Mycomya cissa, Väisänen, Rauno, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3737.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:358CB400-2CF2-4AF1-8DC6-9F8C57721C33 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6152029 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/600087D2-FFA2-4838-5086-FEF6FADA1CB1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mycomya cissa |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mycomya cissa sp. n.
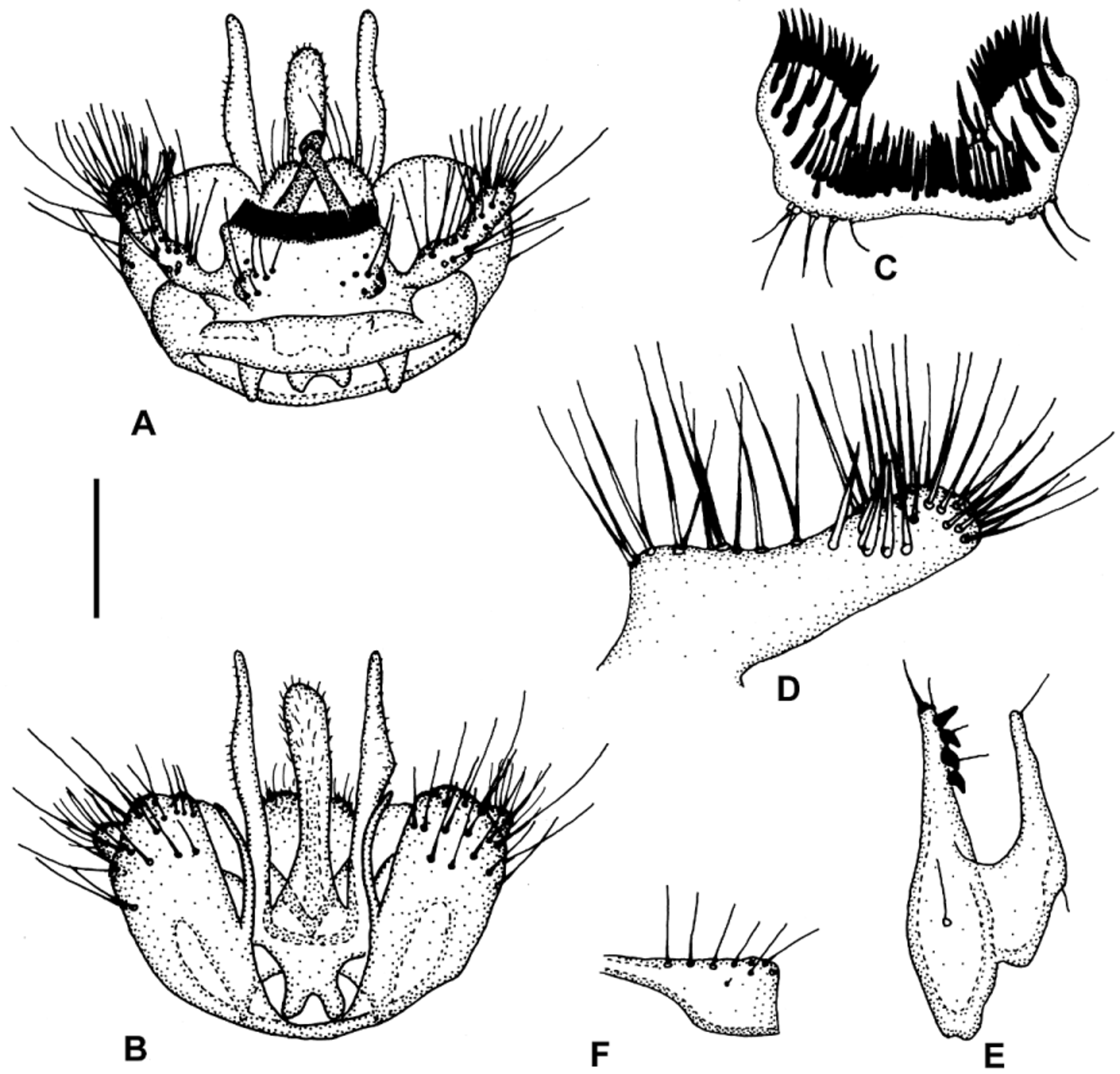
Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A–F
Material studied. Holotype. ♂. MYANMAR, N.E. Burma, Kambaiti, 1800 m, 7.VI. 1934, Malaise (in MZH). Paratypes. Same data as holotype, 2 ♂♂ (MZH).
Description. ♂. Head. Palp brownish, other mouthparts and face yellowish, posterior parts of head brownish. Antenna brownish, scape, pedicel and base of 1st flagellomere yellow. Length of 1st flagellomere about 4x, 2nd flagellomere 2.5x, its width. Thorax. Pronotum yellow, with 3–4 long setae. Scutum yellowish with 3 indistinct brownish longitudinal stripes. Anepisternum yellow. Preepisternum yellow, ventral half brownish. Scutellum brownish, with 4 long setae. Laterotergite brownish. Mediotergite brownish, bare. Wing. Length 3.6–3.8 mm. Wing hyaline. Sc ending in R1 proximad of middle of small cell, Sc1 missing. Apical part of Sc bearing no small setae. Small cell shorter than its width. Cu fork slightly distal to M fork. M ratios: 0.75–0.90, 1.03–1.21. Cu ratios: 0.86–1.00, 1.37–1.56. Small setae: M petiole: 0; M1: 0; M2: 0; Cu petiole: 0; Cu1: 0; Cu2: 0. Halter apically brownish. Legs. Coxae and femora yellow, tibiae and tarsi brownish to brown. Coxa 2 without spur. Leg ratios: bt1:t1 = 0.79–0.81, bt2:t2 = 0.69–0.70, bt3:t3 = 0.60. Abdomen. Tergites brownish, sternites slightly paler. Hypopygium. Figs.1 View FIGURE 1 A–F: yellowish. Tergal part with 1 very wide outer comb of short spines. Some spines also between wide outer comb and 2 inner combs ( Fig.1 View FIGURE 1 C). Inner combs wide, each with 12–14 spines. Only lateral parts of base of outer comb with some setae, its median part bare. Dark inner spur of tergal part apically blunt. Tergal lateral appendage long, relatively slender, about 4x as long as wide, setose, with some slightly flattened, relatively short (slightly longer than width of tergal lateral appendage) subapical setae on inner side ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D; also Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, on both sides of outer comb). Sternal submedian filament ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B, narrow basal extensions of deeply bilobed sternal synsclerite along medial side of its both lobes) relatively short, hardly reaching apex of sternal synsclerites, slightly curved. Gonostylus tapering towards its apex, with 4 subapical teeth, 1 strong apical seta, and relatively large membranous lobe only slightly shorter than main branch of gonostylus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 E). Aedeagus long, slender, with 2 very long slender lateral appendages extending slightly beyond its apex ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B, mid-upper part).
Discussion. Mycomya cissa differs readily from the other species of the subgenus Cesamya in the unique shape and structure of the tergal combs formed by stronger spines ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, 1C) than in the other species. Other diagnostic features include tergal lateral appendage ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D) lacking the curved flattened setae and sternal submedian filament not extending beyond the apex of the sternal synclerite ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B).
Etymology. The species name is a noun in apposition and refers to the green magpie (genus Cissa F. Boie).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |