Parabathylaimus jare Shimada, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.12782/specdiv.26.49 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2656AD30-05F3-4987-B361-FC5A63E50BE0 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038AE379-250B-EE56-FC10-F8A4C662085B |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Parabathylaimus jare Shimada |
| status |
sp. nov. |
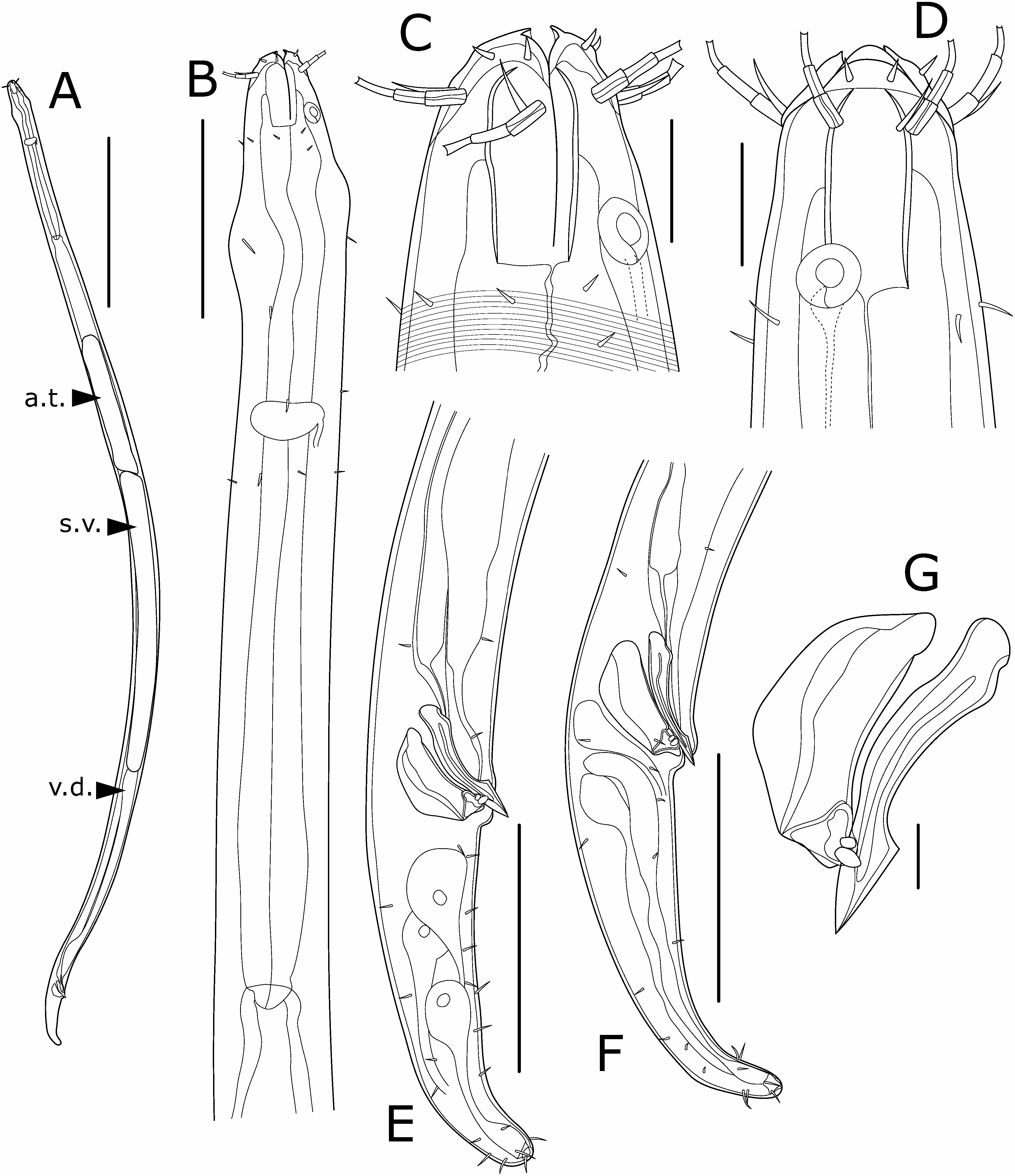
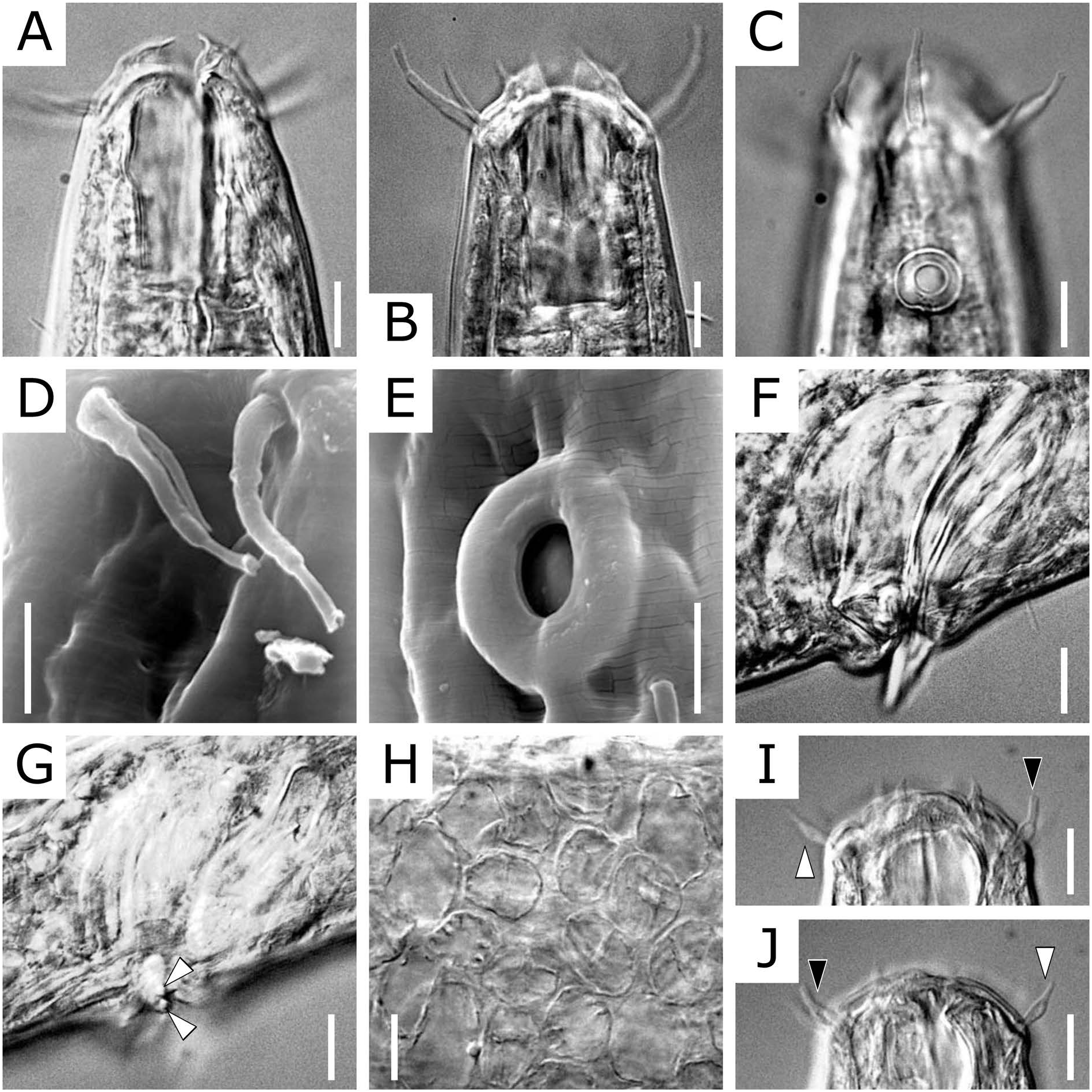
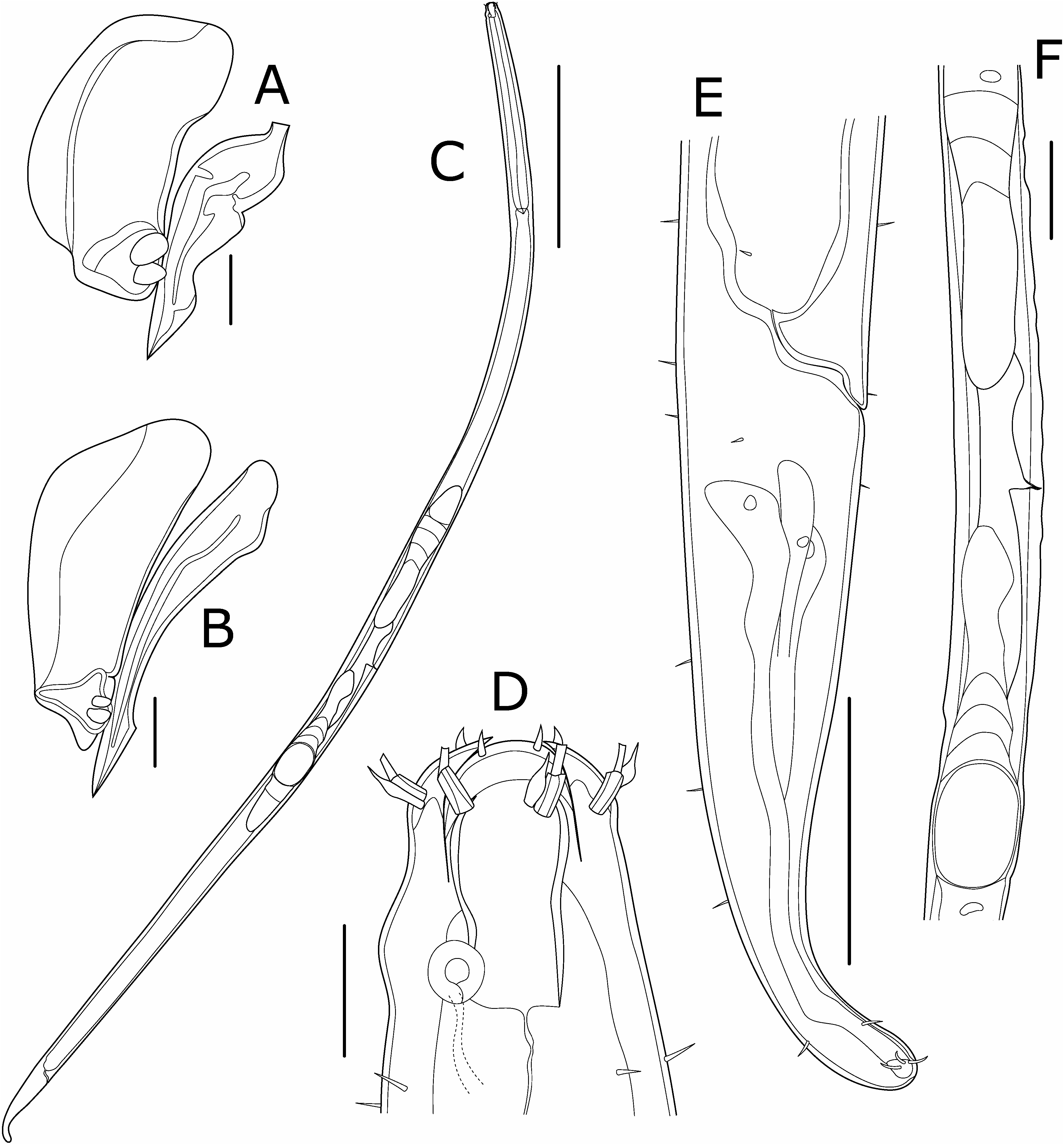
Parabathylaimus jare Shimada , sp. nov. ( Figs 4–6 View Fig View Fig View Fig )
Tripyloididae gen. sp. in Shimada et al. (2017): table 1.
Material examined. Holotype. Male ( ICHUM 5375 View Materials ), formalin fixed, whole mount in glycerin, upper subtidal sandy
sediment, Langhovde ( 69°14′24.3″S, 39°42′55.8″E), Lützow- Holm Bay , Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica GoogleMaps . Paratypes. Three males ( ICHUM 5376–5378 View Materials ) and one female ( ICHUM 5493 View Materials ), formalin fixed, whole mount in glycerin, same collection data as for holotype . Other material. One male, Aucoated for SEM, same collection data as for holotype .
Etymology. The specific name jare is derived from the expedition name JARE 56, and thus treated as indeclinable.
Diagnosis. Six inner labial and four cephalic sensilla not jointed; six outer labial sensilla three-jointed in males and two-jointed in females; amphids at level of posterior end of buccal cavity; spicules short (as long as cloacal body diameter); conical tail without long subterminal setae.
Measurements. See Table 2.
Description of males. Body ( Fig. 4A View Fig ) cylindrical, gradually tapering toward both ends. Cuticle colorless, 2–4 µm thick, with fine transverse striations. Somatic sensilla sparse except in cervical, cloacal, and caudal regions. Head ( Figs 4B–D View Fig , 5A–C View Fig ) rounded at anterior end. Three lips high, deeply incised. Six setiform inner labial sensilla unjointed, acute at distal end, 0.10–0.15 cephalic diameters long, 0.10– 0.25 cephalic diameters from anterior body end. Six setiform outer labial sensilla ( Figs 4C, D View Fig , 5B–D View Fig ) three-jointed, flared at distal end, 0.5–0.7 cephalic diameters long, located 0.4–0.6 cephalic diameters from anterior end. Four setiform cephalic sensilla ( Figs 4C, D View Fig , 5B–D View Fig ) unjointed, acute at distal end, 0.3–0.4 cephalic diameters long, arranged in single circle together with outer labial sensilla. Subcephalic sensilla absent. Amphids ( Figs 4C, D View Fig , 5C, E View Fig ) unispiral with circular or oval aperture and thick cuticular ring, 0.3–0.4 cephalic diameters wide, 1.0–1.1 cephalic diameters or 0.7–0.8 buccal cavity lengths from anterior end (posterior end of amphids at level of posterior end of buccal cavity). Amphidial ducts conspicuous. Buccal cavity ( Figs 4C, D View Fig , 5A, B View Fig ) single, nearly cylindrical in shape, 1.3–1.5 cephalic diameters long and ca. 0.5 cephalic diameters wide (length/width=2.7–2.9). Teeth absent. Pharynx ( Fig. 4B–D View Fig ) surrounding posterior 35–45% of buccal cavity, nearly cylindrical, not expanded at posterior end. Holotype crushed flat in anterior part of pharynx during fixation. Nerve ring located at 35–40% of pharyngeal length. Secretory-excretory system not observed. Cervical sensilla setiform, slightly longer than inner labial sensilla, arranged in eight longitudinal rows, beginning just posterior to buccal cavity, sparser in posterior half of cervical region. Cardia short, surrounded by intestine. Tail ( Fig. 4E, F View Fig ) nearly conical in shape, rounded at posterior end, 3.2–3.5 cloa- cal body diameters long, with three terminal setae (8–9 µm long). Long subterminal setae absent. Rows of ventrolateral and dorsolateral setae (5–8 µm long) on each side in cloacal and caudal regions. Number and position of setae differ among specimens. Three caudal glands located postcloacally. Spinneret distinct. Spicules ( Figs 4G View Fig , 5F View Fig , 6A, B View Fig ) paired, as long as 1.0–1.2 cloacal body diameters or 0.3–0.4 tail lengths, slightly arcuate, constricted proximally but not forming distinct capitulum, acute at distal end, with median lamella and heel-shaped ventral projection. Left spicule in ICHUM 5376 ( Fig. 6A View Fig ) malformed; right spicule similar to those in other males. Gubernaculum ( Figs 4G View Fig , 5F, G View Fig , 6A, B View Fig ) single platelike, as long as 0.9–1.2 cloacal body diameters or 0.8–1.1 spicule lengths, located between spicules, with distal swelling having two tooth-like projections on each side. Precloacal supplement absent. Reproductive system ( Fig. 4A View Fig ) monorchic with outstretched anterior testis, not well developed in ICHUM 5377 or 5378. Testis located on left side of intestine, beginning at 27% of body length from anterior body end, as long as 15% of body length in holotype. Seminal vesicle well developed in holotype but not observed in other specimens, as long as 30% of body length, filled with globular sperm (5–10µm in diameter) ( Fig. 5H View Fig ). Vas deferens observed in all specimens, not strongly muscular.
Description of female. Body ( Fig. 6C View Fig ) similar to males, with following differences. Outer labial sensilla ( Figs 5I, J View Fig , 6D View Fig ) two-jointed, much shorter than in males, 0.3–0.4 cephalic diameters long, 0.3 cephalic diameters from anterior end. Cephalic sensilla ( Figs 5I, J View Fig , 6D View Fig ) unjointed, expanded in middle, 0.2–0.3 cephalic diameters long. Nerve ring indistinct. Tail ( Fig. 6E View Fig ) similar to males in shape but slightly longer, 3.8 anal body diameters long. Ventrolateral and dorsolateral setae also present, but ventrolateral setae sparser than in males. Reproductive system ( Fig. 6C, F View Fig ) didelphic, with opposed, reflexed ovaries: anterior ovary on right side of intestine, beginning at 51% of body length and ending at 38%, as long as 13% of body length; posterior ovary also on right side of intestine, beginning at 58% of body length and ending at 66%, as long as 8% of body length. Total length of reproductive system 28% of body length. No egg present in uteri. Vulva slit-like, located at 55% of body length. Vagina weakly sclerotized, 15 µm long. Sperm not observed in oviduct or uteri.
Remarks. Parabathylaimus jare sp. nov. differs from P. arthropappus in having much shorter outer labial sensilla (shorter than cephalic diameter in P. jare sp. nov.; ca. 1.5 cephalic diameters long in P. arthropappus ), in having the amphids positioned more anteriorly (at the level of the buccal cavity in P. jare sp. nov.; posterior to the buccal cavity in P. arthropappus ), and in lacking subterminal setae as long as the cloacal body diameter at the tail tip (present in P.arthropappus ) (cf. Wieser and Hopper 1967); from P. ponticus in the shorter spicules (as long as the cloacal body diameter in P. jare sp. nov.; twice as long as the cloacal body diameter in P. ponticus ) (cf. Filipjev 1922); from P. profundis in the shape of tail (conical, 3.2–3.8 cloacal/anal body diameters long in P. jare sp. nov.; conico-cylindrical, ca. 7.5 anal body diameters long in P. profundis ) (cf. Filipjev 1927); and from P. denticaudatus in having unjointed inner labial and cephalic sensilla (jointed in P. denticaudatus ), and having the outer labial sensilla three-jointed in males and two-jointed in females (four-jointed in both sexes in P. denticaudatus ) (cf. Schuurmans Stekhoven 1935; Luc and De Coninck 1959). Following is a taxonomic key to Parabathylaimus species (cf. Filipjev 1922, 1927; Allgén 1930; De Coninck and Schuurmans Stekhoven 1933; Wieser and Hopper 1967): 1. Tail conico-cylindrical, with filiform posterior portion.
...................................... P. profundis — Tail conical or clavate............................ 2 2. Spicules twice as long as cloacal body diameter.......
....................................... P. ponticus — Spicules as long as or shorter than cloacal body
diameter....................................... 3 3. Amphids located posterior to buccal cavity...........
................................... P. arthropappus — Amphids located at level of buccal cavity............ 4 4. Inner labial and cephalic sensilla two-jointed, outer
labial sensilla four-jointed in both sexes.............
.................................. P. denticaudatus
— Inner labial and cephalic sensilla unjointed, outer labial sensilla three-jointed in males and two-jointed in females............................. P. jare sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |