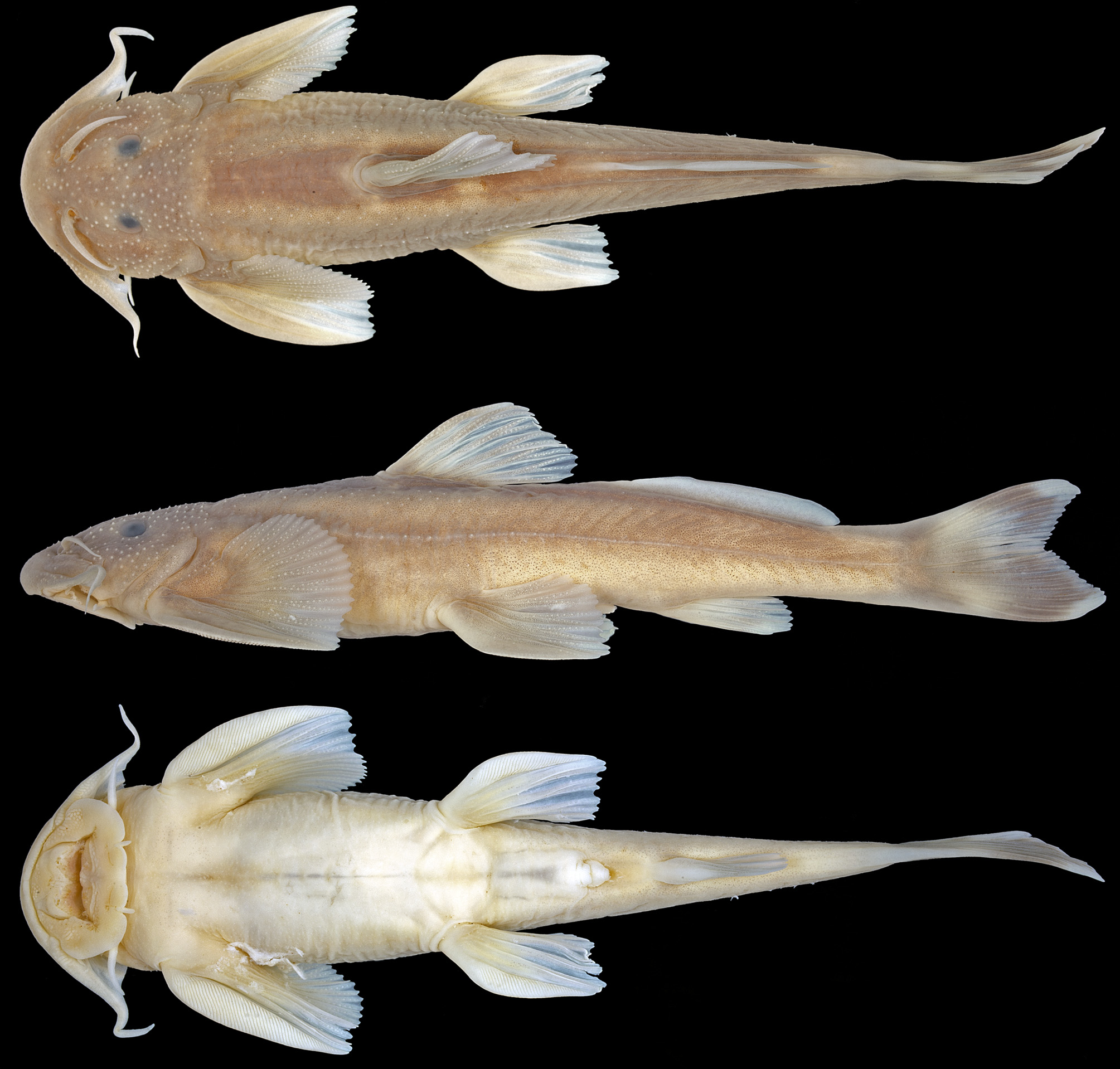
Exostoma effrenum, Ng, Heok Hee & Vidthayanon, Chavalit, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3869.4.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:39555505-B707-4172-BED0-06242CB096EC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5615976 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DC878A-FFC8-FFF8-FF06-7DE1FF2CF28D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Exostoma effrenum |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Exostoma effrenum View in CoL , new species
( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 , 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Type material. Holotype: NIFI 4955, 51.3 mm SL; Thailand: Mae Hong Son Province, Mae La Noi District, Ping Noi stream close to Doi Om Phai in Chiang Mai Province, 18°23'43"N 98°7'56"E; Mae Hong Son Fisheries Station staff, December 1998.
Paratypes: NIFI 3765 (2), 51.6–65.0 mm SL; UMMZ 250050 (1), 54.2 mm SL; data as for holotype. Diagnosis. Exostoma effrenum is distinguished from congeners in having a combination of the following characters: eye diameter 11.5–15.0% HL; head width 18.5–19.8% SL; body depth at anus 10.5–12.4% SL; length of adipose-fin base 25.8–29.0% SL; adipose fin distinctly separate from upper procurrent caudal-fin rays; caudal peduncle length 20.5–21.3% SL; caudal peduncle depth 5.1–7.0% SL; forked caudal fin; 21–22 preanal vertebrae.
Description. Morphometric data as in Table 2 View TABLE 2 . Head and body broad, very strongly depressed, with paired fins greatly enlarged to form elongate ovoid adhesive disc with body. Rostral margin rounded in dorsal view, moderately curved in lateral view. Dorsal profile rising gently and evenly from anterior orbital margin to origin of dorsal fin, then sloping gently ventrally to end of caudal peduncle. Ventral profile flat to anal-fin base, then sloping gently dorsally to end of caudal peduncle. Anus and urogenital openings located at vertical through posterior margin of adpressed pelvic fin. Mouth ventrally directed with broad, thin and papillate lips. Most of premaxillary tooth patches exposed when mouth is closed. Lower lip with prominent labial fold bearing entire posterior margin, notched at insertions of inner mandibular barbels. Postlabial groove on lower jaw present, uninterrupted. Dorsal surface of head covered with conical, moderately dense tubercles.
Jaw teeth distally flattened, oar-shaped and in two rounded triangular patches narrowly separated at midline on upper jaw. Teeth on lower jaw situated in two well-separated, roughly triangular patches. Palate edentulous.
Eyes small, dorsolaterally situated, subcutaneous. Gill openings narrow, extending from base of first pectoralfin ray to level immediately dorsal to base of posteriormost pectoral-fin ray.
Barbels in four pairs. Nasal barbel moderately long, reaching nearly to posterior orbital margin. Maxillary barbel flattened, with flap of skin fringing posterior margin; its tip pointed; ventral surface with numerous striae; extending beyond base of pectoral fin. Inner mandibular barbel slightly flattened, very short; originating from notch on posterior margin of lower lip. Outer mandibular barbel situated lateral to inner mandibular barbel; slightly flattened, reaching to two thirds of distance between its base and base of first pectoral-fin ray.
Dorsal fin without spine, with i,6 (4) rays; surfaces of fin rays covered with conical tubercles. Adipose fin with long base, posterior end separate from upper procurrent caudal-fin rays. Anal fin with ii,4,i (4) rays. Caudal fin weakly forked, with i,7,7,i (4) rays; lower lobe very slightly longer than upper. Pelvic fin greatly enlarged, with convex distal margin and i,5 (4) rays; first ray greatly flattened, with numerous striae on ventral surface; dorsal surfaces of fin rays covered with conical tubercles. Pectoral fin greatly enlarged, without spine and with i,10,i (4) rays; first ray greatly flattened, with numerous striae on ventral surface. Dorsal surface of pectoral-fin rays covered with tubercles. Vertebrae 21+15=36* (2), 22+14=36 (1) or 22+16=38 (1).
Coloration. In 70% ethanol: brown on dorsal and lateral surfaces of head and dorsal surface of body, dark yellow on ventral region. Dark yellow on lateral surfaces of body immediately dorsal and ventral to lateral myoseptum, giving impression of two diffuse brown lines on body: one on lateral myoseptum and another along inter-dorsal region and adipose-fin base. Myotomes along lateral surfaces of body with faint dark outlines. Dorsal fin brown; dorsal surfaces of pectoral and pelvic fins brown, with ventral surfaces of pectoral and pelvic fins dark yellow. Anal fin dark yellow. Base of caudal fin with darker, diffuse brown band contiguous with irregular, wshaped brown band on most of caudal fin. Dorsal surface of nasal and maxillary barbels brown, ventral surface dark yellow. Mandibular barbels dark yellow.
In life ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ): Medium brown on dorsal and lateral surfaces of head and body, fading to tan on ventral surfaces. Numerous pale spots densely distributed over dorsal surfaces of head and predorsal region. Dorsolateral surface of body with two indistinct tan blotches: one below adipose-fin origin and another below middle of adipose-fin base. Dorsal, pectoral and pelvic fins with dusky fin rays and hyaline fin membranes. Base of caudal fin with gently crescentic dark brown bar; middle third of caudal fin with irregular, dark brown w-shaped band. Dorsal surface of nasal and maxillary barbels olive brown, ventral surfaces tan. Mandibular barbels tan.
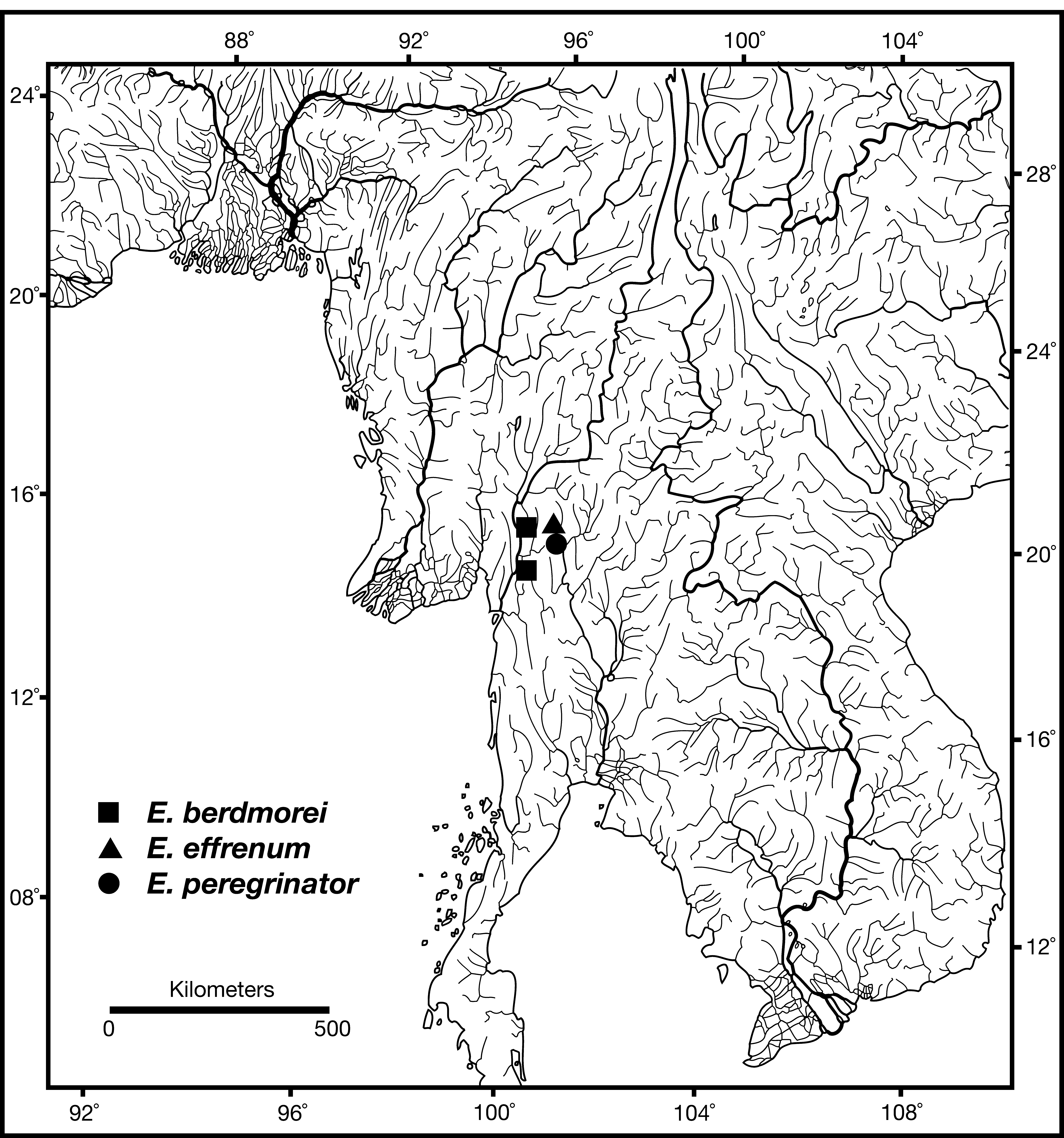
Distribution. This species is known from the upper reaches of the Ping River (one of two main tributaries of the Chao Phraya River) drainage in northwestern Thailand ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ). The record from the Doi Inthanon National Park in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, is based on photographs of specimens (not preserved; Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ) referable to this species we have examined.
Etymology. The specific epithet comes from the Latin adjective effrenus, meaning unbridled. This is used in allusion to the condition of the adipose fin being distinctly separate from the upper principal caudal-fin rays in this species.
TABLE 2. Biometric data for Exostoma effrenum (NIFI 4955, NIFI 3765, UMMZ 250050; n = 4).
| Standard length (mm) | Holotype NIFI 4955 51.3 | Range 51.3–65.0 | Mean±SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| %SL Predorsal length Preanal length | 42.1 70.2 | 40.1–42.1 70.2–71.6 | 40.9±0.90 70.7±0.66 |
| Prepelvic length Prepectoral length Length of dorsal-fin base | 47.2 16.6 14.8 | 46.9–51.1 15.2–16.6 12.9–15.3 | 48.4±1.91 15.7±0.65 14.1±1.18 |
| Length of anal-fin base Pelvic-fin length Pectoral-fin length | 9.7 18.1 24.2 | 6.8–9.7 17.6–20.0 22.1–24.2 | 8.2±1.38 18.5±1.06 23.4±0.92 |
| Caudal-fin length Length of adipose-fin base Dorsal to adipose distance | 25.3 29.0 11.5 | 22.5–25.3 25.8–29.0 10.3–12.3 | 23.8±1.22 27.4±1.31 11.2±0.93 |
| Length of caudal peduncle Depth of caudal peduncle Body depth at anus | 21.2 7.0 11.7 | 20.5–21.3 5.1–7.0 10.5–12.4 | 21.0±0.37 6.2±0.83 11.8±0.90 |
| Pectoral–pelvic distance Head length Head width | 32.9 25.3 19.7 | 29.5–32.9 21.9–25.3 18.5–19.8 | 31.7±1.56 23.4±1.63 19.4±0.59 |
| Head depth %HL Snout length | 12.5 59.7 | 10.5–12.5 57.3–64.6 | 11.8±0.88 60.9±3.11 |
| Interorbital distance Eye diameter Nasal barbel length | 26.9 11.5 43.1 | 26.9–32.7 11.5–15.0 33.6–43.1 | 28.7±2.68 13.7±1.55 36.8±4.27 |
| Maxillary barbel length Inner mandibular barbel length Outer mandibular barbel length | 80.0 9.2 28.5 | 80.0–88.5 8.0–13.0 22.1–28.5 | 83.4±4.06 10.2±2.14 26.5±2.95 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |