Fridericia cusanicaformis, Dózsa-Farkas, Klára, Felföldi, Tamás & Hong, Yong, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4006.1.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E987B43A-E54A-4F64-9829-0B8EBE457E03 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6100534 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/304F8793-681E-FFD1-FF3B-FF7BFEE2AD29 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Fridericia cusanicaformis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Fridericia cusanicaformis View in CoL sp. n.
( Figures 6 View FIGURE 6. F A – C, 7)
Type material. Holotype. NIBRIV0000320521, slide No. 1080, adult whole mount stained with borax carmine. Type locality: site 9: Cheontae mountain, Yeongdong-gun, Cheungcheongnam-do, Korea, 36º06'57.8"N 128º00'30.4"E, 201 m asl, soil and litter layers of forest, leg. Y. Hong, 15.05.2014.
Paratypes. NIBRIV0000320522, slide No. 1082, two adult whole mounts stained specimens from type locality, sampling data as for holotype. P.104.1–2, slide No. 1079, 1081, sampling data as for holotype.
Etymology. Named after the similarity to F. c u s a ni ca Schmelz, 2003.
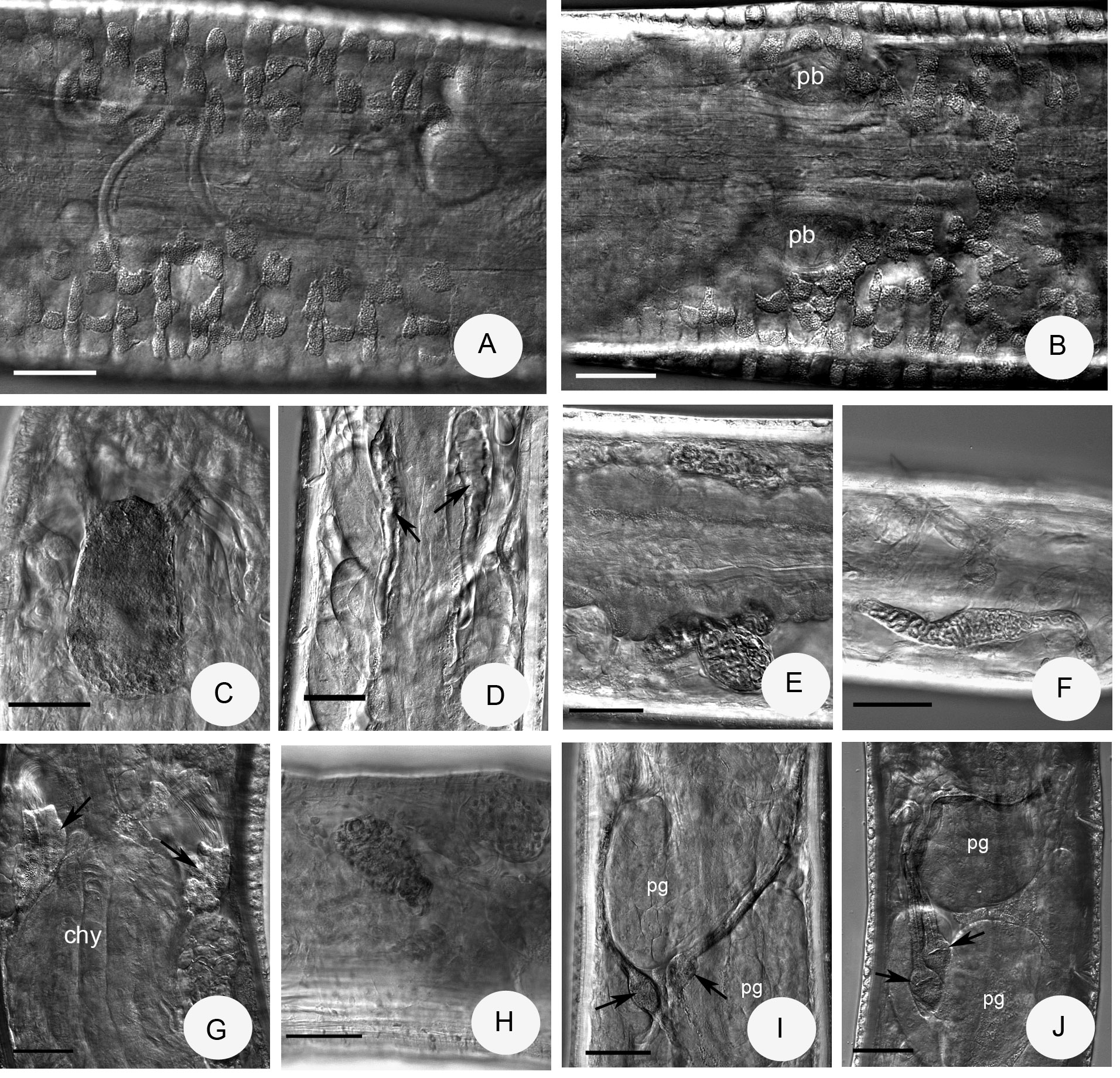
Diagnosis. The new species can be recognized by the following combination of characters: (1) small size (5–7 mm, in vivo), segments 29–32; (2) only one chaeta in the lateral bundles; (3) clitellum only laterally developed: hyalocytes and granulocytes arranged in transverse rows, dorsally and ventrally absent, except 1–3 rows behind bursal slits; (4) four preclitellar pairs of nephridia; (5) coelomo-mucocytes type a, lenticytes large; (6) chylus cells in X–XI; (7) seminal vesicle absent; (8) subneural glands absent; (9) sperm funnel small, cylindrical, collar narrower as funnel body; (10) spermathecae without diverticula, fused proximally, ampullae small (diameter 20–25 µm, in vivo), spermathecal ducts elongate, with small sessile ectal glands.
Description. Holotype 5 mm long, 220 µm wide at VIII and 240 µm at clitellum, fixed, 30 segments. Body length of paratypes 5–7 mm, width 200 µm at VIII and 210–240 µm at clitellum, in vivo. Length of fixed specimens 3.4–5.6 mm, width 180–220 µm at VIII and 200–240 µm at clitellum. Segments 29–32. Chaetal formula: 1,(0) – 1: 2 – 2. Chaetae in preclitellar and postclitellar bundles alike, about 20–25 x 2.5 µm both ventrally and laterally. Chaetae in XII absent. Head pore at 0/I. Dorsal pores from VII. Epidermal gland cells arranged in 1–2 transverse rows per segment. Clitellum in XII–1 /2XIII, only laterally developed, except for 2–3 rows posterior to the bursal slits ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B); dorsal gap of clitellum about 58 µm wide ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A); gland cells arranged in rows, hyalocytes slightly larger (diameter 17–20 x 18 Μm) than granulocytes (diameter 10–12 x 18 Μm, fixed). Thickness of body wall about 10–13 µm, cuticle about 1 µm in fixed specimens.
Brain egg-shaped, about 90–100 Μm long (fixed) and 1.7 times longer than wide ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 C). Oesophageal appendages type a, short, unbranched ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D). First and second pairs of pharyngeal glands united dorsally, third pair dorsally separate; in IV without and in V and VI with ventral lobes. Chloragocytes from V, about 19–23 Μm long, in vivo (fixed 5–10 Μm). Dorsal blood vessel from XIII, blood colourless. Midgut pars tumida in XIX–XXII, occupying 4 segments. Four pairs of preclitellar nephridia from 6/7 to 9/10, length ratio anteseptale: postseptale 1: 1.4–1.6, midventral origin of efferent duct preclitellarly ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E), postclitellarly efferent duct originating terminally ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 F). Coelomo-mucocytes type a (length 20–30 Μm, in vivo, 13–17 µm, fixed), lenticytes large 8–13 Μm long, in vivo (5-8 µm long, fixed) ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. F B). Chylus cells between X–XI, occupying 2 segments ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 G). Seminal vesicle small or absent. Sperm funnels cylindrical, small ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 G), about 70–90 µm long and 1.8–2.3 times as long as wide, in vivo. Funnel length in fixed specimens 55–87 µm ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 H). Collar narrower than funnel body. Spermatozoa about 100 µm long, heads 25–28 µm, in vivo. Diameter of sperm ducts 5 µm, fixed. Male copulatory organs ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B) 40–57 µm long, 30–37 µm wide and 20–32 Μm high, fixed, bursal slits were undeterminable. Subneural glands absent. Spermathecae ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 I,J): one small, sessile ectal gland at the orifice, length about 12–17 µm, fixed. Ectal duct as long as or slightly longer than body diameter, about 195–240 µm long and 10 µm wide, in vivo (125–250 µm, fixed), canal not widened. Ampullae onion-shaped without ental bulbs in ampullae and without diverticula, diameter 20–25 µm, in vivo and fixed alike. Proximal parts of ampullae (18–20 µm long, fixed) merging and joint opening into oesophagus in V. One large mature egg at a time (in specimen No. 1079 four mature eggs).
Distribution and habitat. In Korea only in site 9, Cheontae mountain, Yeongdong-gun, Cheungcheongnamdo Korea, 36˚06’57.8”N 128˚00’30.4”E, 201 m asl, broad-leaved forest.
Differential diagnosis. The shape of the spermathecae in F. cusanicaformis sp. n. is very similar to the spermathecae of six Fridericia species: F. bulboides Nielsen & Christensen, 1959 , F. bretscheri Southern, 1907 , F. semisetosa Dózsa-Farkas, 1970 , F. schmelzi Cech & Dózsa-Farkas, 2005 , F. pretoriana Stephenson, 1930 , F. losangelensis Bell, 1936 ; they differ all from the new species in the maximum number of ventral chaetae, four in first four species, in the case of F. pretoriana 6–8 and in F. losangelensis 4–6 ( Schmelz 2003). Only F. semisetosa has 1 or 0 chaetae in the lateral bundles but differs by the number of preclitellar nephridia (5 pairs). The new species differs from these species discussed by the dorsally absent clitellum. F. cusanica Schmelz, 2003 is most similar to the new species (see etymology of F. cusanicaformis ) in regard to body size, spermathecal form, the maximum number of chaetae per bundle, preclitellar location of chylus cells and oesophageal appendages type a, but F. cusanicaformis differs from F. cusanica by longer spermathecal ducts (as long as or slightly longer than body diameter), only four pairs of preclitellar nephridia, lenticytes larger (8–13 µm long) and the third pairs of pharyngeal glands in VI separate dorsally; moreover the first pharyngeal glands are without ventral lobes. In F. cusanica the spermathecal duct length is 3/4 of body diameter, there are five pairs of preclitellar nephridia, lenticytes are 3–5 µm long, and all pairs of pharyngeal glands with wide dorsal connection and with ventral lobes ( Schmelz 2003).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
SubClass |
Oligochaeta |
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |