Mnioes tawa, Alvarado, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4743.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A3EB2E6D-C484-4E24-9613-572BE7873E21 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3688123 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E887DD-CC5A-FFD2-FF16-FC5B35D5FD3C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mnioes tawa |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mnioes tawa sp. nov.
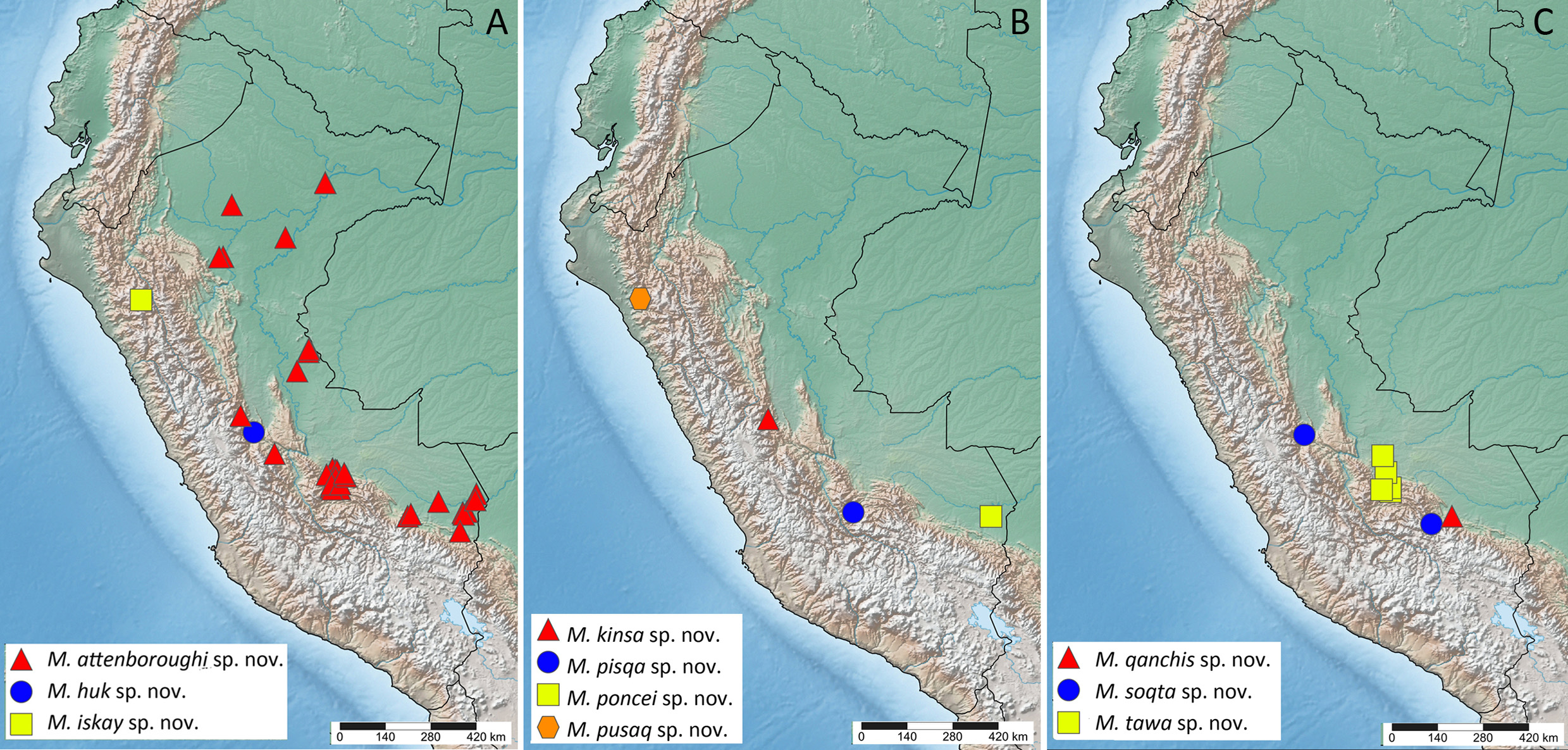
( Figures 8 View FIGURE 8 , 9C View FIGURE 9 )
Diagnosis. Mnioes tawa sp. nov. can be distinguished from its female congeners by the following combination of traits: face, mesoscutum, tegula, and coxae predominantly black, at least with flagellomeres 15–17 entirely white, wings hyaline, and ovipositor sheath 2.5× as long as metatibia; while males are the only ones with mesoscutum black with reddish anterolateral marks. This species is more similar to M. attenboroughi sp. nov. ( vide Remarcks, supra).
Material examined. Holotype: ♀, “ PERÚ: CU. La Convención , Echarate, CC Kitaparay 72º49’11.42”/ 12º12’47.73” 474m 10.xi.2009 Light. C. Espinoza y E. Rázuri ” ( MUSM).
Paratypes: CUZCO: 1♀, La Convención, Echarate, Timpia , 12º6’45.02”S / 72º49’33.52”W, 546m, 25–31.I.2010, C. Espinoza & E. Rázuri, primary forest with pacal GoogleMaps ; 1♀, Camisea , 11º41’20.7”S / 72º56’47”, 493m, 10.VIII.2013 V . Borda ; 2♂♂, Quebrada Coentiari 12º9’56”S / 73º4’2.1”W, 614m, 13–16.VII.2011, A. Alfaro GoogleMaps ; 1♀, Reserva Comunal Matsigenga 12º13’33.81”S / 73º02’6.98”W, 1297m, 3.VIII.2007, A. Asenjo ( MUSM) GoogleMaps .
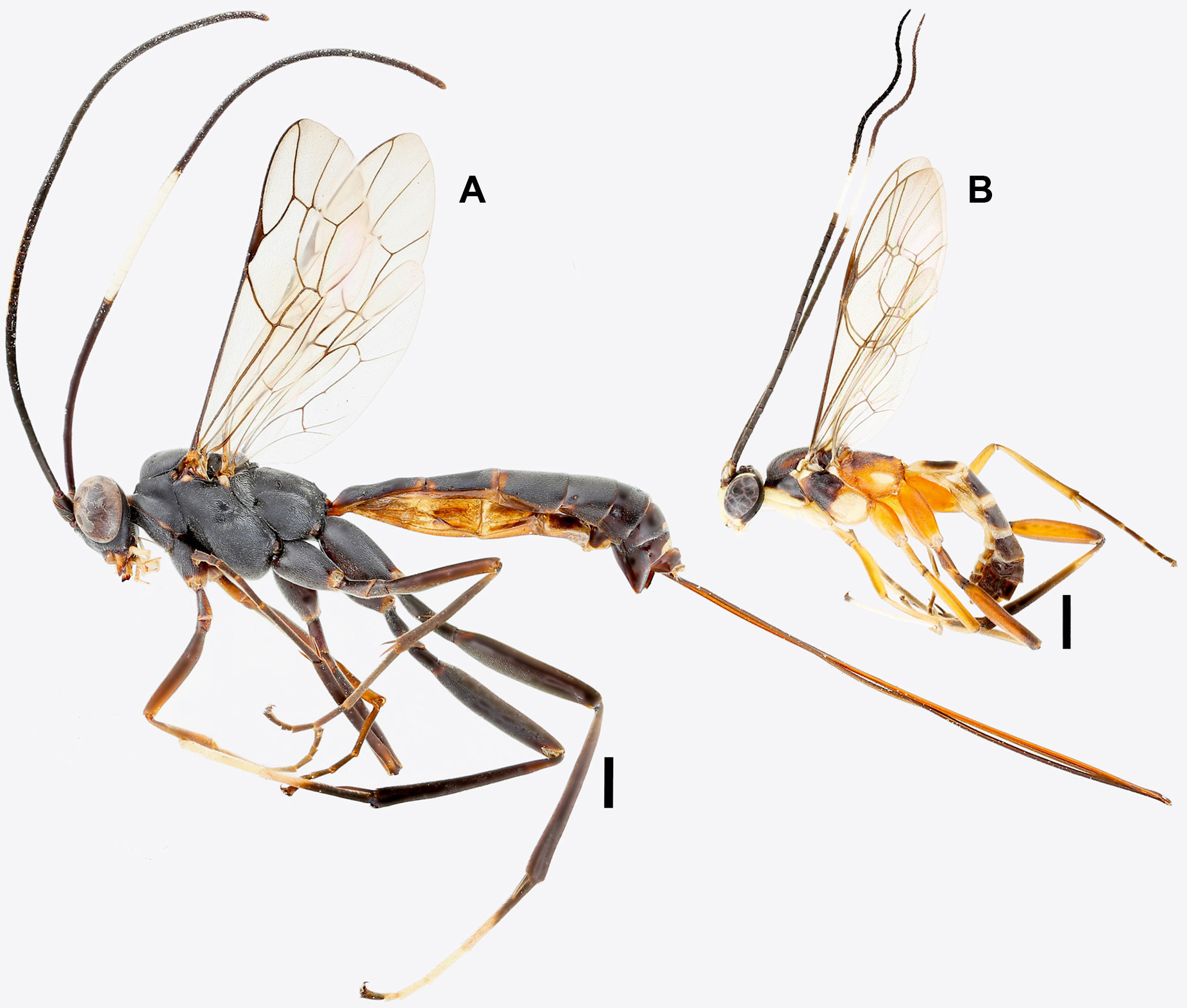
Description of female holotype. Fore wing length 8.4 mm.
Head: Face granulate-punctate and weakly polished, 0.7× as long as wide; clypeus dorsal half granulate-punctate, ventral half granulate, 2.0× as wide as long; malar space 0.6× as long as basal mandibular width; lateral ocellus separated from compound eye by about 1.0× maximum ocellar diameter; distance between ocelli 1.0× maximum ocellar diameter; scape with truncated section V-shaped, with 46 flagellomeres, ratio of length from second to fourth flagellomeres: 3.2:2.7:2.7, subapical flagellomere 1.1× as long as centrally broad.
Mesosoma : Granulate-punctate and weakly polished; notaulus vestigial, weakly impressed anteriorly; subalar prominence low and weakly rounded. Propodeum granulate-punctate; evenly declivous from anterior margin; pleural carina distinct only basally; with a weak, narrow vestige of posterior transverse carina present centrally on an elevation. Fore wing with vein 1m-cu with a ramellus; vein 2m-cu weakly sinuate, with a two bullae, with abscissa and with a stub on spurious vein; 2rs-m 2.3× as long as abscissa of M between 2rs-m and 2m-cu. Hind wing with length of abscissa of Cu1 between Cu1 and 1A 0.2× as long as length of vein Cu1 between M and Cu1.
Metasoma: Metasomal tergites granulate, matte; tergite I 2.2× as long as posteriorly wide; tergite II 1.2× as long as posteriorly wide; ovipositor sheath 2.5× as long as metatibia.
Colour: Head black; mandible centrally, ventral half of clypeus, and palpi off-white; orbit (between antennal socket and median ocellus) white; antenna black with flagellomeres 8–18 dorsally white. Mesosoma ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ) predominantly black; anterior margin of pronotum off-white (dorsally white), subalar prominence and dorsal most section of mesepisternum white; humeral plate basally white, grading distally to brown scutellum medially off-white. Prothoracic leg with coxa black, ventrally and distal end off-white; trochanter, trochantellus, femur, and tarsus brown but ventrally light brown; tibia light brown. Mesothoracic leg black, distal end of coxa off-white. Metathoracic leg predominantly black, distal half of basitarsus and tarsomere 2–4 white. Wings hyaline. Metasomal tergites predominantly black; anterior and posterior margins of tergite I–II and anterior margin of tergite III off-white, tergites V–VII mid-posterior margin white. Ovipositor sheath black.
Variation of female paratypes. Fore wing length 7.9–8.8 mm. They differ from the holotype in the following features: clypeus 1.9–2.1× as wide as long; lateral ocellus separated from compound eye by about 1.0–1.2× maximum ocellar diameter; distance between ocelli 1.0–1.1× maximum ocellar diameter; antenna with 43–44 flagellomeres, ratio of length from third to fourth flagellomeres: 2.7–2.9:2.7–2.8, subapical flagellomere 1.0–1.1× as long as centrally broad; fore wing with vein 2m-cu with or without a stub of spurious vein; tergite I 2.4× as long as posteriorly wide; tergite II 1.3–1.6× as long as posteriorly wide; antenna black with flagellomeres 7 or 9–17 dorsally white; and metathoracic coxa ventrally reddish. Within the coloration: antenna black with flagellomeres 7 or 9–17 dorsally white; metathoracic coxa, in some individuals, ventrally reddish.
Male. Fore wing length 6.0– 6.4 mm. The male individuals ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ) differ from the females in the following features: face 0.8× as long as wide; lateral ocellus separated from compound eye by about 0.9× maximum ocellar diameter; distance between ocelli 0.7× maximum ocellar diameter; antenna with 41–42 flagellomeres, ratio of length from second to fourth flagellomeres: 3.5–3.6:3.4–3.5:3.4–3.5, subapical flagellomere 2.2–2.3× as long as centrally broad; propodeum without pleural carina; fore wing with vein 1m-cu without or with a small ramellus, vein 2m-cu with one long bulla and without a stub on spurious vein, 2rs-m 1.8× as long as abscissa of M between 2rs-m and 2m-cu; hind wing with length of abscissa of Cu1 between Cu1 and 1A 0.1× as long as length of vein Cu1 between M and Cu; and tergite I 2.0× × as long as posteriorly wide; tergite II 1.3× × as long as posteriorly wide.
Colour (male): Head predominantly light yellow; frons centrally, vertex, gena, and occiput black; antenna predominantly black, scape and pedicel ventrally light yellow, flagellomeres black with flagellomeres 13–21 at leas dorsally white and with flagellomeres 15–17 or 15–20 completely white. Mesosoma with pronotum predominantly black but anterior margin of pronotum and postero-dorsal corner light yellow; mesoscutum black with reddish anterolateral mark; mesopleuron with anterior half dark brown, mesopleuron with posterior half, subalar prominence, dorsal most section of mesepisternum, tegula and humeral plate light yellow; metapleuron orange with a light-yellow spot; propodeum orange, centrally brown. Prothoracic leg with coxa white; trochanter dorsally, trochantellus, and femur light brown; tarsus brown. Mesothoracic predominantly orange; coxa ventrally, trochanter, trochantellus, femur, and tibia off-white; tarsus light brown. Metathoracic leg with coxa orange; trochanter, trochantellus, and femur reddish brown; tibia, basal half of basitarsus, distal half of tarsomere 4 and tarsomere 5 dark brown; distal half of basitarsus, tarsomere 2–3, and basal half of tarsomere 4 white. Wings hyaline. Metasomal tergites predominantly black; tergite I–IV anterior and posterior margins off-white, posterior margins of tergite V–VII off-white or blackish (in some individuals anteriorly off-white).
Distribution. Cusco ( Fig. 9C View FIGURE 9 ), between 474–1297m.
Etymology. The specific epithet tawa means “four” in Quechua. It is treated as a noun masculine in apposi- tion.
| CC |
CSIRO Canberra Rhizobium Collection |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |