Glossoscolex (Glossoscolex) giocondoi, Bartz, Marie Luise Carolina, James, Samuel Wooster, Pasini, Amarildo & Brown, George Gardner, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.282225 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:632E318C-BAFD-423A-A546-A8E4B4F463B2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6177005 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EB87EE-FFF4-FFAD-3EBD-4762DBC14597 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Glossoscolex (Glossoscolex) giocondoi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Glossoscolex (Glossoscolex) giocondoi n. sp. Bartz & James
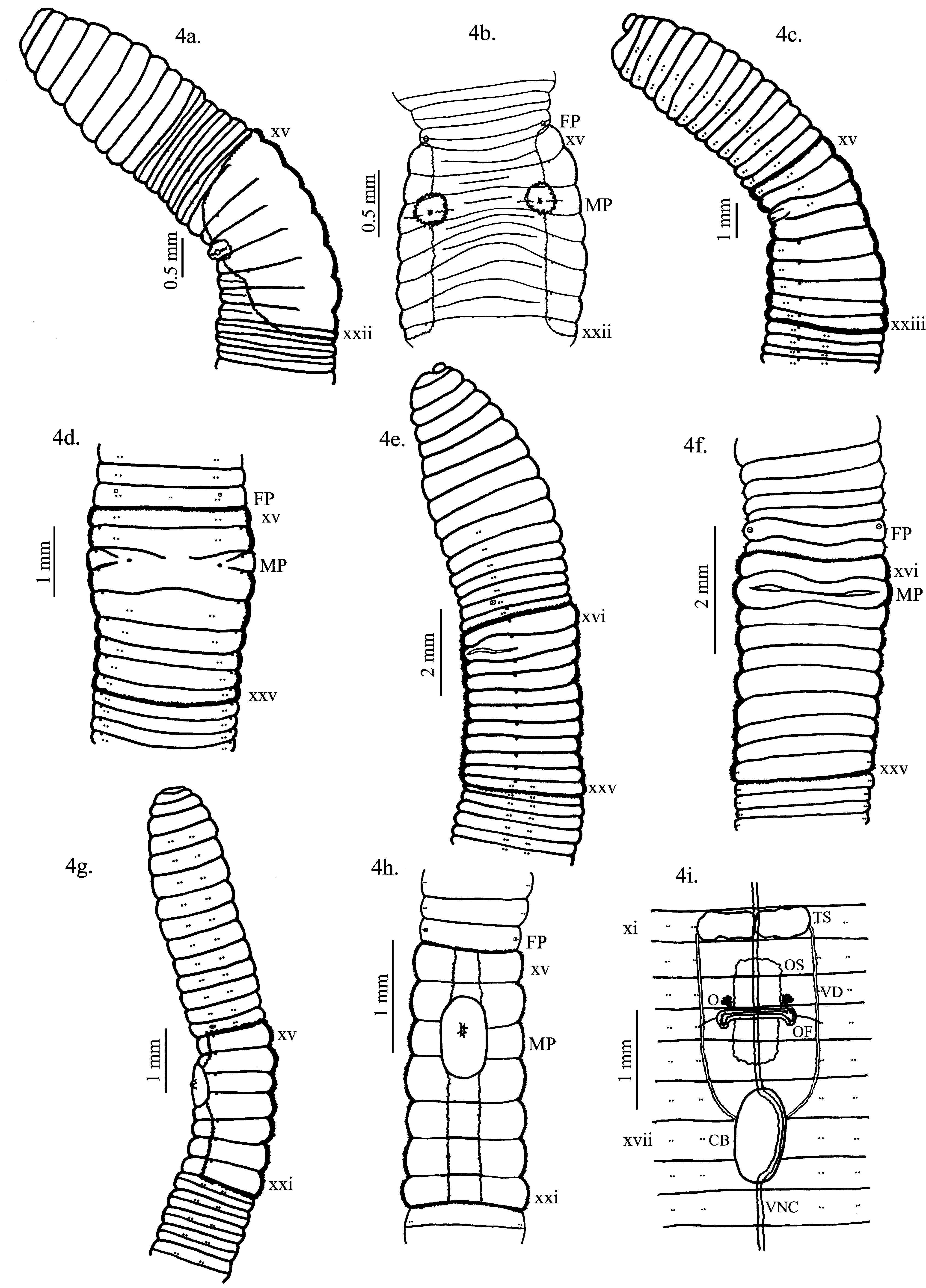
( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 e,f, Table 1)
Holotype. COFM BRPR 0020 one adult, primary forest soil, Parque Estadual Mata dos Godoy, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil; 23º26.99’S, 51º15.42’W, 593 masl, 12 May 2004, G.G. Brown and S.W. James colls.
Paratypes. A - COFM BRPR 0323 one adult and B - COFM BRPR 0021 one adult, primary forest soil, Parque Estadual Mata dos Godoy, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil; 23º26.99’S, 51º15.42’W, 593 masl, 12 May 2004, G.G. Brown and S.W. James colls..
Other material. MZUSP 1411 two adults, primary forest soil, Parque Estadual Mata dos Godoy, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil; 23º26.99’S, 51º15.42’W, 593 masl, 12 May 2004, G.G. Brown and S.W. James colls.; COFM BRPR 0085 one adult, soybean field, Santa Helena Farm, Cafeara, Paraná, Brazil; 22º50.26’S, 51º41.92’W, 338 masl, 10 February 2005, G.G. Brown coll.; COFM BRPR 0087 one adult (amputated) and one preclitellate and MZUSP 1412 one adult, pasture, Santa Helena Farm, Cafeara, Paraná, Brazil; 22º50.26’S, 51º41.92’W, 338 masl, 1 July 2004, G.G. Brown coll.; MZUSP 1413 one adult and three juvenile, harvested wheat field, São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil, 23º24.872’S, 51º18.847’W, 666 masl, 30 September 2009, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.; BRPR 0127 one adult, two preclitellates, one juvenile, pasture, São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil, 23º24.872’S, 51º18.847’W, 666 masl, 19 June 2008, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.; MZUSP 1414 two adults, pasture, São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil, 23º24.872’S, 51º18.847’W, 666 masl, 19 June 2008, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.; COFM BRPR 0128 one adult, pasture converted in annual crop (wheat), São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil, 23º24.872’S, 51º 1 8.847’W, 666 masl, 30 September 2009, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.; COFM BRSP 0017 two adults (one amputated), soybean culture, Fazenda Gruta Azul, Taciba, São Paulo, Brazil, 22º32.92’S, 51º22.55’W, 440 masl, 15 Abril 2004, G.G. Brown and A. Pavão colls.; BRSP 0024 one adult and one preclitellate, soybean culture, Fazenda Gruta Azul, Taciba, São Paulo Brasil, 22º32.92’S, 51º22.55’W, 440 masl, 0 7 November 2002, G.G. Brown, coll.; MZUSP 1415 two adults, soybean culture, Fazenda Gruta Azul, Taciba, São Paulo, Brazil, 22º32.92’S, 51º22.55’W, 440 masl, 0 7 November 2002, G.G. Brown coll.
Etymology. The species is named in honor for the farmer Octavio Giocondo, owner of the São José Farm.
Description. Dimensions: Holotype 82 mm by 3.2 mm at x, 3.7 mm at clitellum, 2.8 mm at xl, 226 segments; Paratypes A – 74 mm by 3.5 mm at x, 2,8 at clitellum, 3.1 mm at xl, 191 segments; B – 57 mm by 2.8 at x, 3.0 at clitellum, 2.7 at xl, 196 segments. Setae ab commence on xi, c on xii, d on xxv, before clitellum setae very tiny and hardly visible. Setae closely paired throughout; genital setae absent; setal formula AA:AB:BC:CD:DD = 36:1.5:6:1:31 at xl. Prostomium prolobous. Unpigmented. Ovipores on small papillae in ventral equatorial line 0.2–0.3mm lateral to a in xiv; male pores 1.3–2.1 mm apart on xvii within paired lateral slits; clitellum annular, xvi–xxv ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 e). Nephropores just above b.
Septa 6/7–9/10 equally thick, muscular, 10/11 thinner but muscular, 11/12 around heart and testes sacs, septa 12/13/14 united by circumesophageal membrane isolating villous interior from other septal contents of xiii, which are medial to membrane. Alimentary canal with large cylindrical gizzard in vi; esophagus with wide angle lamellae chevron pattern vii–ix, valvular in xiv; intestinal origin xiv, xv; typhlosole origin xv, end after clxx, open folds xv–xvii, strongly zig-zag folded xviii, xix–xxxiii, zig-zag with ventral edge bent over to form pockets xxiii–xxxv, after gradually becoming simple lamina. Calciferous glands paired xii, composite-tubular type, bean shaped, sessile on dorsal esophageal wall; blood vessels to gland include large branch of dorsal vessel to approximate center of each gland, two coalescing vessels from ventral gland margin to extra-esophageal vessel. Gland opening to esophagus near dorsum, large with lip along ventral margin. Holonephric, vesiculate; ducts to body wall near level of b.
Vascular system with ventral trunk, single dorsal trunk, lateral vessels in vii–ix, latero-esophageal hearts in x–xi. Extra-esophageal vessel from pharyngeal glands, passes along ventral-lateral face of gizzard, esophagus back to calciferous glands; supraesophageal vessel in x–xi.
Ovaries, ovarian funnels free in xiii adjacent to seminal vesicle tube passing through xiii; spermathecae absent.
Male sexual system metandric, testes and funnels in U shaped sac with hearts enclosed; medial to hearts of xi, pass narrow tubes to seminal vesicles; seminal vesicles expand from narrow tubes in xiv, penetrate septa and range posteriorly along intestine to xxiii–xxxv; seminal vesicles simple elongate sacs with parallel blood vessels on median side of longitudinal axis of vesicle; vasa deferentia long, looped from xi, form dense zig-zag on body wall en route to ventro-lateral face of small lenticular copulatory bulbs; bulbs extend over xvi–xviii but occupy septallydefined space of xvii. Copulatory bulbs with thin muscular outer layer, dense, delicate glandular inner surface with small lumen leading to male pore at approximate center of bulb connection to body wall; lumen undulating in three dimensions; no transverse muscle bands crossing over bulbs; bulbs with anterior, posterior apices attached by short stout muscles to body wall.
Remarks. Glossoscolex (Glossoscolex) giocondoi is closest to G. (G.) vizottoi Righi, 1971 and to G. (G.) primaensis n. sp. (see above). The differences between G. (G.) giocondoi and G. (G.) vizottoi are as follows, with the characteristics of the latter in parentheses: length 74–109 mm (130–438 mm), number of segments 191–341 (220–245), setae ab commence on xi, c on xii, d on xxv (setae beginning in segment vii), setal ratios 36:1.5:6:1:31 (50:2.5:17.5:2:67), septa 12/13/14 united by circumesophageal membrane isolating villous interior from other septal contents of xiii (no such development in septa 12/13/14), seminal vesicles simple elongate sacs (tubular, sinuous and very elongate), copulatory bulbs small lenticular (thick tubular). Glossoscolex (G.) giocondoi differs from G. (G.) primaensis by: form of the clitellum annular (saddle), the form of the copulatory bulbs small lenticular (large, long and oval), enclosed hearts in xi (last hearts in xi free), U shaped testes sacs (testes sacs united ventrally). Glossoscolex (G.) giocondoi has clitellar male pores in xvii. According to species groups defined for the subgenus Glossocolex by the male pore location, Glossoscolex (G.) giocondoi falls in the truncatus group ( Michaelsen 1918, Righi 1978).
Glossoscolex (G.) giocondoi corresponds to Glossoscolex n. sp. 12 and Glossoscolex n. sp. 1, as cited in Brown and James (2006, 2007a, b), Brown et al. (2004, 2008), James and Brown (2006, 2008), Fragoso and Brown (2007) and Sautter et al. (2006, 2007).
| MZUSP |
Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |