Siamopsis khoratensis, Savatenalinton, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2017.384 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3A46429B-2499-4909-AD9D-E3328E4A667D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3853180 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3DCD40C9-3A9B-4E3A-AAAC-BDD6AEA1BD4C |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:3DCD40C9-3A9B-4E3A-AAAC-BDD6AEA1BD4C |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Siamopsis khoratensis |
| status |
gen. et sp. nov. |
Siamopsis khoratensis gen. et sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:3DCD40C9-3A9B-4E3A-AAAC-BDD6AEA1BD4C
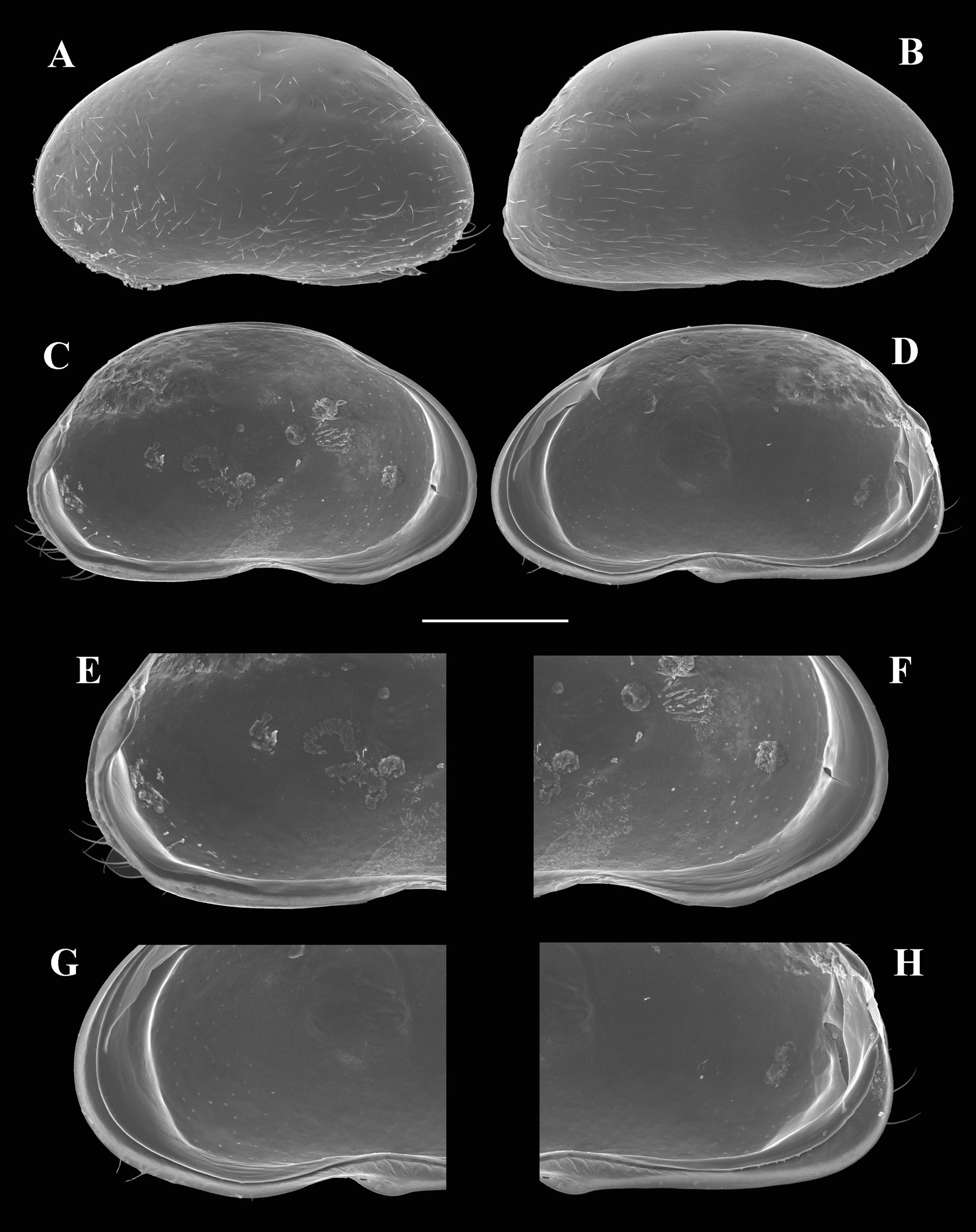
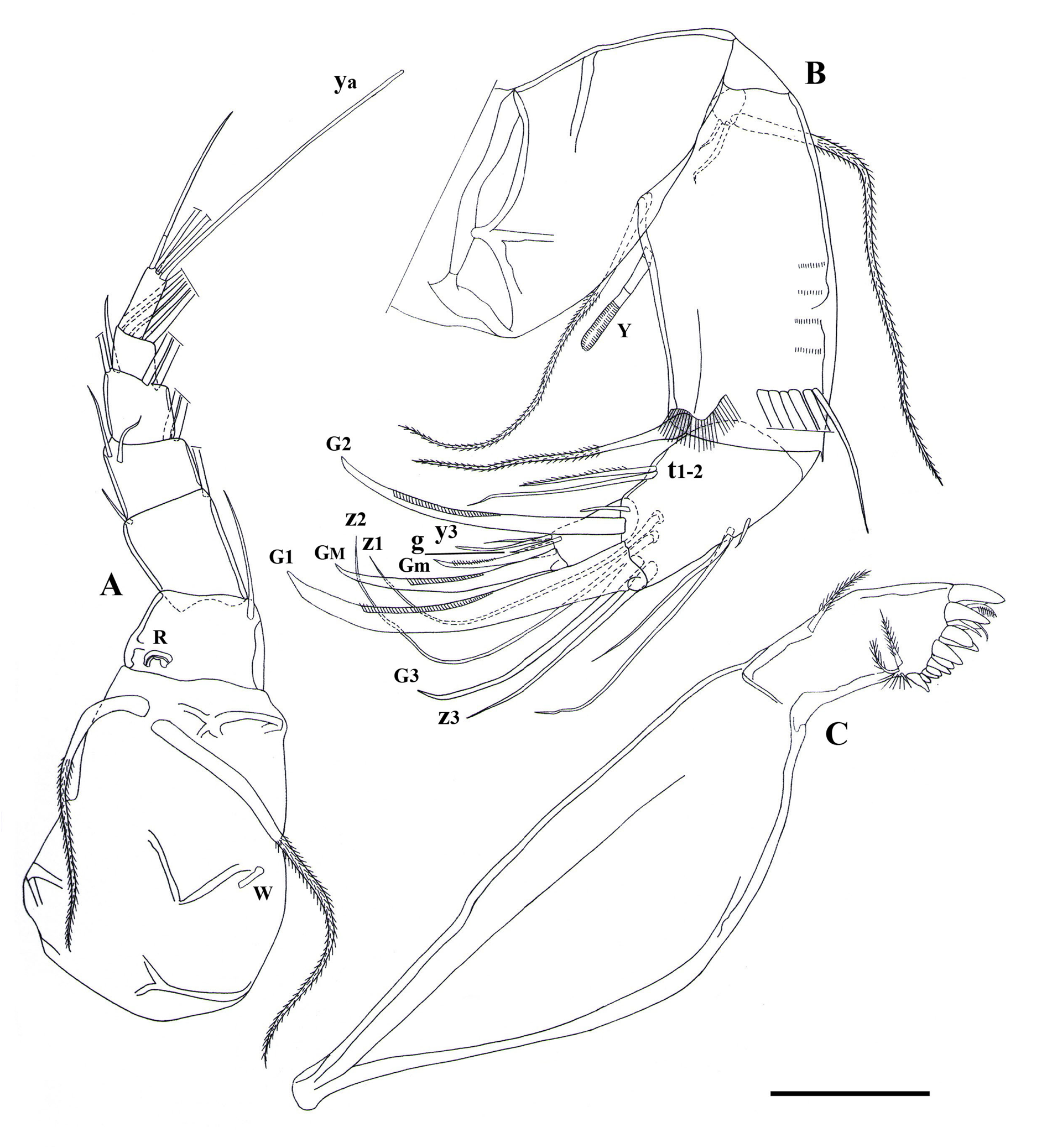
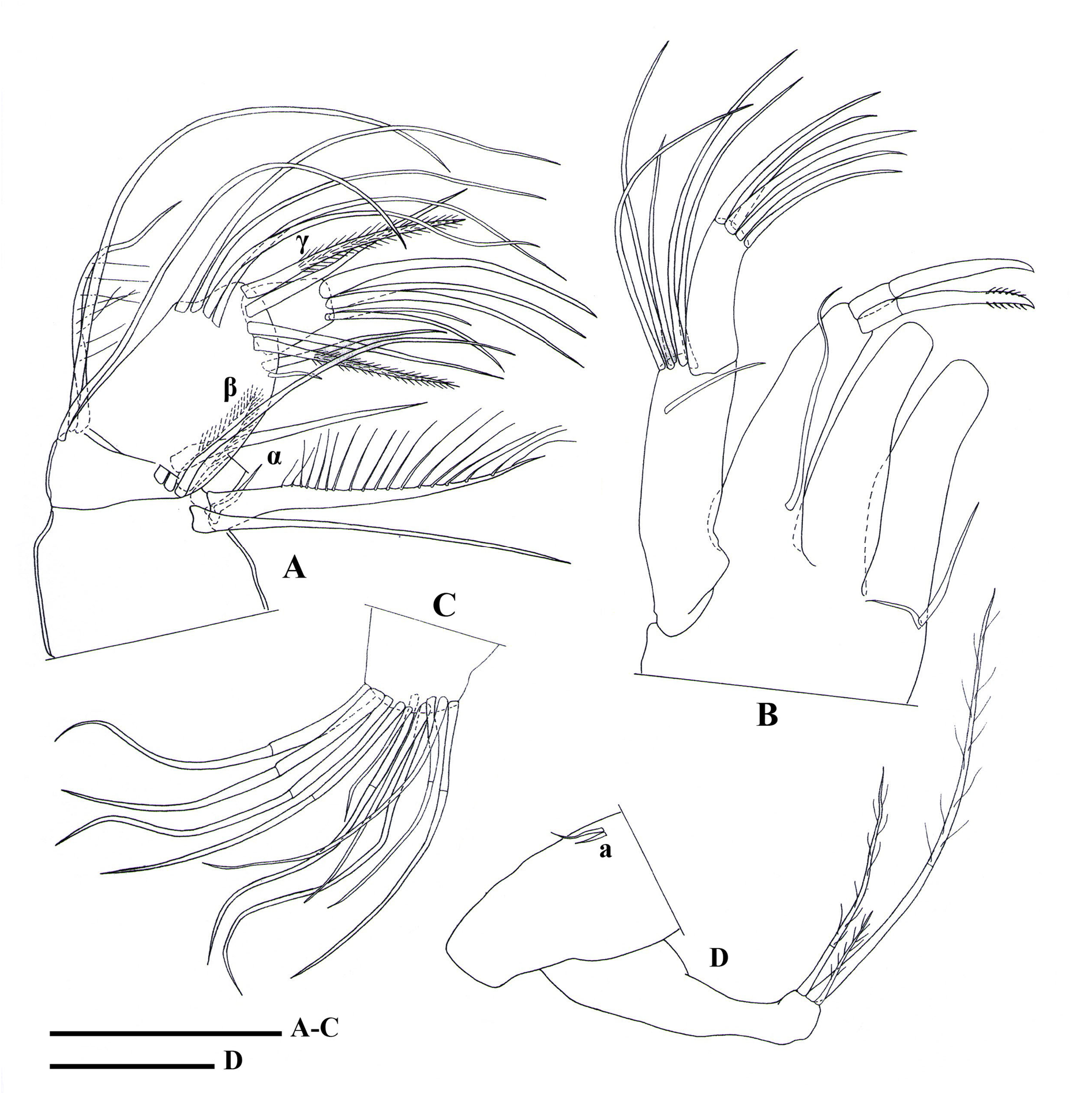
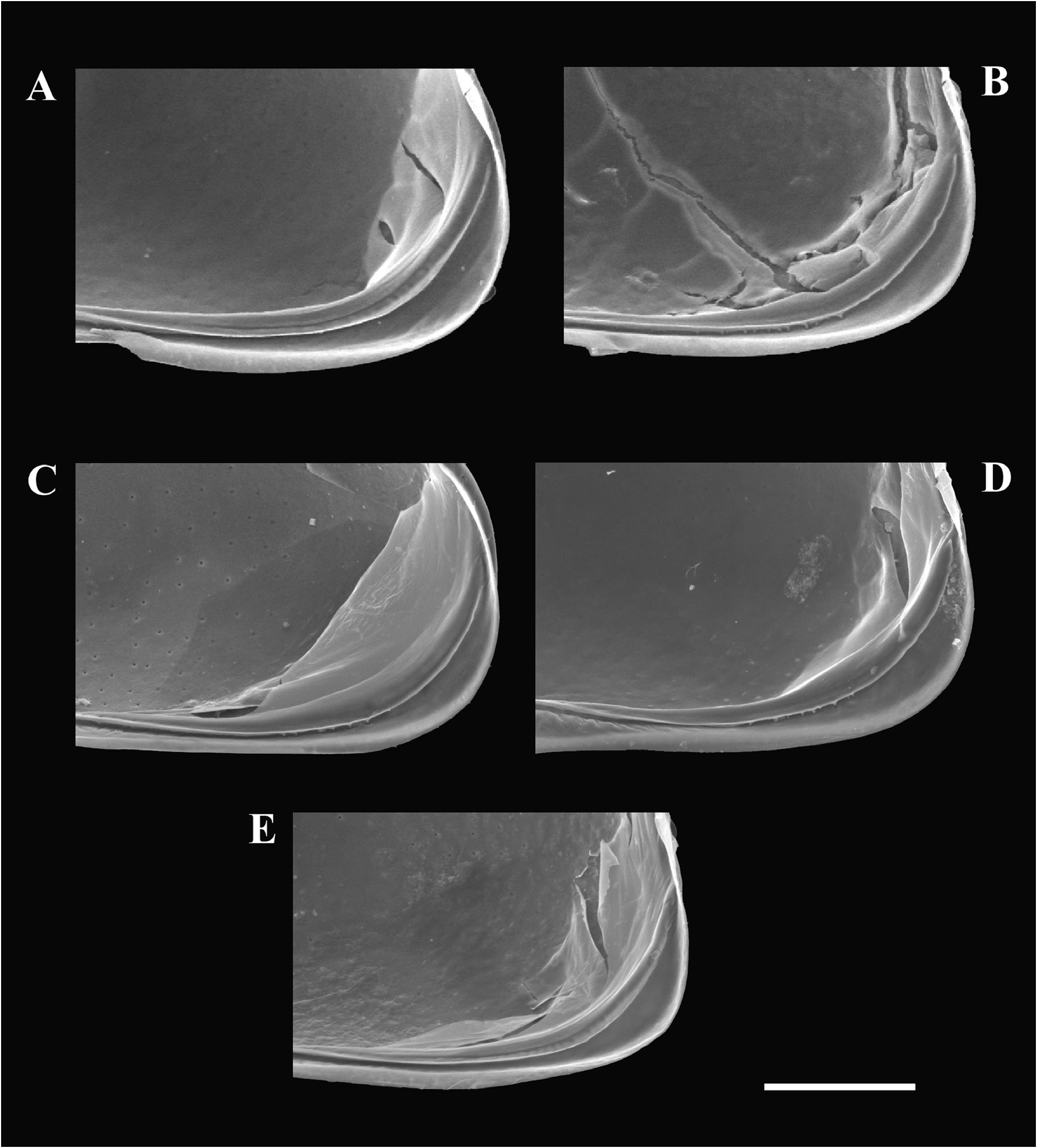
Figs 11–14 View Fig View Fig View Fig View Fig , 19D View Fig , 20 View Fig
Diagnosis
Carapace in lateral view elongated, dorsal margin flat at middle part of carapace, RV overlapping LV anteriorly, ventrally and posteriorly. Valve surface set with long (rim-pore) setae and shallow pits dispersedly. LV in internal view with large selvage anteriorly, valve margins subequally rounded anteriorly and posteriorly, postero-dorsal plate broad, with a small anterior tooth-like tubercle. RV in internal view with large selvage anteriorly, posterior margin curved inwardly at slightly above mid height, posterior inner list internally set with small tubercle-like structures at postero-ventral part. Third endite of Mx1 with two large bristles, one distally serrated, one smooth. CR cylindrical in shape, with flagellum-like seta.
Etymology
The species is named after Nakhon Ratchasima Province, also called “ Khorat ”, where the new species was discovered.
Material examined
Holotype
THAILAND: ♀, with soft parts dissected in glycerine on a sealed glass slide and valves stored dry in a micropalaeontological slide ( MSU-ZOC.204 ).
Paratypes
THAILAND: 1 ♀, stored as the holotype ( MSU-ZOC.205); 1 ♀, carapace stored dry in a micropalaeontological slide ( MSU-ZOC.206).
Type locality
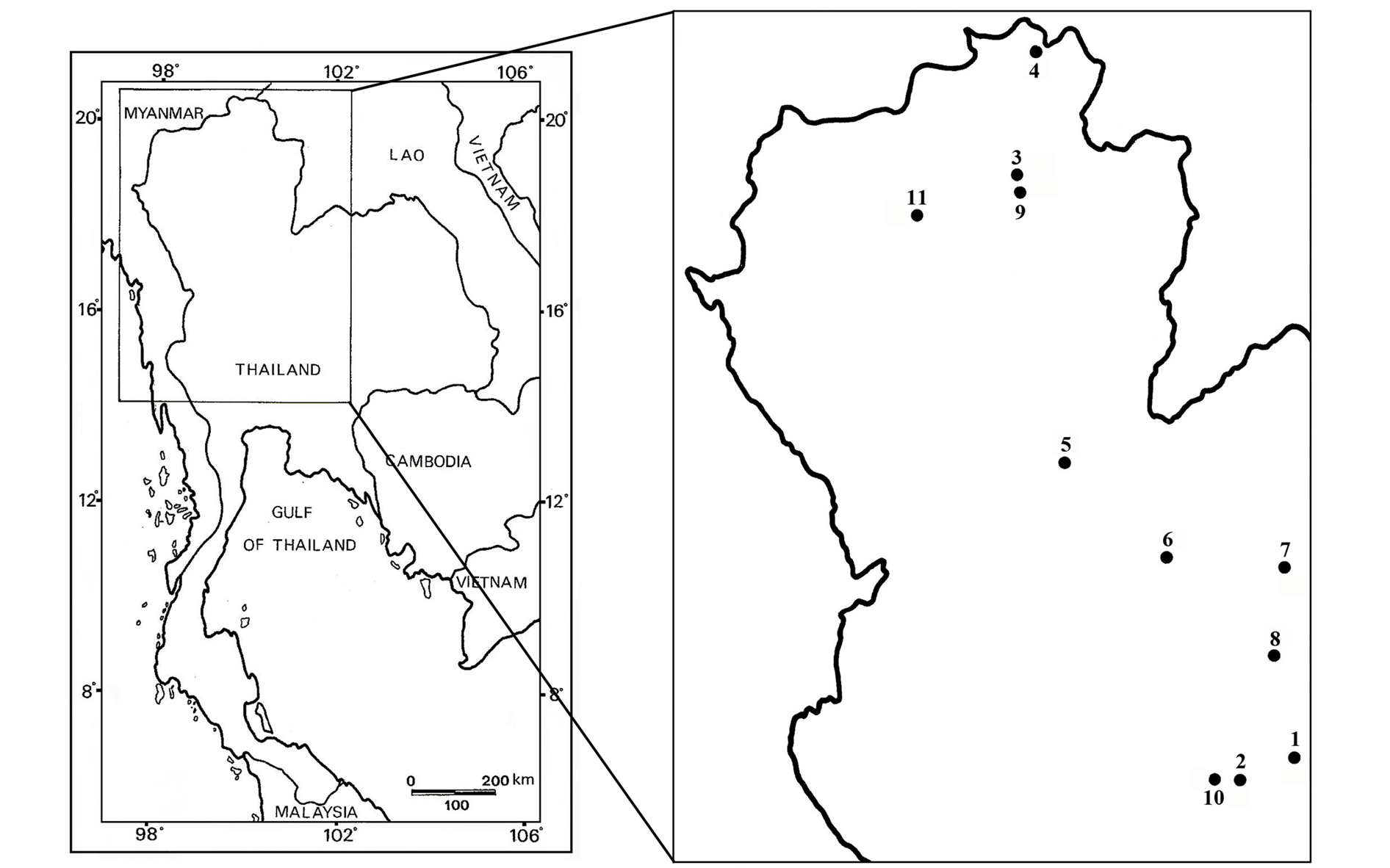
THAILAND: Nakhon Ratchasima Province, Muang District, irrigation ditch (locality 1 in Fig. 20 View Fig ), 14°43′46″ N, 104°33′56″ E, 5 Oct. 2010. Accompanying ostracod fauna: Cypris subglobosa , Cyprinotus uenoi, Stenocypris cf. orientalis, Siamopsis suttajiti gen. et sp. nov., S. renateae gen. et sp. nov. and S. planitia gen. et sp. nov.
Differential diagnosis
Siamopsis khoratensis gen. et sp. nov. has S. planitia gen. et sp. nov. as its closest congener. The obvious diagnostic characters are the morphology of the postero-dorsal plate of the LV in internal view and of the RV posterior inner list. The plate is broad and has a small tooth-like tubercle at the anterior part in S. khoratensis gen. et sp. nov., while it is elongated and has no tooth-like tubercle in S. planitia gen. et sp. nov. The RV posterior inner list is set with small tubercle-like structures at the postero-ventral part in S. khoratensis gen. et sp. nov., whereas it is smooth in S. planitia gen. et sp. nov.
Measurements (mean, in μm)
LV (n = 2), L = 616, H = 371; RV (n = 2), L = 626, H = 373.
Description
Female
CARAPACE. In lateral view elongated, dorsal margin flat at middle part of carapace, both margins subequally rounded anteriorly and posteriorly, RV overlapping LV anteriorly, ventrally and posteriorly, valve surface set with long setae, long rim-pore setae and shallow pits dispersedly ( Fig. 11 View Fig A–B). Carapace in dorsal view elliptical, with greatest width situated at mid-length.
VALVES. LV in interior view ( Fig. 11C View Fig ) with large selvage anteriorly, valve margins subequally rounded anteriorly and posteriorly, ventral margin sinuous at ca mid-length, postero-dorsal plate broad, set with a small anterior tooth-like tubercle, inner lamella anteriorly broader than posteriorly. RV in interior view ( Fig. 11D View Fig ) with large selvage anteriorly, valve margins subequally rounded anteriorly and posteriorly, ventral margin sinuous at ca mid-length, posterior margin recurved inwardly slightly above mid height, calcified inner lamella with inner lists anteriorly and posteriorly, postero-ventral inner-list internally set with small tubercle-like structures.
A1 ( Fig. 12A View Fig ). Seven-segmented, first segment with large proximal Wouters organ, one long dorsosubapical seta (reaching beyond tip of next segment) and two long ventro-apical setae. Second segment slightly wider than long, with one long dorso-apical seta (reaching tip of next segment) and Rome organ. Third segment bearing two setae: one long dorso-apical (reaching tip of penultimate segment) and one short ventro-apical setae. Fourth segment with two long dorsal setae and two short ventral setae (both reaching beyond half of fifth segment). Fifth segment dorsally with two long setae, ventrally with two (one long, one short) setae, short one reaching mid-length of terminal segment. Penultimate segment with four long apical setae. Terminal segment with three (two long, one short) apical setae and very long aesthetasc ya, length of short seta ca half that of aesthetasc ya.
A2 ( Fig. 12B View Fig ). Exopodite with three (one long, two short) setae, long one reaching beyond tip of first endopodal segment. First endopodal segment with five long (reaching far beyond tip of terminal claws) and one short natatory setae, length of shortest seta ca half that of penultimate segment, aesthetasc Y long, ventro-apical seta long, extending beyond tip of terminal segment. Penultimate segment undivided, distally with three serrated claws (G1, G2, G3), G2 shorter (length of G2 ca 6/7 that of G1), aesthetasc y2 long (ca half that of terminal segment), z1–z3 setae long; this segment medially with two subequally long dorsal setae and two ventral setae of unequal length (t1–t2). Terminal segment distally with two serrated claws (GM and Gm), length of Gm slightly more than half that of GM; medially with short g-seta and ventral aesthetasc y3, length of accompanying seta ca ⅔ that of aesthetasc y3.
MD PALP ( Fig. 13A View Fig ). First segment with two large setae, one long and slender seta, and a short, smooth α-seta. Second segment dorsally with three unequally long apical setae; ventrally with group of three long hirsute setae, one shorter hirsute seta and plumose, cone-shaped β-seta with pointed tip. Penultimate segment consisting of three groups of setae: dorsally with group of four unequal, long, subapical setae; laterally with apical γ-seta and three further apical setae (two smooth, one hirsute), the former thin and long (length ca 2.2 times that of terminal segment); ventrally with two subapical setae, one very long (reaching beyond tip of terminal segment), one short (ca half that of terminal segment). Terminal segment elongated, bearing three claws and two shorter setae.
MX 1 ( Fig. 13B View Fig ). With two-segmented palp, basal segment of palp dorsally with group of five long, unequal apical setae; ventrally with one short subapical seta. Terminal segment very elongated (length ca 3.3 times width), apically with three claws and two setae. Third endite with two (one smooth, one
serrated) large bristles. Sideways-directed bristles on first endite unequally long, length of short one ca half that of long one.
T1 ( Fig. 13 View Fig C–D). Protopodite with two unequally short a-setae, b- and d-setae absent, distally with ca 11 hirsute apical setae of unequal length. Endopodite a weakly built palp, with one very long, hirsute and two unequally short apical setae.
T2 ( Fig. 14A View Fig ). With d2 seta (d1 absent). Second segment with short e-seta (reaching mid-length of penultimate segment). Penultimate segment divided, proximal segment bearing long f-seta (reaching beyond tip of terminal segment), distal segment with pair of apical setae (long g-seta, one short), length of g-seta almost the same as that of h1 seta. Terminal segment with two (one dorsally, one ventrally) apical h1 and h3 setae (length of former ca ⅓ that of claw, latter short) and serrated claw (h2), length of h2 longer than that of penultimate segment.
T3 ( Fig. 14B View Fig ). A cleaning limb. First segment with long d1, d2 and dp setae, d1 and d2 setae subequal in length. Second segment with long apical e-seta (reaching half of next segment). Third segment with medially long f-seta (reaching tip of segment). Terminal segment with an apical pincer and one reflexed subapical seta, length of latter equal to that of third segment.
CR ( Fig. 14C View Fig ). Reduced, flagellum-like, cylindrical in shape, with a small lateral seta and long apical seta, length of latter ca 1.8 times that of ramus.
Male
Unknown.
Ecology
The new species has been encountered at only one locality, in Nakhon Ratchasima Province. It occurs at a pH of 7.0 and a temperature of 28.5°C.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |