Pediobius sasae, Hansson, Christer, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.172985 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6494784 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038B87FF-B465-0133-FEEF-78E5FD1CBE43 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pediobius sasae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pediobius sasae sp. nov.
Figs 1–15 View FIGURES 1 – 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURES 4 – 10 View FIGURES 11 – 13 View FIGURES 14 – 15
Diagnosis
Upper half of occiput strongly concave ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 4 – 10 ); occipital margin strongly carinate, especially strong in the dorsolateral corners of the occiput ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 4 – 10 ); transverse pronotal carina weakly developed or absent ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 – 13 ).
Description
Length of body female 2.5–3.4 mm, male 2.0– 2.7 mm.
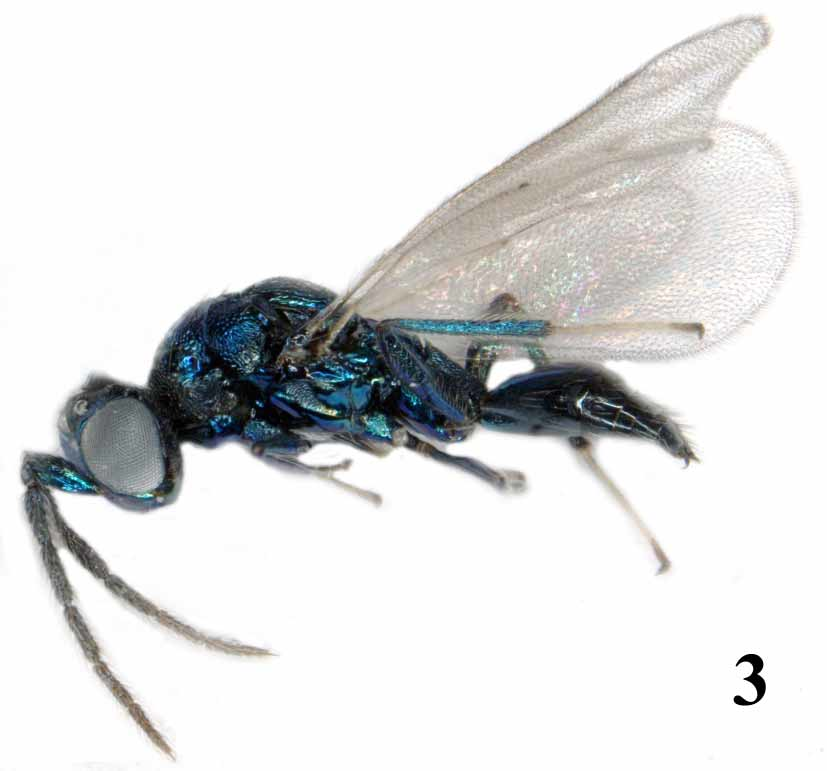
Female ( Figs 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 2 ), colour: Scape goldengreen, pedicel and flagellomeres 1–3 dark brown with a metallic tinge, flagellomeres 4–5 pale brown, or all flagellomeres dark brown with a metallic tinge. Frons goldenred with goldengreen spots, to entirely goldengreen; lower face and malar space metallic purple. Vertex dark goldenpurple. Mesoscutum goldengreen, sometimes with a metallic blue tinge. Scutellum and axillae dark goldenpurple. Dorsellum and propodeum goldengreen, sometimes with a metallic blue tinge. Coxae, femora and tibiae goldengreen with a metallic blue tinge; tarsal segments 1–3 yellowishwhite, segment 4 dark brown. Wings hyaline. Petiole dark goldenpurple. Gaster with first tergite goldengreen, remaining tergites dark goldenpurple.
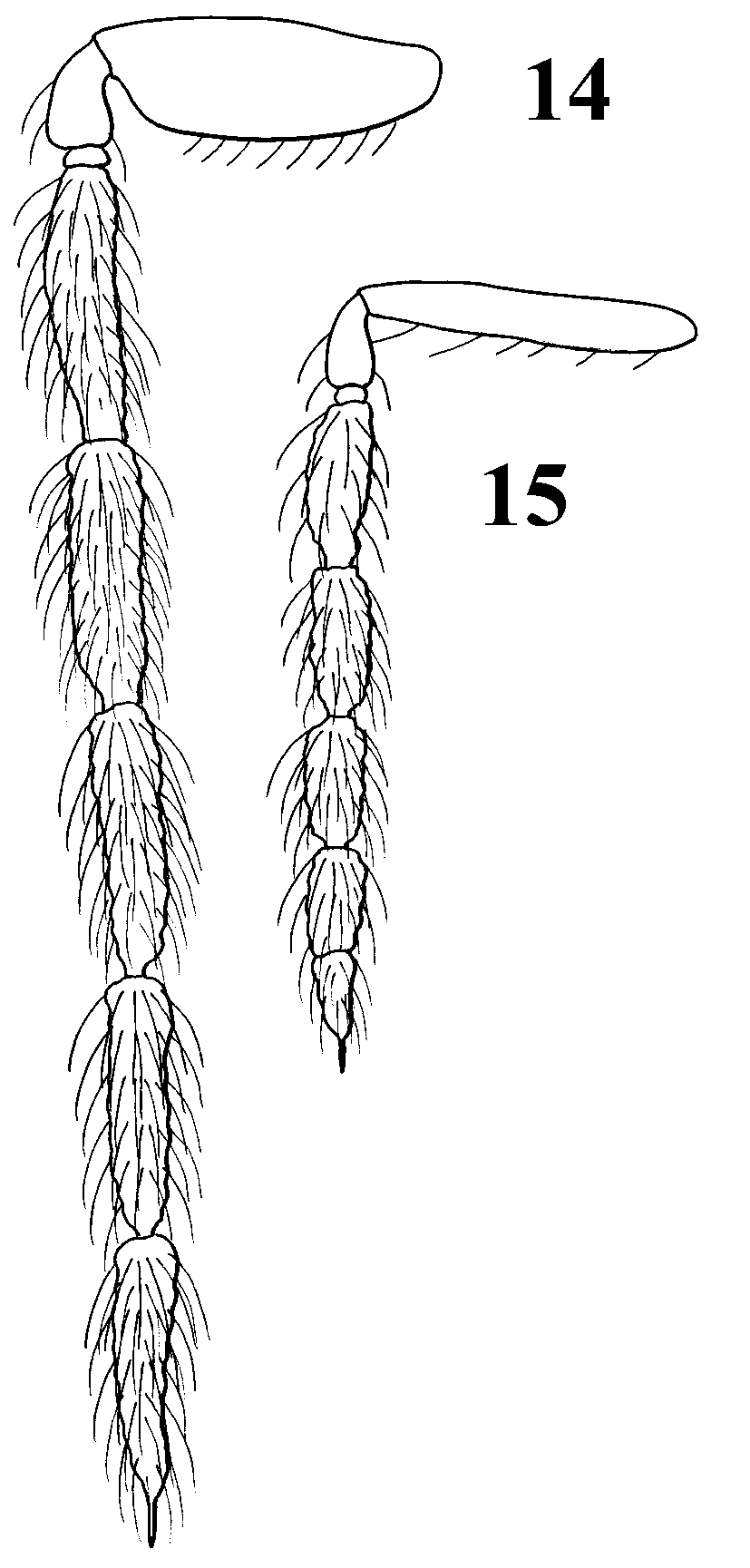
Antenna as in Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14 – 15 , i.e. with ratios of the length of scape/pedicel/flagellomeres 1 to 5: 3.9:1.0:1.8:1.6:1.4:1.1:1.2. Frons with weak reticulation, shiny; frontal suture Vshaped; antennal scrobes as distinct narrow grooves, joining frontal suture separately. Vertex with strong reticulation. Malar sulcus absent or indicated by fine and small meshed reticulation. Occipital margin with a strong carina. Eyes with scattered short hairs. Ratios of height of head/width of head 0.71:1; length of head/width of head 0.52:1; height of eye/malar space/ width of mouth opening 6.9:1.0:4.3; distances between posterior ocelli/between posterior ocelli and eye/between posterior ocelli and occipital margin 8.0:4.0:1.0; width of head/ width of thorax across shoulders 1.3:1.
Thoracic dorsum strongly convex. Pronotum well developed, with a weakly developed transverse carina close to posterior margin, carina absent in some specimens. Mesoscutum with strong reticulation; notaular depressions indistinct, entirely reticulate. With a short but wide hole between midlobe of mesoscutum and scutellum. Scutellum strongly convex with strong reticulation throughout. Dorsellum flat and smooth, with two shallow foveae anterolaterally. Propodeum smooth and shiny; submedian carinae closest medially, diverging posteriorly and anteriorly from this point; propodeal callus with two setae. Fore wing speculum closed below. Ratios of length of fore wing/length of marginal vein/height of fore wing 1.9:1.3:1.0; length of postmarginal vein/length of stigmal vein 1.5:1.
Petiole 0.83X as long as wide, with strong small meshed reticulation. Gaster elongate with posterior part pointed; first tergite smooth and shiny, remaining tergites with fine reticulation and with posterior margin smooth and shiny. Ratio of length of mesosoma/ length of gaster 0.58–0.61:1.
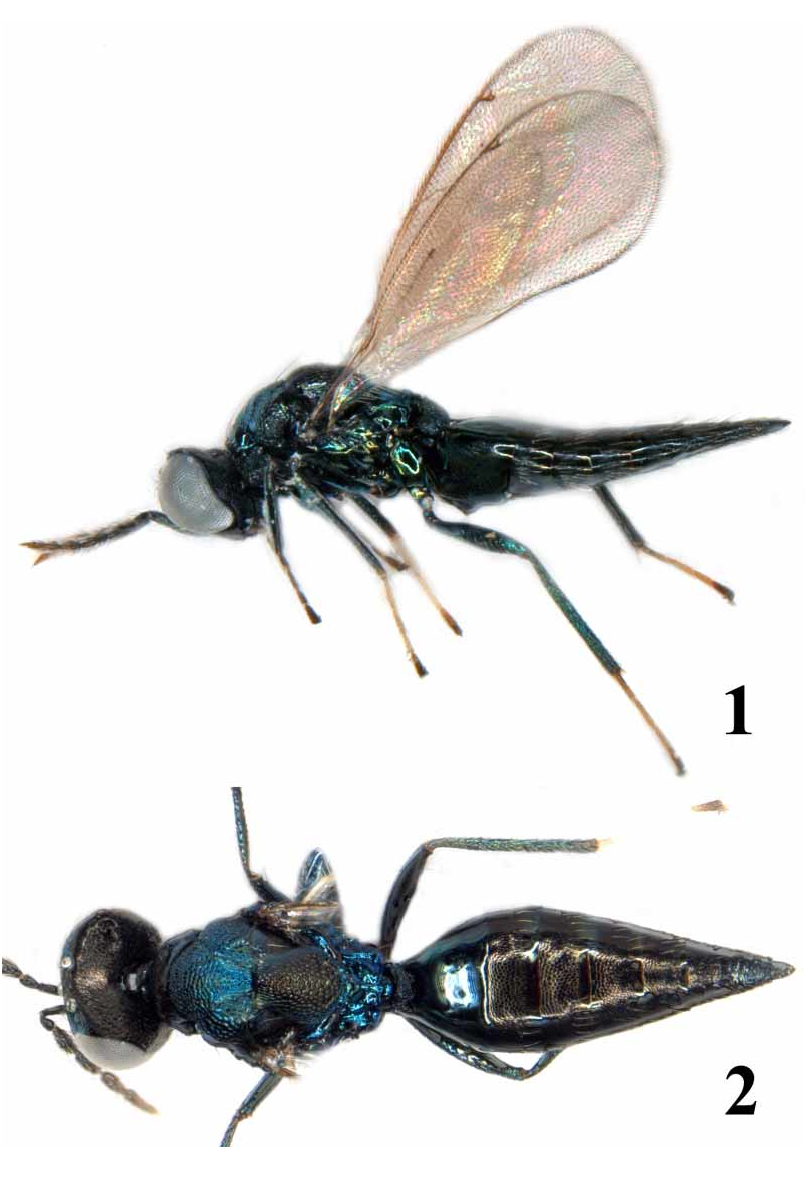
Male ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ), colour: Scape metallic bluishgreen; flagellum with flagellomere 5 slightly paler than 1–4, all flagellomeres with metallic tinges. Frons goldengreen with metallic blue tinges. Scutellum entirely dark goldenpurple as in female, or with median part dark goldenpurple and with sides and posterior part metallic bluishgreen. Mesoscutum, dorsellum and propodeum metallic bluishgreen. Gaster with first tergite metallic bluishgreen with purple tinges. Colour otherwise as in female.
Antenna as in Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14 – 15 , i.e. with ratios of the length of scape/pedicel/flagellomeres 1 to 5: 3.5:1.0:2.6:2.5:2.6:2.5:3.0. Ratios of height of head/width of head 0.70:1; length of head/width of head 0.43:1; height of eye/malar space/width of mouth opening 2.6:1.0:1.8; distances between posterior ocelli/between posterior ocelli and eye/between posterior ocelli and occipital margin 9.0:5.0:1.0; width of head/width of thorax across shoulders 1.3:1. Head otherwise as in female.
Ratios of length of fore wing/length of marginal vein/height of fore wing 1.8:1.1:1.0; length of postmarginal vein/length of stigmal vein 1.5:1. Mesosoma otherwise as in female.
Petiole 1.3–1.7X as long as wide. Genitalia as in most species of subfamily Entedoninae ( Hansson 1996) ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 4 – 10 ), i.e. with digitus as long as wide, two equally large digital spines, volsellar setae short and relatively slender, and parameres only slightly protruding. Ratio of length of mesosoma/length of gaster 1.2–1.5:1. Petiole and gaster otherwise as in female.
Description
Length of body female 2.5–3.4 mm, male 2.0– 2.7 mm.
Female ( Figs 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 2 ), colour: Scape goldengreen, pedicel and flagellomeres 1–3 dark brown with a metallic tinge, flagellomeres 4–5 pale brown, or all flagellomeres dark brown with a metallic tinge. Frons goldenred with goldengreen spots, to entirely goldengreen; lower face and malar space metallic purple. Vertex dark goldenpurple. Mesoscutum goldengreen, sometimes with a metallic blue tinge. Scutellum and axillae dark goldenpurple. Dorsellum and propodeum goldengreen, sometimes with a metallic blue tinge. Coxae, femora and tibiae goldengreen with a metallic blue tinge; tarsal segments 1–3 yellowishwhite, segment 4 dark brown. Wings hyaline. Petiole dark goldenpurple. Gaster with first tergite goldengreen, remaining tergites dark goldenpurple.
Antenna as in Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14 – 15 , i.e. with ratios of the length of scape/pedicel/flagellomeres 1 to 5: 3.9:1.0:1.8:1.6:1.4:1.1:1.2. Frons with weak reticulation, shiny; frontal suture Vshaped; antennal scrobes as distinct narrow grooves, joining frontal suture separately. Vertex with strong reticulation. Malar sulcus absent or indicated by fine and small meshed reticulation. Occipital margin with a strong carina. Eyes with scattered short hairs. Ratios of height of head/width of head 0.71:1; length of head/width of head 0.52:1; height of eye/malar space/ width of mouth opening 6.9:1.0:4.3; distances between posterior ocelli/between posterior ocelli and eye/between posterior ocelli and occipital margin 8.0:4.0:1.0; width of head/ width of thorax across shoulders 1.3:1.
Thoracic dorsum strongly convex. Pronotum well developed, with a weakly developed transverse carina close to posterior margin, carina absent in some specimens. Mesoscutum with strong reticulation; notaular depressions indistinct, entirely reticulate. With a short but wide hole between midlobe of mesoscutum and scutellum. Scutellum strongly convex with strong reticulation throughout. Dorsellum flat and smooth, with two shallow foveae anterolaterally. Propodeum smooth and shiny; submedian carinae closest medially, diverging posteriorly and anteriorly from this point; propodeal callus with two setae. Fore wing speculum closed below. Ratios of length of fore wing/length of marginal vein/height of fore wing 1.9:1.3:1.0; length of postmarginal vein/length of stigmal vein 1.5:1.
Petiole 0.83X as long as wide, with strong small meshed reticulation. Gaster elongate with posterior part pointed; first tergite smooth and shiny, remaining tergites with fine reticulation and with posterior margin smooth and shiny. Ratio of length of mesosoma/ length of gaster 0.58–0.61:1.
Male ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ), colour: Scape metallic bluishgreen; flagellum with flagellomere 5 slightly paler than 1–4, all flagellomeres with metallic tinges. Frons goldengreen with metallic blue tinges. Scutellum entirely dark goldenpurple as in female, or with median part dark goldenpurple and with sides and posterior part metallic bluishgreen. Mesoscutum, dorsellum and propodeum metallic bluishgreen. Gaster with first tergite metallic bluishgreen with purple tinges. Colour otherwise as in female.
Antenna as in Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14 – 15 , i.e. with ratios of the length of scape/pedicel/flagellomeres 1 to 5: 3.5:1.0:2.6:2.5:2.6:2.5:3.0. Ratios of height of head/width of head 0.70:1; length of head/width of head 0.43:1; height of eye/malar space/width of mouth opening 2.6:1.0:1.8; distances between posterior ocelli/between posterior ocelli and eye/between posterior ocelli and occipital margin 9.0:5.0:1.0; width of head/width of thorax across shoulders 1.3:1. Head otherwise as in female.
Ratios of length of fore wing/length of marginal vein/height of fore wing 1.8:1.1:1.0; length of postmarginal vein/length of stigmal vein 1.5:1. Mesosoma otherwise as in female.
Petiole 1.3–1.7X as long as wide. Genitalia as in most species of subfamily Entedoninae ( Hansson 1996) ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 4 – 10 ), i.e. with digitus as long as wide, two equally large digital spines, volsellar setae short and relatively slender, and parameres only slightly protruding. Ratio of length of mesosoma/length of gaster 1.2–1.5:1. Petiole and gaster otherwise as in female.
volsellar setae.
Biology
Parasitoid of an unidentified gall midge belonging to the tribe Oligotrophini ( Diptera : Cecidomyiidae ) forming galls on dwarf bamboo ( Sasa nipponica Makino & Shibata ). Possibly also a hyperparasitoid of Torymus sp. ( Hymenoptera : Torymidae ).
Distribution
Japan (Nara Prefecture, Mt. Ôdaigahara).
Material examined
Holotype female labeled “ Japan: Nara Prefecture, Mt. Ôdaigahara, 34°11’N, 136°06’E, 1540 m, 24.iv.2003, A. Ueda” (Lund University Zoology Museum, Sweden). Paratypes: 79 females and 50 males with same label data as holotype (Australian National Insect Collection, Canberra; Canadian National Collection of Insects, Ottawa; collection of Christer Hansson; Hokkaido University Museum, Japan; Lund University Zoology Museum, Sweden; Natural History Museum, London, England; Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, Washington, D.C., U.S.A.; Texas A&M University collection, College Station, U.S.A.; University of California, Riverside, U.S.A.).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |