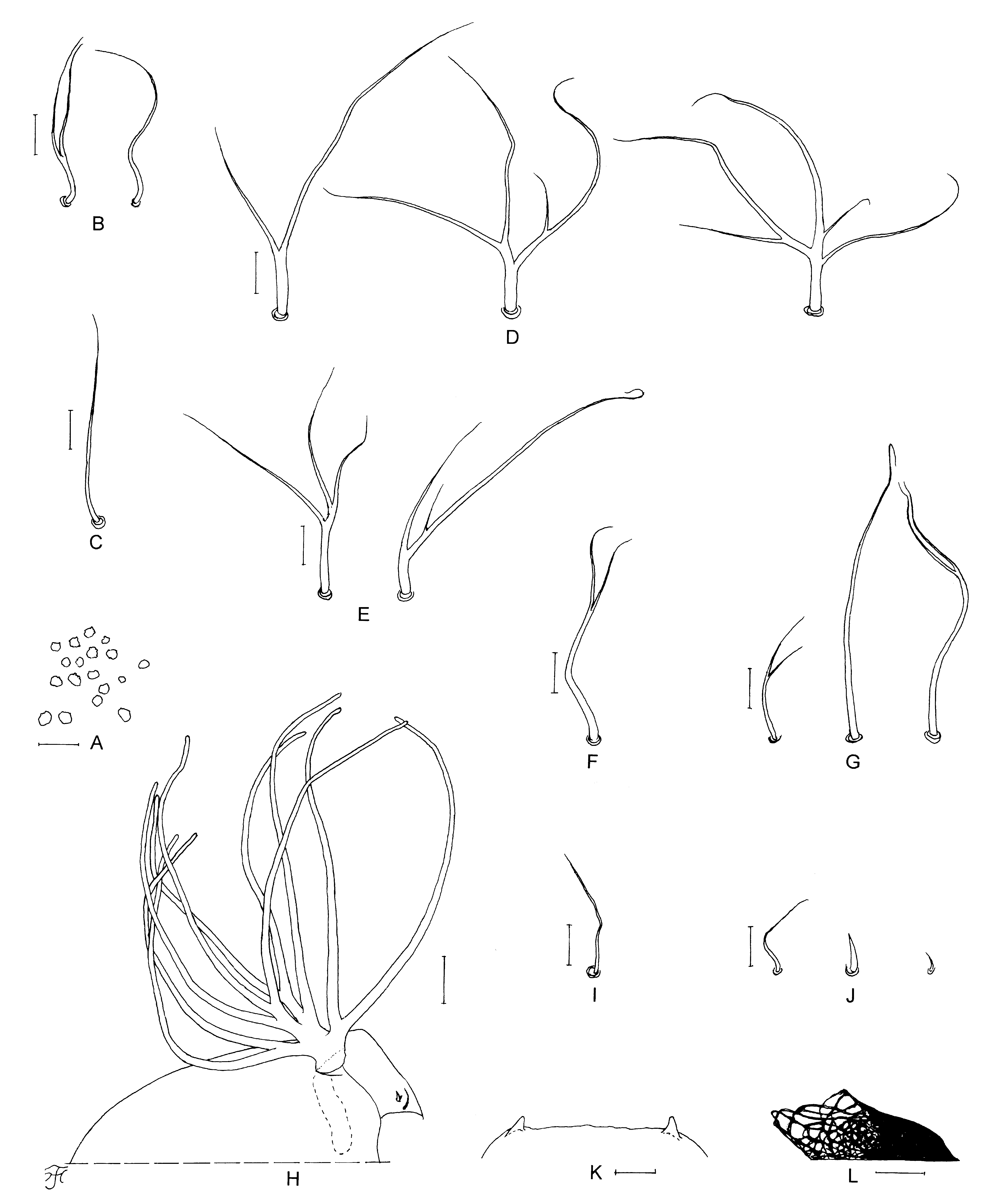
Male. Body length 2.9 mm. Head. Nearly as wide as thorax. Upper-eye large facets in 18 vertical columns and 19 horizontal rows. Clypeus black, thickly white pruinose and iridescent when illuminated at certain angles, with dark-brown hairs along and near lateral margins (most of central portion bare). Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, dark brown except scape and pedicel light brown and base of first flagellomere yellow; first flagellomere elongate, 1.6 times length of second one. Maxillary palp with five segments, mediumbrown except first and second segments ochreous and fifth segment grayish light-brown; proportional lengths of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.0:1.3:2.9; third segment ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 A) of normal size; sensory vesicle ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 A) ellipsoidal, 0.2–0.3 times length of third segment, and with small opening. Thorax. Scutum black, with whitishpruinose pattern, i.e., anterior pair of large spots on shoulders extended posteriorly along lateral margins and connected to large transverse spot entirely covering prescutellar area, anterior pair of large spots divided into anterior half and posterior half, either of which disappears depending on direction of lights; all these spots brilliantly iridescent when illuminated at certain angles; scutum uniformly and moderately covered with yellow recumbent short hairs and with several dark-brown long upright hairs on prescutellar area. Scutellum medium brown, with dark-brown long upright hairs and yellow short hairs. Postnotum brownish black, shiny and whitish pruinose when illuminated at certain angles and bare. Pleural membrane bare. Katepisternum longer than deep, brownish black, and bare. Legs. Foreleg: coxa yellowish white; trochanter light brown; femur light brown with apical tip medium brown; tibia medium brown to brownish black; tarsus black, with moderate dorsal hair crest; basitarsus greatly dilated, 5.8–6.3 times as long as its greatest width. Midleg: coxa brownish black; trochanter medium brown except base whitish; femur medium brown with apical cap dark brown; tibia medium to dark brown except extreme base yellowish white; tarsus medium brown except basal two-thirds of basitarsus yellowish white. Hind leg: coxa brownish black; trochanter yellowish white; femur medium brown except base whitish yellow and apical cap dark brown; tibia dark brown to brownish black except base yellowish white; tarsus medium brown except basal half of basitarsus and basal one-third of second tarsomere whitish yellow; basitarsus ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 B) enlarged, slightly widened toward apical one-third, then slightly narrowed, 3.9–4.0 times as long as wide, and 0.8– 0.9 and 0.9–1.0 times as wide as greatest widths of hind tibia and femur, respectively; calcipala ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 B) developed, small, slightly shorter than its basal width, and 0.3 times as wide as greatest width of basitarsus; pedisulcus ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 B) well developed. Wing. Length 2.3 mm. Other characters as in female except subcosta with hairs on basal half or little more, and basal portion of radius with four or five hairs on apical half or little less. Halter . White except base darkened. Abdomen. Basal scale brownish black, with fringe of dark-brown long hairs. Dorsal surface of abdomen dark brown to brownish black, moderately covered with dark-brown short to mediumlong hairs; segments 2, 5, 6 and 7 each with pair of whitish pruinose spots (brilliantly iridescent when illuminated at certain angles) dorsolaterally, those on segment 2 broadly connected in middle to each other. Genitalia. Coxites, styles and ventral plate in ventral view as in Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 C; coxite in ventrolateral view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 D) rectangular, 0.76 times as long as wide; style in ventrolateral view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 E) 1.6 times length of coxite, 3.4 times as long as greatest width near base, somewhat narrowed to little more than basal half, then slightly widened and nearly parallel-sided, with subapical spine; style in medial view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 F) somewhat flattened dorsoventally, with short basal protuberance directed dorsomedially, with several cone-like spines along its anterior margin. Ventral plate in ventral view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 C) with body broad, with lateral margins gently convex, anterior margin deeply concave, and posterior margin nearly straight or slightly concave; body bearing prominent median process sharply narrowed to round tip; body covered with minute setae medially; arms short, stout, divergent from base; ventral plate in lateral view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 G) with median process abruptly bent ventrally at nearly right angle; ventral plate in caudal view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 H) in form of equilateral triangle, and bare. Median sclerite in lateral view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 G) arising anterior to anteromedian portion of ventral plate, and in middle curved dorsally; median sclerite in caudal view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 I) nearly parallel-sided. Paramere in caudal view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 J) enlarged basally, with several hooks apically. Aedeagal membrane in caudal view ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 K) sparsely covered with minute setae; dorsal plate not sclerotized. Abdominal segment 10 ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 L, M) with two to five hairs and 10–12 shorter hairs on ventral surface and two to seven hairs on lateral surface; cercus ( Fig. 53 View FIGURE 53 L, M) small, with 16 or 17 distinct hairs.
Pupa. Body length 2.5–3.0 mm. Head. Integument light ochreous, moderately covered with relatively large tubercles having few to several secondary projections on frons ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 A), and moderately with round or cone-like small ones without secondary projections on face; frons with two pairs of unbranched or bifid short to mediumlong trichomes with straight apices ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 B); face with pair of unbranched medium-long trichomes with straight apices ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 C), as long as or longer or shorter than frontal trichomes. Thorax. Integument light ochreous, moderately covered with relatively large tubercles (similar to those on frons) except lateral surfaces and dorsal surface of posterior half of thorax moderately covered with relatively smaller round or cone-like tubercles; thorax on each side with three long trichomes with two to five branches ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 D) anterodorsally, two bifid or trifid long trichomes ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 E) anterolaterally, one unbranched or bifid medium-long trichome ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 F) mediolaterally, and three trichomes with coiled or straight apices (two unbranched or bifid long, one bifid short) ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 G) ventrolaterally. Gill ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 H) with 10 thread-like filaments arranged as 2+[(1+2)+(2+1)]+2 from dorsal to ventral; dorsal and ventral pairs with short stalk, two middle triplets with short stalk; all filaments subequal in length (0.7– 1.0 mm) and thickness, though ventral filament of ventral pair slightly thicker than other filaments (relative thickness of filaments from dorsal to ventral when compared basally 1.0:1.0:0.8–1.0:0.8–0.9:0.9–1.0:0.8 –1.0:0.8– 1.0:1.0–1.1:1.0–1.3:1.1–1.3); all filaments light brown, covered with sharply-defined annular ridges and furrows and densely covered with minute tubercles, relatively larger ones on ridges and smaller one on interridges. Abdomen. Dorsally, all segments nearly transparent except segments 1 and 9 light yellow; segment 1 without tubercles, with one unbranched short seta ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 I) on each side; segment 2 with one unbranched short seta and five minute setae, of which four are stout and one slender ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 J) on each side; segments 3 and 4 each with four distinct hooks and one short spinous seta on each side; all setae and hooks unbranched; segments 5, 6, 7 and 9 lacking spine-combs; segment 8 with distinct spine-combs in transverse row; segments 6–9 each with comb-like groups of minute spines on each side; segment 9 with pair of cone-like terminal hooks ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 K). Ventrally, all segment unpigmented except segment 9 yellowish; segments 4–8 each with comb-like groups of minute spines; segment 5 with pair of bifid stout hooklets submedially and few unbranched minute setae on each side; segments 6 and 7 each with pair of bifid inner and unbranched outer stout hooklets somewhat separated from each other and few unbranched minute setae on each side. Grapnel-shaped hooklets absent on each side of segment 9. Cocoon ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 L). Light ochreous, shoe-shaped, with several small to large open spaces anterolaterally on each side; posterior half with floor; posterior half thickly woven and individual threads almost invisible; 3.0– 3.6 mm long by 1.2–1.5 mm wide; height 0.8–1.0 mm.
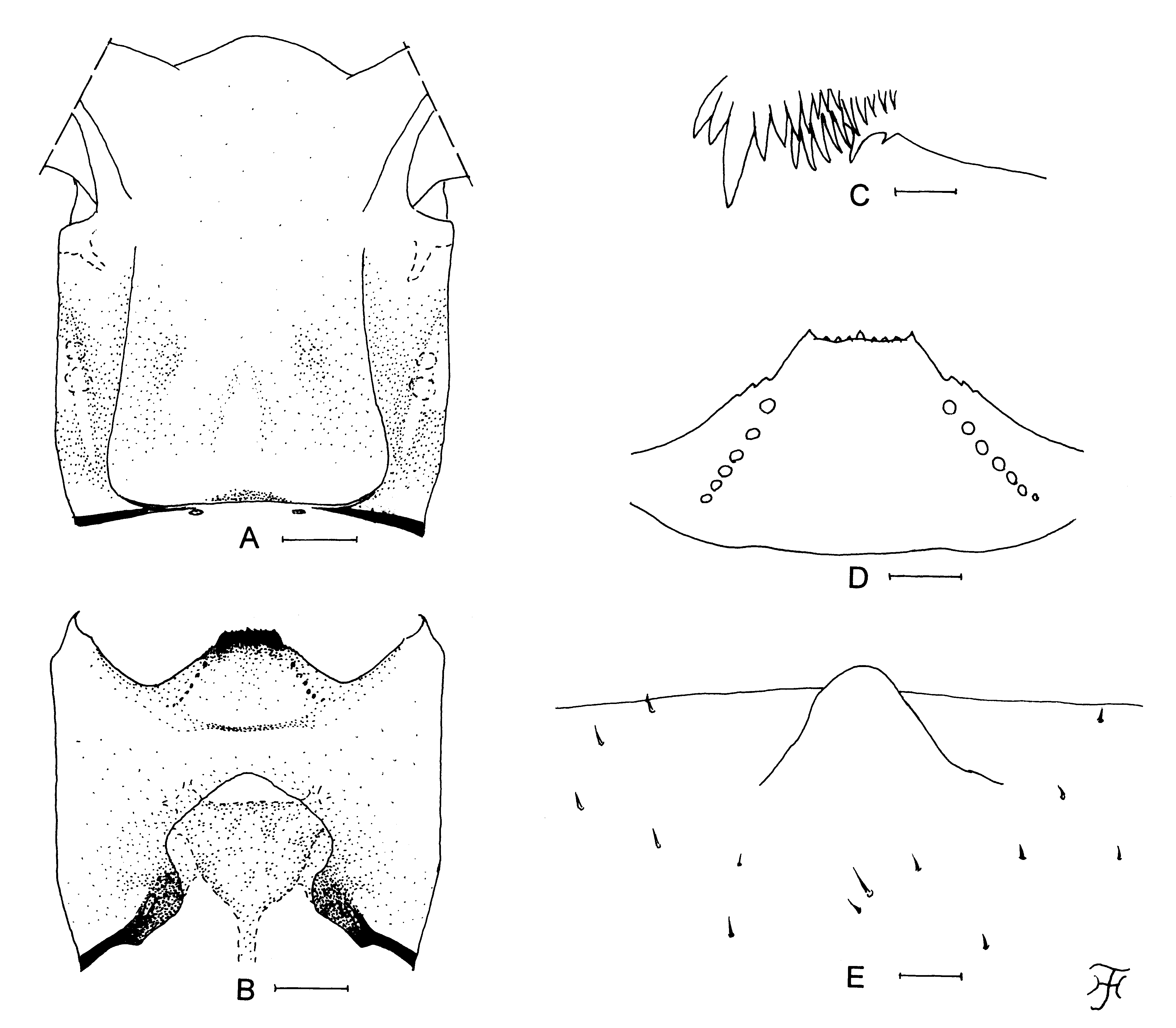
Mature larva. Body length 5.3–6.0 mm. Body dark gray. Abdomen in lateral view gradually widened from segment 1 to segment 7, then narrowed to segment 9. Head. Cephalic apotome ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 A) whitish yellow on anterior two-fifths, dark yellow to ochreous on posterior three-fifths, with area along posterior margin darkened; head spots obscured except mediolateral spots often faintly negative; lateral surface of head capsule yellow to ochreous (in one larva, widely medium brown), except eye-spot region whitish and areas above and posterior to eye-spot region darkened; eyebrow distinct; spots near posterior margin and below eye-spot region obscured or faintly negative; ventral surface of head capsule ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 B) yellow to ochreous; elongate spots on each side of postgenal cleft faintly negative. Antenna composed of three articles and apical sensillum, slightly longer than stem of labral fan; length ratio of three articles (from base to tip) 1.0:1.3:0.5–0.7. Labral fan with 53–56 primary rays. Mandible ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 C) with mandibular serration composed of two teeth (one medium-sized, one small); main tooth at right angle against mandible on apical side; comb-teeth gradually decreased in length from first to third; supernumerary serrations absent (though one minute tooth present between two mandibular teeth in left mandible of one larva). Hypostoma ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 D) with nine anterior teeth, of which median and corner teeth subequal in length to each other, followed by three intermediate teeth on each side; lateral margins serrate apically; six or seven hypostomal bristles divergent posteriorly from lateral border on each side. Postgenal cleft ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 B) large, rounded, 3.7–4.0 times length of postgenal bridge; sheath of subesophageal ganglion weakly or moderately pigmented. Cervical sclerites on each side composed of light-brown elliptical piece, not fused to occiput. Thorax and Abdomen. Histoblast of pharate pupal gill with 10 thread-like slender filaments. Thoracic cuticle sparsely covered with minute colorless setae. Abdominal segments 1–7 each with pair of cone-like dorsolateral protuberances ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 E). Abdominal cuticle sparsely covered with minute colorless setae ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 E), and moderately covered with short colorless setae on each side of anal sclerite. Rectal scales present. Rectal organ of three lobes, each with 12–15 finger-like secondary lobules. Anal sclerite X-shaped, with short broad anterior arms 0.65 times length of posterior ones and with forked apices; three or four sensilla on base of anal sclerite; four sensilla posterior to posterior arms. Last abdominal segment not bulged laterally and lacking ventral papillae. Posterior circlet with 134–138 rows of hooklets with up to 21–23 hooklets per row.
Type material. HOLOTYPE: Male (with its associated pupal exuviae and cocoon) in 80% ethanol, labeled in a vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 39, Holotype, Simulium (S.) tavanense , Male, coll. Vietnam, 21-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.], collected from a stream (width 1.0 m, depth 8 cm, bottom of pebbles, water temperature 13˚C, exposed to the sun, elevation 1,048 m, 22˚18’33.255’’N/103˚53’12.129’’E), flowing near forest, Tavan , Sapa , Lao Cai Province, northern Vietnam , 21-XII-2014, by H. Takaoka, M. Sofian-Azirun, Z. Ya’cob, C.D. Chen & K.W. Lau. PARATYPES. One male (with its associated pupal exuviae and cocoon) and three mature larvae, in 80% ethanol, same data as those of the holotype labeled in a vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 39, Paratype, Simulium (S.) tavanense , coll. Vietnam, 21-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.]; two females (all with their associated pupal exuviae and cocoons) in 80% ethanol, labeled in each vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 39, Paratype, Simulium (S.) tavanense , Female, coll. Vietnam, 21-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.], collected from a stream (width 1.0 m, depth 7 cm, bottom sandy, water temperature 17˚C, exposed to the sun, elevation 999 m, 22˚18’23.788’’N/103˚53’42.780’’E), slowly flowing in a grassland, Tavan , Sapa , Lao Cai Province, northern Vietnam , 21-XII-2014, by H. Takaoka, M. Sofian-Azirun, Z. Ya’cob, C.D. Chen & K.W. Lau.
Biological notes. The pupae and larvae of this new species were collected from grass leaves trailing in the current. Associated species were S. (G.) hongthaii , S. (S.) daoense sp. nov., S. (S.) doipuiense (complex) and S. (S.) phuluence sp. nov.
Distribution. Vietnam (Lao Cai).
Etymology. The species name tavanense refers to the name of the locality, Ta Van, where this new species was collected.
Remarks. Simulium (S.) tavanense sp. nov. is assigned to the S. striatum species-group, defined by Takaoka and Davies (1996), by the unique shape of the female terminalia and male genitalia ( Figs. 52 View FIGURE 52 D–H, 53C). This new species is characterized by having a haired basal portion of the radius of the female and male, male scutum covered with yellow short hairs, and pupal gill with 10 slender filaments of almost the same thickness, arranged as 2+[(1+2)+(2+1)]+2 filaments from dorsal to ventral ( Fig. 54 View FIGURE 54 H), and larval body with paired protuberances ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 E).
None of known species of the S. striatum species-group have hairs on the basal portion of the radial vein and on the subcosta in the male, as in this new species.
On the other hand, five species— S. (S.) grisescens Brunetti from India ( Brunetti 1911; Puri 1932d), S. (S.) quinquestriatum (Shiraki) from Taiwan ( Shiraki 1935; Takaoka 1979), S. (S.) pingtungense Huang & Takaoka from Taiwan ( Huang and Takaoka 2008), S. (S.) taythienense Takaoka, Sofian-Azirun & Ya’cob from Vietnam ( Takaoka et al. 2014a) and S. (S.) wuzhishanense Chen from China (Chen 2003) —have a haired basal portion of the radial vein in the female and a similar arrangement of the pupal gill filaments. Apart from the haired subcosta and haired basal portion of the radial vein in the male, this new species is distinguished from S. (S.) grisescens by the male hind basitarsus, which is 0.87 times as wide as the hind tibia (almost the same width as the hind tibia in S. (S.) grisescens ), and from the latter three species by the number of upper-eye facets, which are in 18 vertical columns and 19 horizontal rows in this new species but in 16 horizontal rows in S. (S.) quinquestriatum , in 19 vertical columns and 20 horizontal rows in S. (S.) pingtungense and in 12 vertical columns and 14 horizontal rows in S. (S.) wuzhishanense . This new species differs from S. (S.) grisescens , S. (S.) pingtungense and S. (S.) taythienense by the yellow short hairs on the male scutum (copper-colored short hairs in S. (S.) grisescens and brassy short hairs in S. (S.) pingtungense and S. (S.) taythienense ) and from S. (S.) pingtungense and S. (S.) wuzhishanense by the presence of paired dorsal protuberances on the larval abdomen (protuberances absent in the latter two species).
This new species is distinguished from S. (S.) xuandai Takaoka, Sofian-Azirun & Ya’cob described from a single male reared from a pupa from Vietnam ( Takaoka et al. 2014a) by the male upper-eye facets in 18 vertical columns and 19 horizontal rows (20 vertical columns and 20 horizontal rows in S. (S.) xuandai ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Simulium |
Simulium (Simulium) thailandicum Takaoka & Suzuki, 1984
| Takaoka, Hiroyuki, Sofian-Azirun, Mohd, Ya’Cob, Zubaidah, Chen, Chee Dhang, Lau, Koon Weng, Low, Van Lun, Pham, Xuan Da & Adler, Peter H. 2017 |
Simulium (Simulium) thailandicum
| Takaoka 1984: 37 |