Glyptothorax jayarami, Rameshori, Yumnam & Vishwanath, Waikhom, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.208491 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5657605 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F51A87BB-FFAB-D422-D0DB-FF44F917F956 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Glyptothorax jayarami |
| status |
sp. nov. |
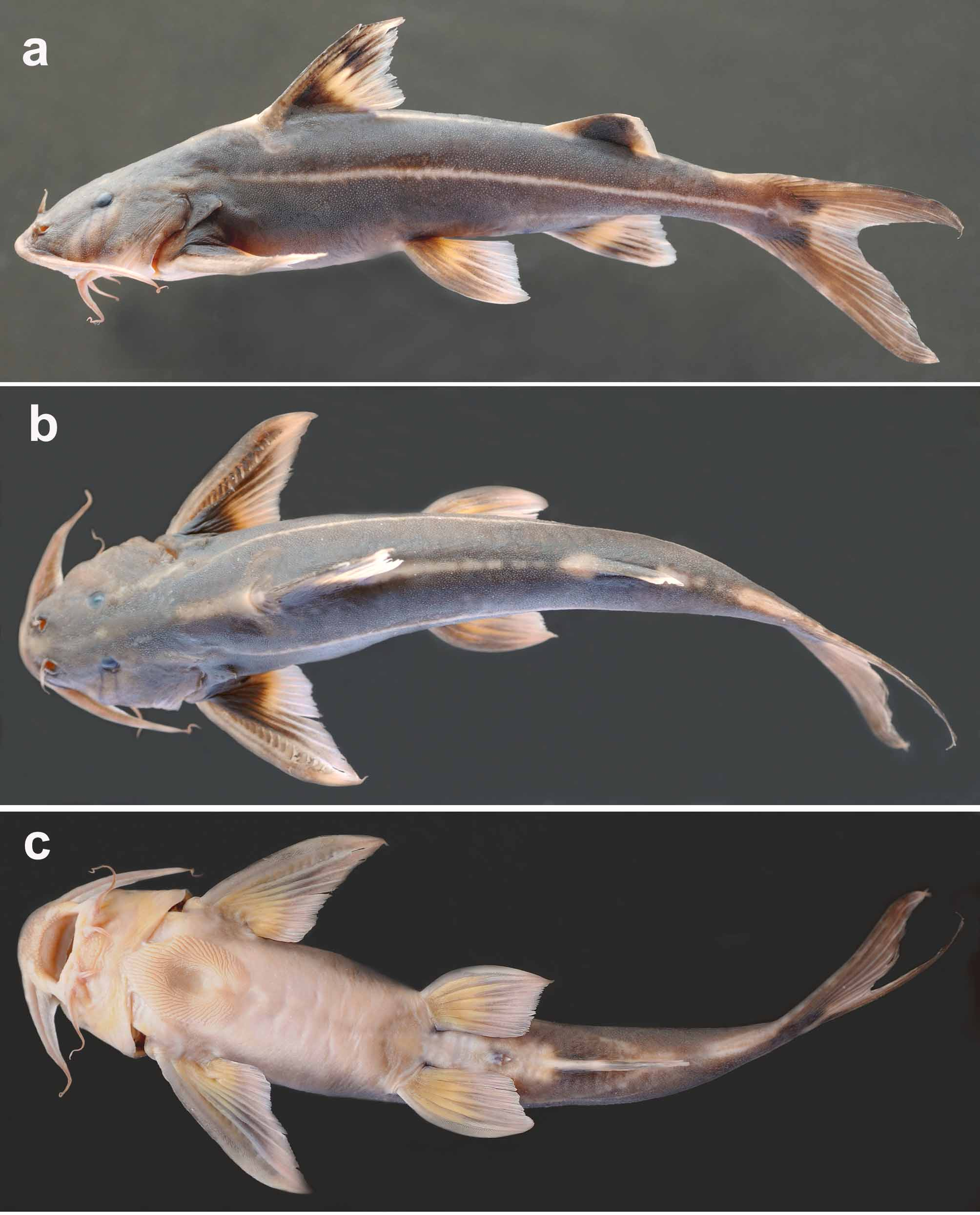
Glyptothorax jayarami View in CoL , new species
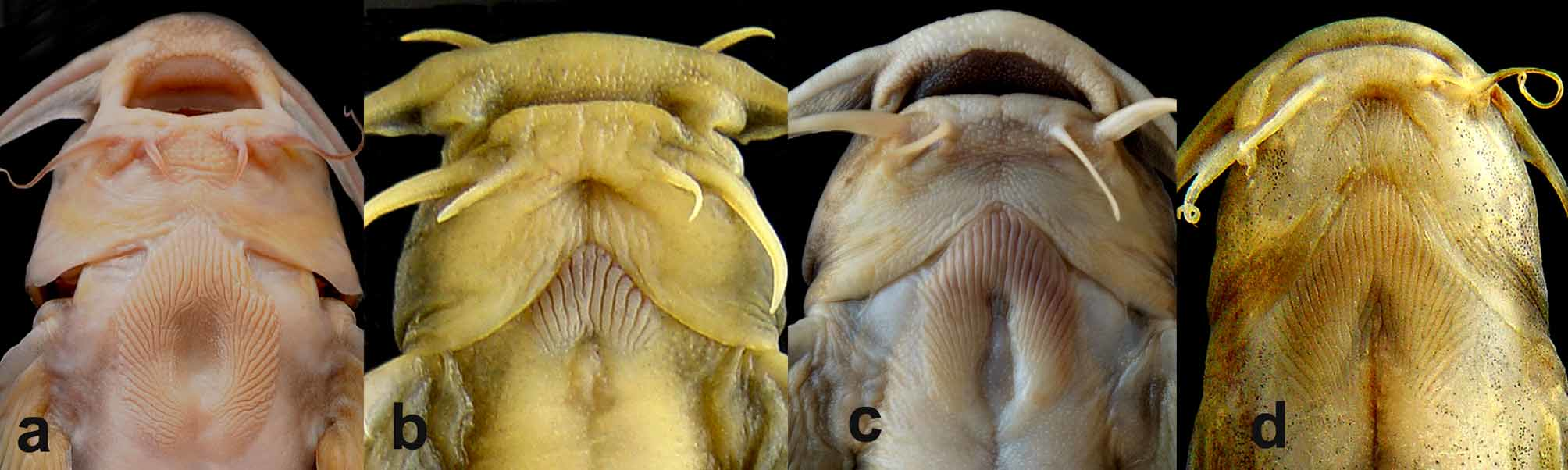
( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 )
Type material. Holotype: MUMF 14012, 104.5 mm SL; India: Mizoram state, Lawntlai District, Kaladan River at Kolchaw, 22˚23'N 92˚57'E; Nebeshwar et al., 27 April 2008.
Paratypes: MUMF 14013–14022 (9), 53.3–89.4 mm SL; same data as holotype. One paratype ( MUMF 14022, 84.8 mm SL), dissected for osteology.
Diagnosis. Glyptothorax jayarami is distinguished from its congeners by having an elongate, ovoid thoracic adhesive apparatus with an oval central depression, the apparatus not reaching the gular region; the base of the caudal fin with two blackish-brown blotches behind the hypural plate; the occipital process not in contact with the anterior nuchal-plate element; a long dorsal spine (17.9–19.5 % SL); the ventral surfaces of simple and adjacent branched rays of the pectoral and pelvic fins with well developed plicae, and first branchial arch with eight to nine gill rakers.
Description. Morphometric data as in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Body elongate, spindle-shaped. Dorsal profile rising gradually, evenly from tip of snout to origin of dorsal fin, then sloping ventrally from origin of dorsal fin to end of caudal peduncle. Ventral profile slightly concave upto origin of pelvic fin, then sloping gently dorsally from origin of pelvic fin to end of caudal peduncle. Anus and urogenital openings located at one-third distance from anterior of origin of pelvic fin. Skin with dense tuberculations all over body. Lateral line complete, midlateral. Vertebrae 17+19=36. Gills on first branchial arch long, bearing 2+7=9 (2) or 2+6=8 (3) rakers, with forked tip on 3rd and 6th ceratobranchial rakers in two specimens (MUMF 14015 and MUMF 14022) respectively ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ).
Head depressed, broad, triangular in lateral view. Snout prominent with bluntly-pointed tip. Anterior and posterior nares large, separated only by base of nasal barbel. Gill opening wide, extending directly from beneath posttemporal to isthmus. Osseous part of dorsal and lateral surface of head covered with thick, densely tuberculate skin. Eye ovoid, longer horizontal axis, located in mid-head length. Occipital process not in contact with anterior nuchal plate element.
Barbels in four pairs. Nasal barbel short, not reaching anterior margin of eye when adpressed, extending halfway between its base and anterior orbital margin. Maxillary barbel long, broad, thick at base, extending upto middle of pectoral-fin base. Outer mandibular barbel with broad, stumpy base; longer than inner mandibular barbel, reaching base of pectoral spine, present posterolateral to inner mandibular barbel.
Mouth inferior, with broad, papillated fleshy lips. Upper jaw longer than lower jaw; premaxillary tooth band partially visible with mouth closed. Teeth small, villiform. Premaxillary teeth arranged in irregular rows on broad semilunate band. Dentary teeth in two narrow crescentric bands separated at midline.
Dorsal fin with I,5,i rays, its origin nearer to snout tip than to origin of caudal fin, its distal margin slightly concave in middle. Dorsal spine strong, long, straight, smooth anteriorly, finely serrated posteriorly with 5(4) or 6(4) or 7(2) serrae. Adipose fin short, its anterior margin straight, posterior margin slightly convex. Anal fin with iii,8,i rays, its origin at level of origin of adipose fin, its posterior margin gently concave. Caudal fin deeply forked, with i,8,7,i rays, procurrent rays symmetrical, extending slightly ahead of hypural notch. Pectoral fin with I,8,i rays, extending vertically through origin of dorsal-fin base. Pectoral spine smooth anteriorly, covered with thick skin, serrated posteriorly with 11–15 serrae. Ventral surfaces of simple and adjacent branched ray of pectoral fin with obliquely arranged plicae ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 a). Pelvic fin with I,5 rays, originating slightly behind dorsal-fin base, extending up to origin of anal fin when adpressed. Ventral surfaces of simple and adjacent branched ray of pelvic fin with well developed plicae arranged obliquely on simple ray, longitudinally on branched ray ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 b).
Thoracic adhesive apparatus elongate ovoid, consisting of prominent oval central median depression, opening posteriorly. Central median depression enveloped by one or two layers of discontinuous unculiferous ridges. Median ridges arranged longitudinally. Lateral ridges uninterrupted, radiating from median depression anterolaterally, branched at anterior end ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Adhesive apparatus not reaching gular region.
Coloration. In 10% formalin: dorsal and lateral surfaces of head and body dark brown fading to light brown, ventral surface upto origin of pelvic fin beige. Two beige stripes on body: a mid-dorsal one, extending behind dorsal-fin base and another midlateral, originating at level of origin of pectoral fin, both stripes reaching base of caudal fin. Dorsal, pectoral and pelvic fins with dark-brown bases with hyaline margins. Adipose fin dark brown, its distal margin hyaline. Anal-fin base brown with hyaline margin. Caudal fin with two blackish-brown blotches at caudalfin base, tip of both lobes hyaline. Nasal, maxillary barbels brown dorsally, beige ventrally. Mandibular barbels hyaline.
Distribution. Glyptothorax jayarami is known presently only from the type locality, the Kaladan River at Kolchaw in Mizoram, India ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ).
Etymology. The species is named in memory of K.C. Jayaram, who made a substantial contribution to Indian ichthyology.
TABLE 1. Biometric data of holotype and nine paratypes of Glyptothorax jayarami (n = 10).
| Holotype MUMF 14012 | Range | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard length (mm) | 104.5 | 53.3–104.5 | |
| In % SL Predorsal length | 36.3 | 35.8–40.2 | 37.2±1.4 |
| Preanal length Prepelvic length Prepectoral length | 67.4 51.7 21.2 | 64.4–71.4 47.5–52.7 16.8–21.2 | 67.8±2.0 50.2±1.3 18.7±1.3 |
| Length of dorsal-fin base Length of dorsal spine Anal-fin base length | 13.8 19.3 19.4 | 12.8–15.0 17.9–19.5 19.2–21.2 | 13.9±0.7 18.9±0.6 19.9±0.6 |
| Pelvic-fin length Pectoral-fin length Caudal-fin length | 18.6 26.7 28.8 | 16.4–19.1 26.3–27.8 25.9–29.1 | 17.9±0.8 26.8±0.6 27.8±1.0 |
| Length of adipose-fin base Dorsal to adipose distance Post-adipose distance | 13.4 24.6 10.7 | 10.9–15.5 22.0–24.6 9.6–13.2 | 13.1±1.5 23.4±0.8 11.1±1.2 |
| Length of caudal peduncle Depth of caudal peduncle Body depth at anus | 26.1 6.2 14.8 | 23.3–26.6 5.5–7.9 13.1–15.0 | 24.8±1.1 6.9±0.8 14.3±0.6 |
| Head length Head width Head depth | 25.9 20.1 16.4 | 24.8–27.0 16.7–20.1 11.6–16.4 | 25.9±0.6 18.2±1.0 14.3±1.6 |
| Length of adhesive apparatus Width of adhesive apparatus | 15.6 10.5 | 14.9–17.6 9.6–11.3 | 16.3±0.8 10.3±0.5 |
| In %HL | |||
| Snout length Interorbital distance Eye diameter Nasal barbel length Maxillary barbel length Inner mandibular barbel | 55.8 25.3 9.8 20.7 86.2 25.8 | 28.1–55.8 25.4–29.7 9.8–13.3 17.0–38.1 69.2–116.4 24.1–39.9 | 35.8±11.3 27.0±1.5 10.7±1.6 22.9±7.0 85.7±16.8 28.4±5.7 |
| Outer mandibular barbel | 44.4 | 32.8–66.7 | 43.5±10.4 |
| MUMF |
Department of Life Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |