Eothinia elongata (Ehrenberg, 1832)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.273458 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5680520 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A9F574-FFBD-B557-FEFE-FEE8FDACF961 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Eothinia elongata (Ehrenberg, 1832) |
| status |
|
Eothinia elongata (Ehrenberg, 1832) View in CoL
Several fairly large specimens were found in the sample. All investigated specimens had trophi of bdelloid rotifers in their stomach. The species has not been recorded from Greenland previously, but has been found in Europe ( Glascott 1893; Berzins 1949, 1978; Wulfert 1960), Russia and former Soviet Union ( Kutikova 1962, 1970), Asia ( Fernando & Zankai 1981; Sharma & Pant 1985), Australia ( Koste & Shiel 1980, 1991), North America ( Harring & Myers 1922; Chengalath & Koste 1989) and Brazil ( Segers & Dumont 1995). It is considered a rare cosmopolite.
The species is distinguished by its trophi morphology combined with the presence of one large salivary gland, and one cerebral and two frontal eyes. The recorded specimens were generally typical but deviated in some details in the trophi.
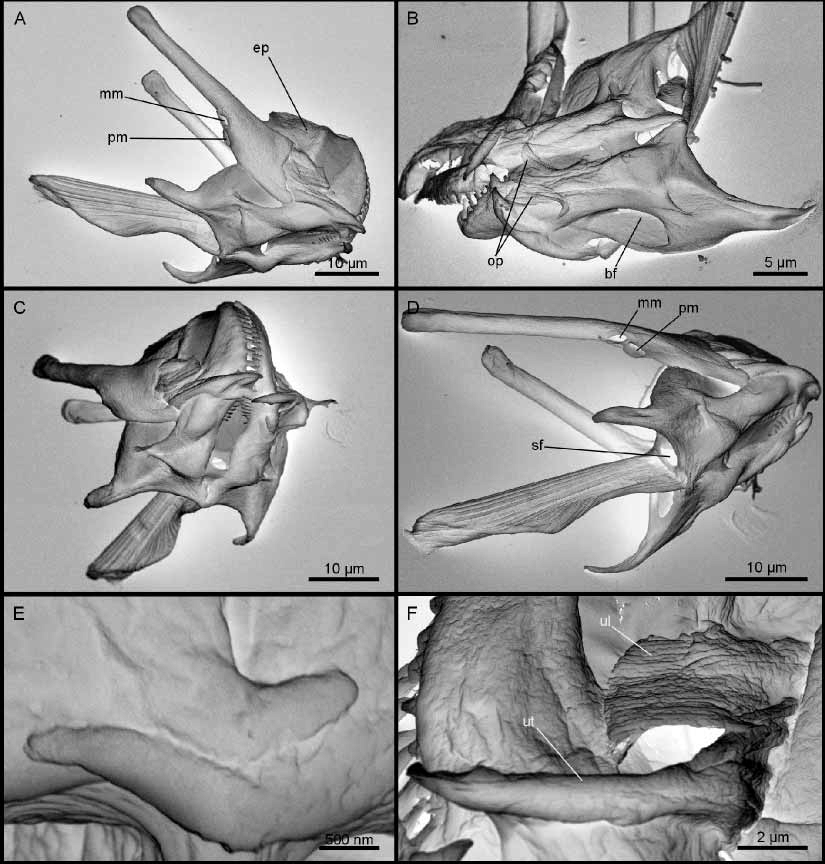
Trophi from two specimens were prepared for SEM ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). The rami are large and slightly asymmetrical, with long, pointed alulae ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A–D). Most posteriorly on the ventral side, two extensions from each ramus form a small hinge ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E). Basifenestrae and subbasifenestrae are present. The apical rami parts bend dorsally and have a dense row of fine teeth ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C). Each ramus has approximately 20 teeth. A pair of small, twisted, fanshaped oral plates is attached on the ventral side of rami ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B). The fulcrum is clearly divided into a dorsal and a ventral part ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A, C–D). The dorsal part is broadened laterally and composed of relatively thick sclerofibrillae that are arranged both sidebyside and on top of each other. The ventral fulcrum part is much narrower laterally, composed of one horizontal row of thick sclerofibrillae. Each uncus has one tooth with a basal lamella ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 F). Each manubrium is composed of a long distal cauda and a small proximal head. The head is formed by the walls of the medial and posterior manubrium chambers. Apertures from both chambers are located 1/3 from the proximal end of the manubrium ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A, D). A paired epipharynx composed of two large, fanshaped plates is present ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A). Both Harring and Myers (1922) and Wulfert (1960) illustrate the epipharyngeal elements as rodshaped sclerites with expanded distal terminals. However, their descriptions are probably based on a misinterpretation. Most of the epipharyngeal fans are extremely delicate and feebly visible with LM whereas the central parts are more robust. This may cause the sclerites to appear more rodshaped in LM. Measurements: Body: 504 µm; toes 37 µm; trophi 64 µm; rami 38 µm; fulcrum 37 µm; manubria 47 µm; unci 17 µm; epipharynx 15 µm; oral plates 6 µm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |