Mormidea cornicollis Stål, 1860
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3768.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:076F3E92-066C-46A0-9ADE-09D3AA8F8707 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5584491 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A487D3-9A31-033A-E497-24ACE9BFFDA2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mormidea cornicollis Stål, 1860 |
| status |
|
Mormidea cornicollis Stål, 1860
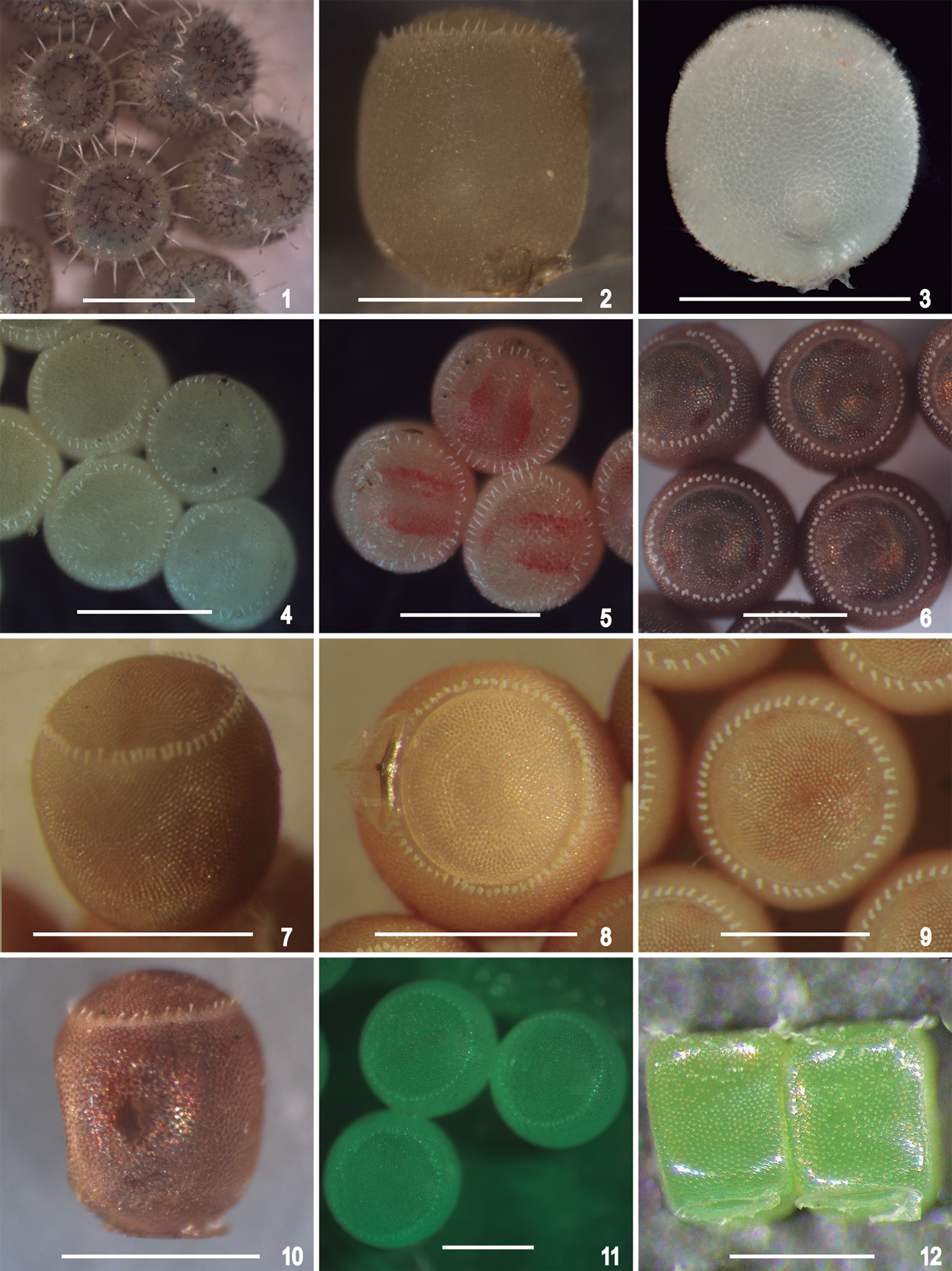
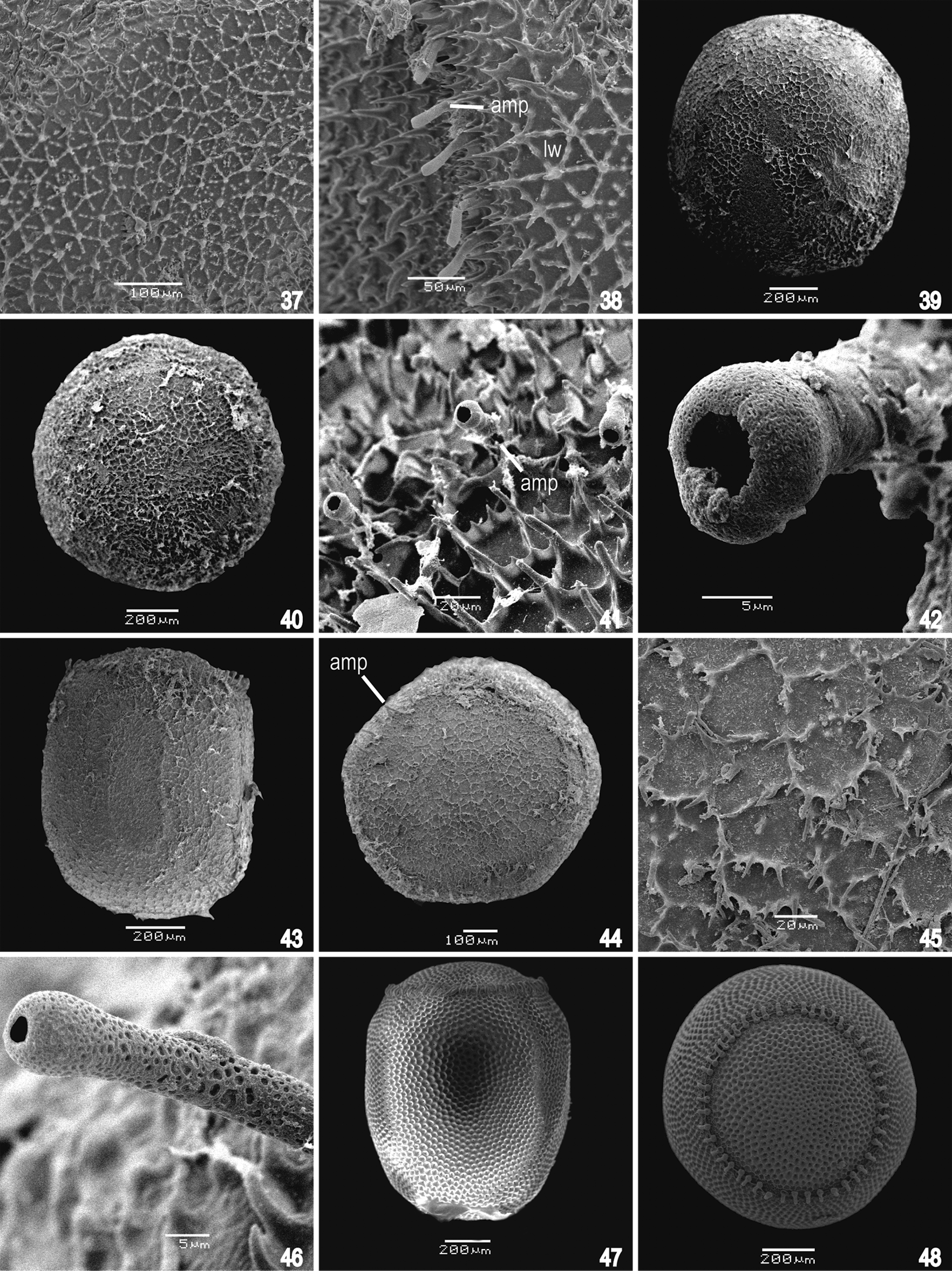
( Figs. 4, 5 View FIGURES 1 – 12 , 43–46 View FIGURES 37 – 48 ; Tab. 2 View TABLE 2 )
Eggs barrel-shaped; light yellow prior to embryonic development; operculum round and convex; chorion translucent and spinose ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 12 ). Eggs darker, with two irregular red stripes and red eyes evident in anterior view after embryonic development ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 12 ). The eclosion line not evident under SM, and the AMPs are circularly arranged in a row around the anterior pole, white, and moderately long ( Figs. 4, 5 View FIGURES 1 – 12 ).
Under SEM, the chorion surface is spinose, and the spines are short. The interconnected spines form faintly distinct polygonal markings at the lateral wall; the sculpture pattern is altered where the eggs were attached to another ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 37 – 48 ). The operculum is similarly sculptured, displaying spines of different sizes, and the polygonal markings are especially apparent ( Figs. 44, 45 View FIGURES 37 – 48 ). The eclosion line is not discernible. The AMPs are slender, only slightly clubbed, and bear circular and apical openings ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 37 – 48 ). Their surface is clearly spongy under higher magnification ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 37 – 48 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Pentatominae |
|
Genus |