Podotarsonemus indicus Seeman, Lindquist & Husband, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4418.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A63167F9-4B7E-4CC2-A409-8F11DF7C9D95 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5960604 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/57045804-FF98-8A45-FF10-B410923F88A4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Podotarsonemus indicus Seeman, Lindquist & Husband |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Podotarsonemus indicus Seeman, Lindquist & Husband sp. nov.
Figures 16–19 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 View FIGURE 18 View FIGURE 19
Type material. Holotype. Adult female. INDIA, Madras, Dist. Coimbatore, Coimbatore, P.S. Nathan, 5 Jul. 1946, ex Scelimena kempi (Hancock) , RWH VII2010 (slide 1). In UMMZ.
Paratypes. 15 females, 11 males, 2 larvae, as follows. 11 females, 11 males, 1 larva same data as holotype. 3 females, 1 larva, same data as holotype except 26 Nov. 1945. 1 female, same data as holotype except 3 Nov. 1947. In UMMZ, except 1 female, 1 male, 1 larva in CNCI and 1 female, 1 male in QM.
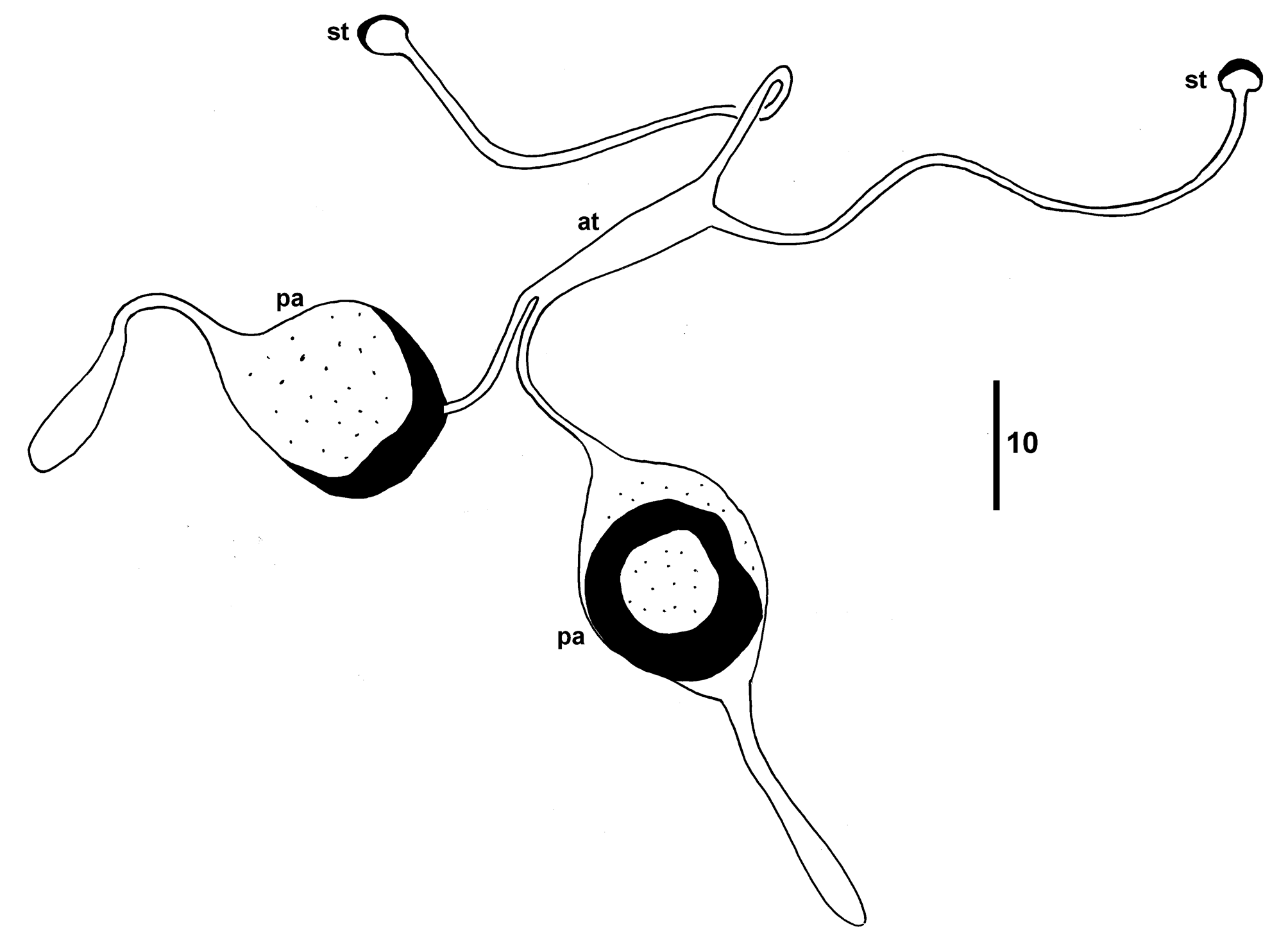
Diagnosis. Female and male: Palps with 2 setae; chelicerae without teeth; prodorsal plate with punctate sculpturing; femora I–II without setae lʹ, d; genua II–III bare; tarsi II–III with 5 setae, uʹʹ present; trochanter IV with 1 seta. Female: Setae sc1 present; vestigial setae v2 expressed as alveoli within prodorsal shield; coxisternal plates III–IV separated by longitudinal striae; setae h not attenuate, <30 long; femorogenu IV without seta; tracheal atria fused, post-atrial sac heavily sclerotized, punctate. Male: Genital capsule without copulatory flanges; setae h1 rudimentary, like h2; leg I with tibia and tarsus fused; femorogenu IV bare; tibia IV with solenidion and attenuate terminal seta; tarsus IV rudimentary, subterminal. Larva: Setae h1-2, ps2 attenuate, setae ps1 short; leg I with separate tibia and tarsus, with 2 rudimentary claws.
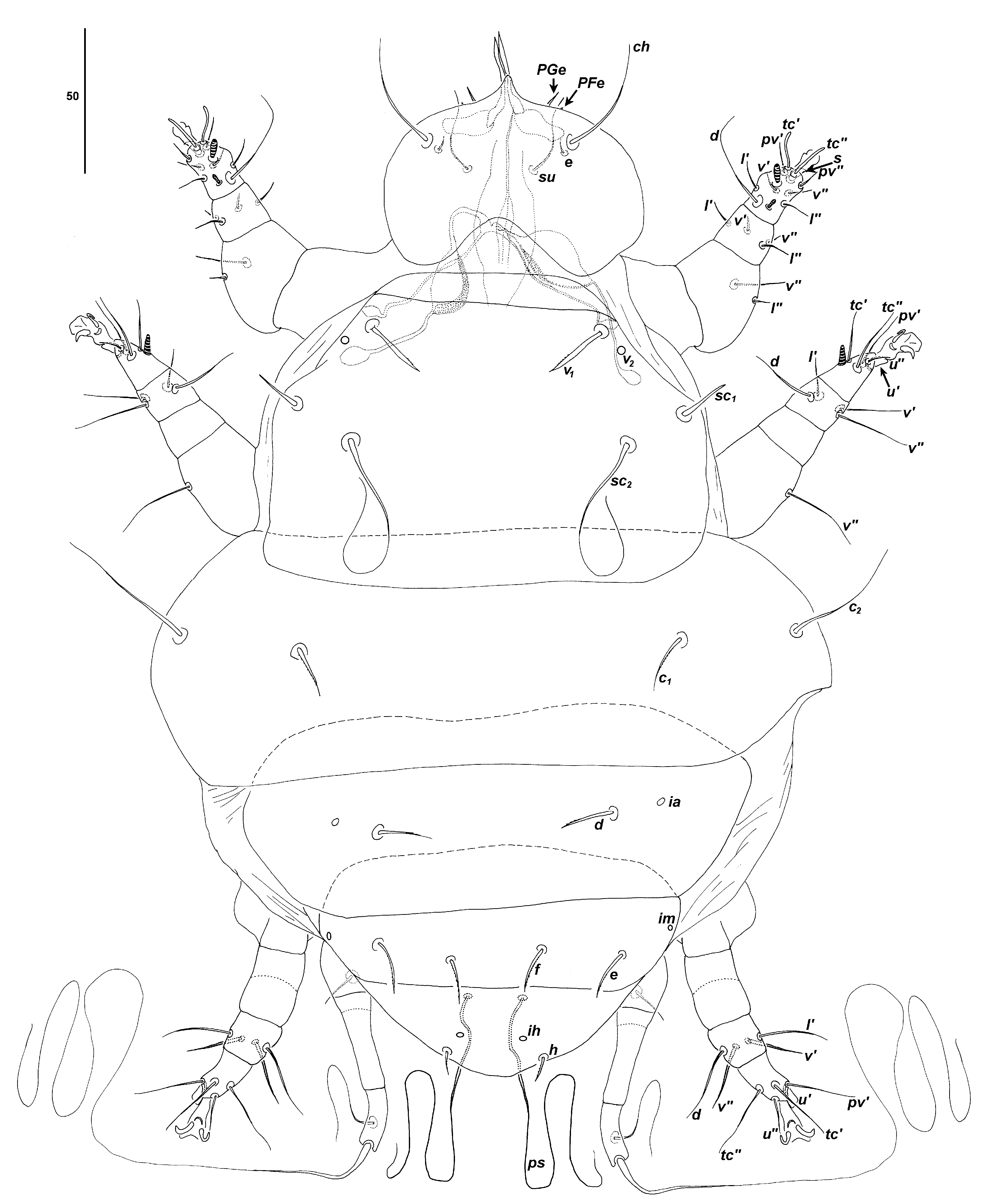
Description. ADULT FEMALE ( Figures 16–17 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 , n = 9 measured)
Gnathosoma . Length 57–67, width 68–71. Palps 9–13, with 2 setae (8 and 3 long). Cheliceral stylets 28–31, without teeth. Pharynx length 41–50, width 20–23. Dorsal setae ch 35–42, ventral setae su 27–32, palpcoxal setae e 7–8.
Idiosoma . Length 242–300 (physogastric 600), width 226–240. Tracheal atria fused, post-atrial sac heavily sclerotized, punctate, with single long terminal extension of trachea. Prodorsal plate with punctate sculpturing, 103–110 long, 148–174 wide; with 3 pairs of setae: v1 21 –26, thickened, with small barbs, sc 1 17–21, sc2 67–78, and vestigial v2. Distance between setae v1-v1 63 –75, v2-v2 68 –82, sc1-sc1 124–140, sc2-sc2 83–106, v1 -sc2 33– 38. Plates C, D, EF with punctate sculpturing. Setae c1, d, e, f thickened, with small barbs, c 1 18–20, c2 51–65, d 17–20, e 15–21, f 15–20. Distance between setae c1-c1 122–128, c2-c2 201–209, c1-c2 35–38, d-d 64–76, e-e 73– 80, f-f 28–34. Plate H variably covered by EF, setae h not attenuate, 11–26. Distance between setae h-h 31–37. Cupules ia, im, ih present. Setae ps attenuate> 300, distance between setae ps-ps 9–12. Coxisternal setae attenuate, 1a 80 (often broken), 2a > 120 (often broken), 3a > 100, 3b > 100. Distance between setae 1a-1a 26–31, 2a-2a 59– 63, 3a-3a 15–18, 3b-3b 35–43; alveolar vestiges of setae 1b and 2b present. Coxisternal plates III–IV separated by longitudinal striae; coxisternal plates III convex anteriorly, sometimes just reaching posterior margin of coxisterna II.
Legs. Leg lengths: I 71 –73, II 75 –79, III 70 –73. Leg IV Fe-Ge length 33–34, Ti-Ta length 20–22. Leg III, femur and genu fused, line of fusion apparent and one specimen with asymmetric separation of femur and genu.
Femur I lʹʹ 5–6, vʹʹ 15–28; genu I lʹ 9–11, lʹʹ 9–10, vʹ 3–5, vʹʹ 4–5; tibia and tarsus I fused, tibial setae d 31–34, lʹ 9–12, lʹʹ 9–11, vʹ 6–7, vʹʹ 11–13, solenidion φ 3–4, tarsal setae tcʹ 12–14, tcʹʹ 12–13, pvʹ 10–13, pvʹʹ 8–10, s spinelike, 6–7, solenidion ω 7–8.
Femur II vʹʹ 15–24; tibia II d 24–30, lʹ 6–11, vʹ 13–21, vʹʹ 15–25; tarsus II tcʹ 16–17, tcʹʹ 18, pvʹ 13–15, uʹ spinelike, 7, uʹʹ 6–8, solenidion ω 6–7.
Tibia III d 24–32, lʹ 14–20, vʹ 18–22, vʹʹ 17–23; tarsus III tcʹ 17–22, tcʹʹ 26–32, pvʹ 15–17, uʹ spine-like, 8, uʹʹ 5– 6.
Trochanter IV with seta 11–13; tibiotarsus with ventral tibial seta 45–60, terminal tarsal seta> 400.
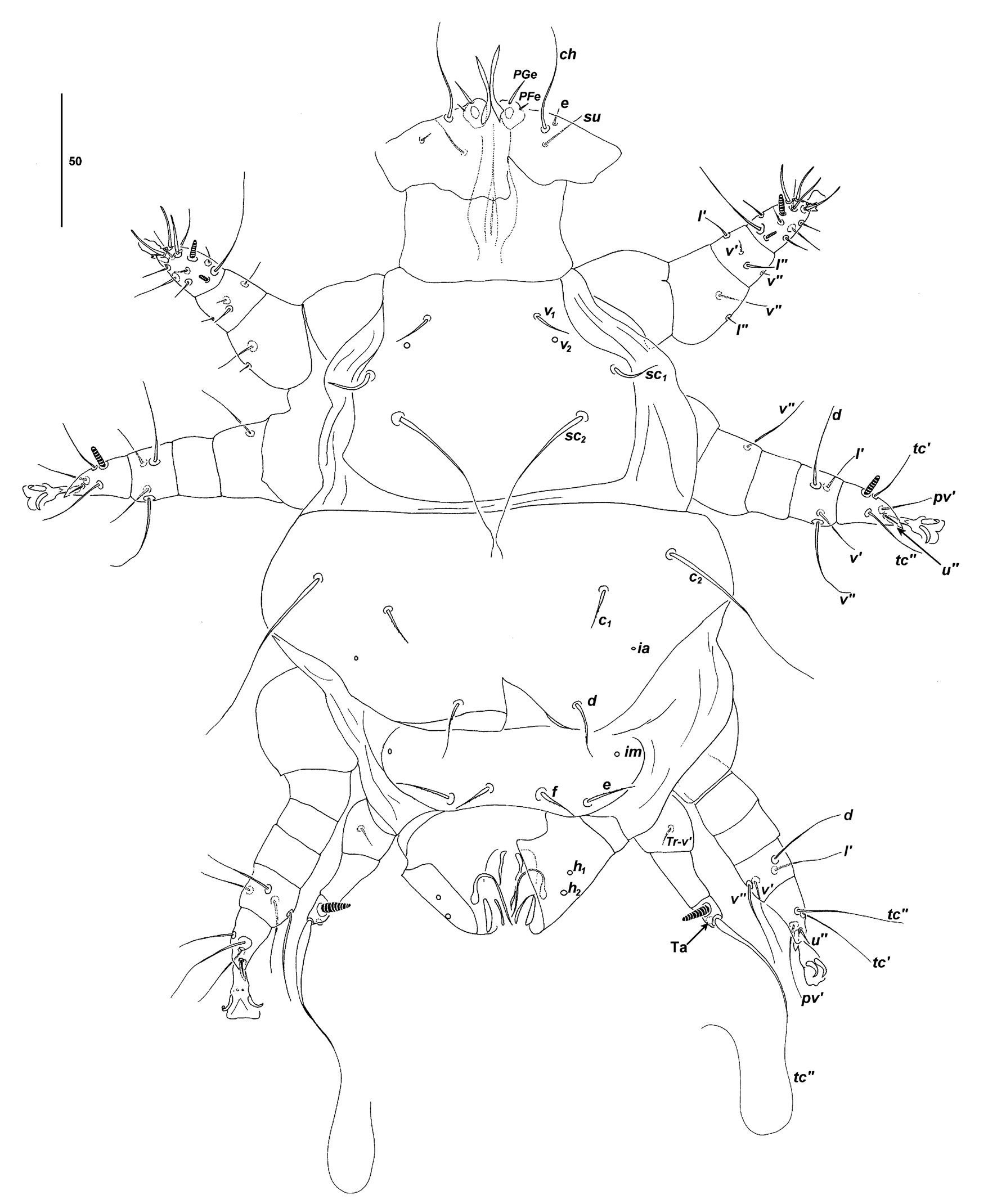
ADULT MALE ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 , n = 5 measured)
Gnathosoma . Similar to female. Length 61, width 66. Palps 11–12. Cheliceral stylets 2 5–26, without teeth. Pharynx length 34–35, width 18. Dorsal setae 39–41, ventral setae 7, palpcoxal setae 3.
Idiosoma . Length 170–238, width 168–179. Prodorsal plate punctate, 74 long, 104–105 wide; with 3 pairs of setae ( v1 14 –18, sc 1 17–18, sc2 75–78) and vestigial v2. Distance between setae v1-v1 34 –38, v2-v2 44 –50, sc1-sc1 87–90, sc2-sc2 64– 65, v1 -sc 2 29–32. Plate CD punctate. Setae c1 tapering, with few barbs, 7, c2 attenuate, 70–84, d with few barbs, 19–20; setae c 1 in nearly transverse alignment with c2. Plate EF punctate, e 18–19, f 16, with few barbs. Distance between setae c1-c1 64, c2-c2 134, c1-c 2 21–25, d-d 33, e-e 47–51, f-f 16. Cupules ia, im present. Genital capsule 43 long, 51 wide, bearing alveolar remnants of h1, h2; ventral flanges absent. Coxisternal setae attenuate 1a 30–36, 2a 28–30, 3a > 190, 3b > 30. Distance between setae 1a-1a 33–35, 2a-2a 56–59, 3a-3a 19–23, 3b-3b 29–31; setae 1a at level of or just posterior to ap1, setae 2b usually just posterior to ap2 (one specimen with asymmetrical position of setae 2b far posterior to ap2). Apodemes: ap2 not reaching medially obsolete ap sj; ap5 obsolete.
Legs. Leg lengths: I 70 –72, II 83 –89, III 83 –85, IV 52 –54. Leg III, femur and genu separate.
Femur I, lʹʹ 5–8, vʹʹ 30; genu I lʹ 8–12, lʹʹ 7–8, vʹ 4, vʹʹ 3–4; tibia and tarsus I fused, tibial setae d 44–50, lʹ 7–10, lʹʹ 10, vʹ 7, vʹʹ 15, solenidion φ 5, tarsal setae ftʹ 16, ftʹʹ 15, tcʹ 15–17, tcʹʹ 15–17, pvʹ 12, pvʹʹ 14, s spine-like, 7, solenidion ω 7–8.
Femur II vʹʹ 25; tibia II d 38–42, lʹ 27–29, vʹ 10–18, vʹʹ 31–32; tarsus II pvʹ 6–9, tcʹ 18–20, tcʹʹ 18–20, uʹʹ 5–6, uʹ spine-like, 6, solenidion ω 8.
Tibia III d 32–35, lʹ 27–30, vʹ 26–32, vʹʹ 23–25; tarsus III pvʹ 17–20, tcʹ 27–28, tcʹʹ 25–29, uʹ spine-like, 7, uʹʹ 5– 6.
Trochanter IV with seta, 8; femorogenu IV bare; tibia IV φ 11, terminal seta attenuate, 150; tarsus IV rudimentary, subterminal.
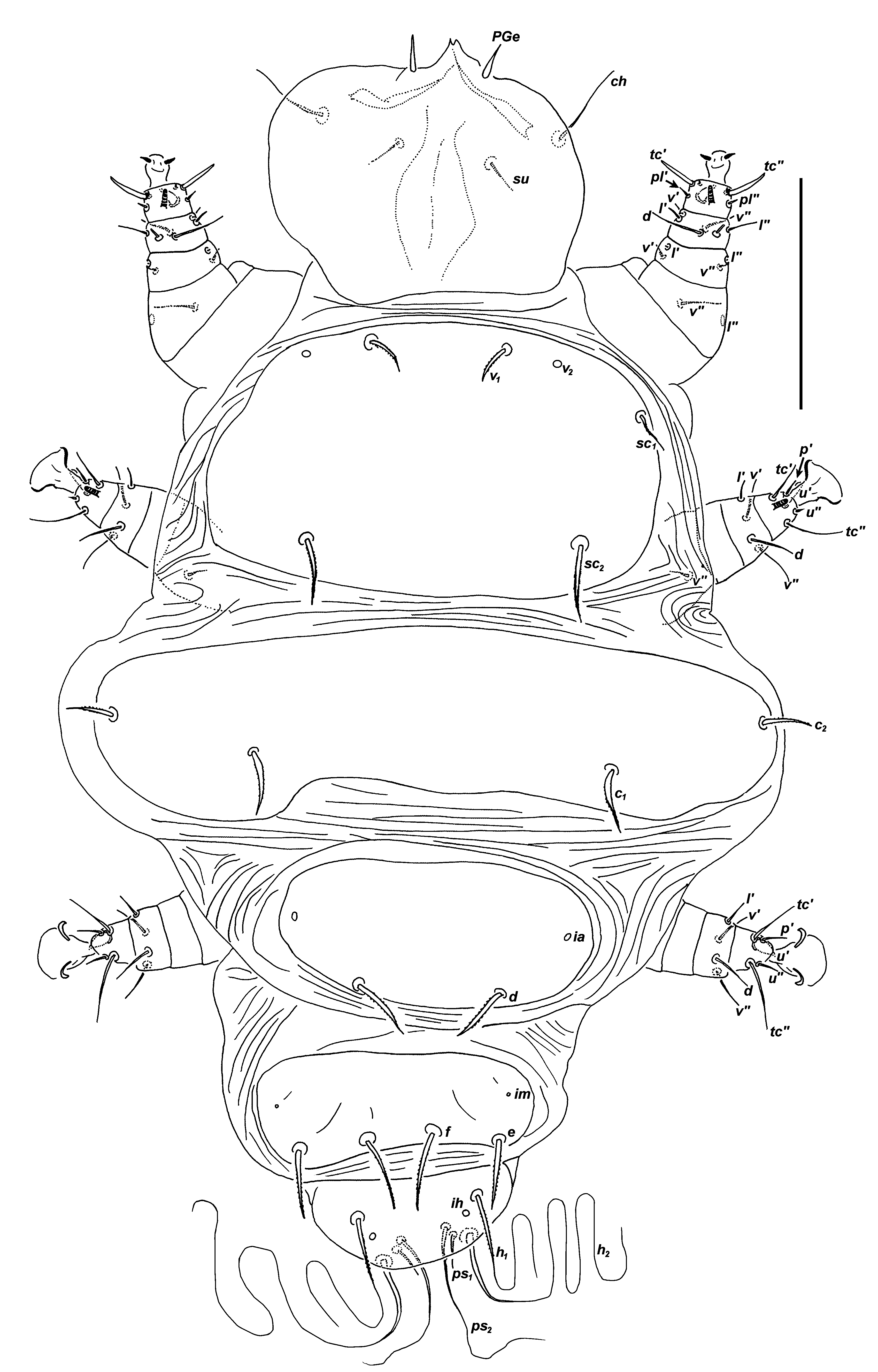
LARVA ( Fig. 19 View FIGURE 19 , n = 1 measured)
Gnathosoma . Length 46, width not measurable. Palp length 5, with 2 setae (lengths 6 and minute). Cheliceral stylets 26, without teeth. Pharynx length 29, width 18. Dorsal setae 18, ventral setae 9.
Idiosoma . Length 225, width 160. Prodorsal plate smooth, 60 long, 95 wide; with 3 pairs of tapering, weakly barbed setae ( v1 10, sc1 8, sc2 17) and vestigial v2. Distance between setae v1-v1 28, v2-v2 49, sc1-sc1 not measurable as sc1 missing on left hand side, sc2-sc2 58, v1 -sc2 41. Plates C, D, EF smooth. Setae tapering, weakly barbed, c1 17, c2 14, d 14, e 12, f 15. Distance between setae c1-c1 76, c2-c2 130, c1-c2 30, d-d 28, e-e 41, f-f 13. Plate H smooth, setae h1 long, 65, h2 ventral,> 120. Distance between setae h1 24. Cupules ia, im, ih present. Setae ps1 fine, 8, ps2 attenuate 60. Coxisternal setae attenuate, 1a 36, 2a 41, 3a > 40, 3b 30. Distance between setae 1a-1a 36, 2a-2a 41, 3a-3a 37, 3b-3b 35. Longitudinal striae between coxisterna III–IV.
Legs. Femur I, lʹʹ rudimentary, vʹʹ 10; genu I lʹ, lʹʹ rudimentary, vʹ 3, vʹʹ 2; tibia and tarsus I separate, tibial setae d 15, lʹ 4, lʹʹ 4, vʹ 3, vʹʹ 6, solenidion φ 3, tarsal setae tcʹ 9, tcʹʹ 9, pvʹ 3, pvʹʹ 6, s spine-like, 5, solenidion ω 4.
Femur II vʹʹ 7; tibia II d 9, lʹ 5, vʹ 11, vʹʹ 11; tarsus II tcʹ 7, tcʹʹ 12, pʹ 4, uʹ spine-like, 5, uʹʹ 2, solenidion ω 3.
Tibia III d 9, lʹ 6, vʹ 10, vʹʹ 10; tarsus III tcʹ 6, tcʹʹ 13, pʹ 4, uʹ spine-like, 5, uʹʹ 3. Leg I with 2 rudimentary claws.
Etymology. The species name indicus refers to the country where the type specimens were collected.
Differential diagnosis. Podotarsonemus indicus belongs to the australiensis species group ( P. australiensis , P. indicus , P. zuluensis ) whose females retain a seta on trochanter IV, have longitudinal striae between coxisterna III– IV and have setae h not attenuated. Of these species, P. indicus most closely resembles P. zuluensis but is distinguished by having: females with tracheal atria fused (free in other Podotarsonemus ), females with alveolar remnants of setae v2 within the prodorsal shield (anterolateral invaginations of prodorsal shield in P. zuluensis ), females and males retaining seta u″ on tarsus II (absent in P. zuluensis ), males with setae c2 much longer (> ×4) than c1 (<× 2 in P. zuluensis ) and tibia IV having an attenuate terminal seta and subterminal solenidion (lacking terminal seta and solenidion terminal in P. zuluensis ), and larvae with setae h1-2 and ps2 attenuate (short in P. zuluensis ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Acarapinae |
|
Genus |