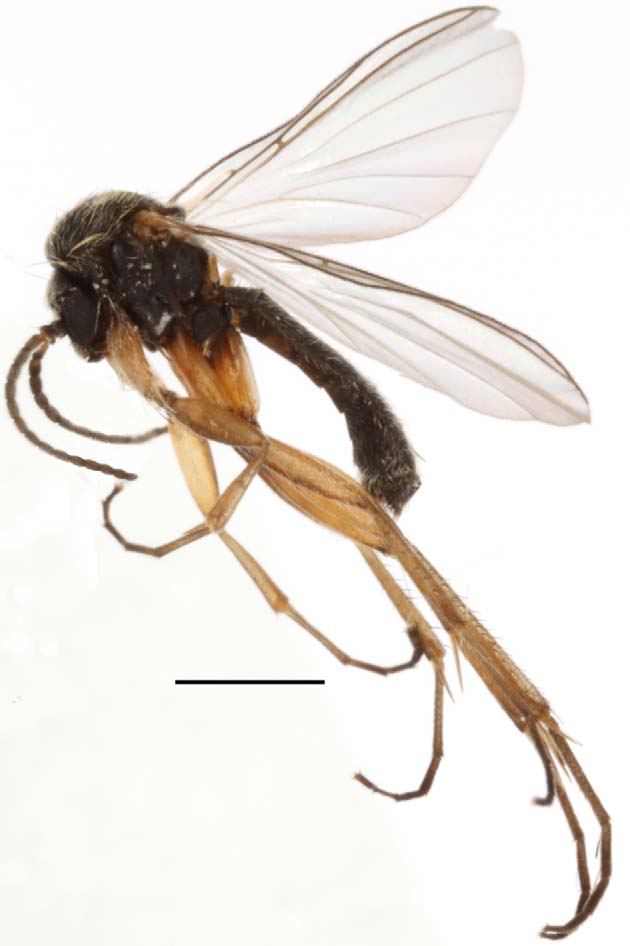
Docosia chimganica, Kurina, Olavi & Ševčík, Jan, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.213192 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6180633 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/15369321-645C-FF9B-33AE-FDF9FE4AFF67 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Docosia chimganica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Docosia chimganica sp. nov.
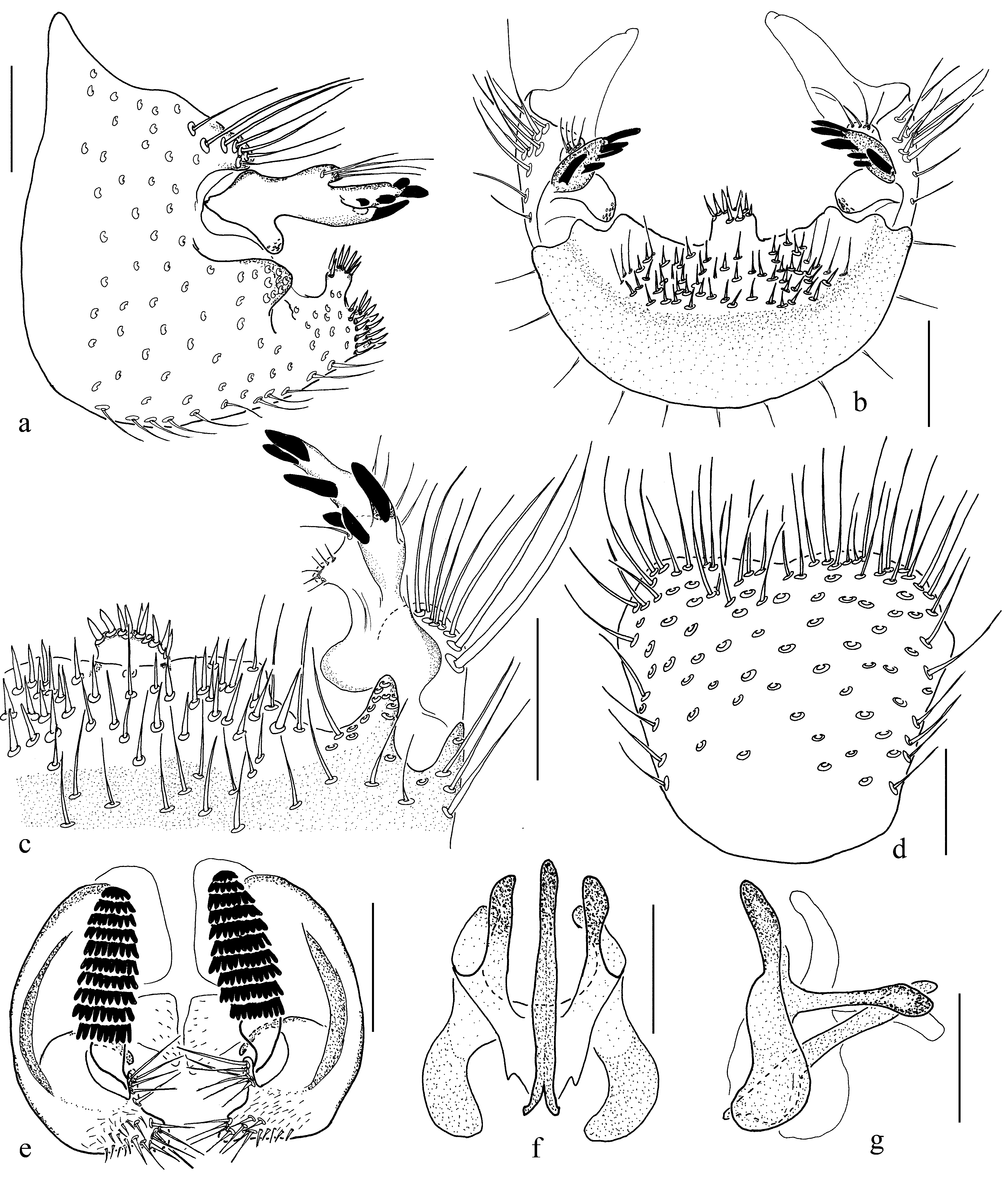
Figures 2 View FIGURE 2 , 5 View FIGURE 5 .
Type material. Holotype. 3, UZBEKISTAN, Chatkal Mts., Chimgan, 41°30’57,7’’N 70°01’44,4’’E, 1820 m a.s.l. light trap, 11.v.2008 (A. Pototski leg.) [ IZBE, micropinned].
Paratypes. 3, same as holotype [ IZBE, micropinned]; 233, UZBEKISTAN, Chatkal Mts., Chimgan, 41°30’57,7’’N 70°01’44,4’’E, 1820 m a.s.l. light trap, 12.v.2008 (A. Selin leg.) [ IZBE, micropinned]; 3, Mekhnad close to Syr-Darja river, 41°01’03,5’’N 68°36’28,7’’E, light trap, 10.v.2008 (A. Selin leg.) [ IZBE, micropinned].
Description. Male. Body length 3.02–3.25, 3.1 [3.02] (n=5).
Head black with numerous pale setae. Three ocelli, with laterals separated from eye margins by a distance less than their own diameter. Clypeus dark brown, with pale setae. Mouthparts light brown. Palpus with first two segments brownish and remaining segments yellow. Scape, pedicel and all flagellomeres dark brown and with short pale setae. Flagellomeres cylindrical, median flagellomeres about 1.6 times as long as broad, apical flagellomere conical, 2.4 times as long as broad at base.
All parts of thorax black with yellowish white bristles and setae. Scutellum with numerous setae, including a pair of strong marginal bristles and several weaker marginal bristles not arranged to distinct pairs. Antepronotum and proepisternum with bristles and setae. Upper part of antepronotum with a strong bristle crossing the neck. Laterotergite and other pleural parts bare. Halteres yellow.
Legs. Coxae yellow except of mid- and hind coxae slightly brownish basally. Femora yellow, hind femur darkened apically. All trochanters brown. Tibiae yellow apart of hind tibia apically darkened and thickened with denser setosity. Tarsal segments seem more brownish because of dense setae. Midtibia with 5–6 a, 5–6 d, 1–3 av, 2–3 p and 3–5pv. Hind tibia with 13–15 a, 10–14 d, 3–4 av. Mid- and hind tibiae with two apicoventral spinules between spurs. Ratio of femur to tibia for fore-, mid- and hind legs: 1.15–1.43, 1.29 [1.20]; 1.00–1.28, 1.11 [1.28]; 0.75–0.82, 0,78 [0.76]. Ratio of tibia to basitarsus for fore-, mid- and hind legs: 1.11–1.50, 1.32 [1.50]; 1.15–1.54, 1.34 [1.15]; 1.58–1.86, 1.79 [1.73].
Wings hyaline, length 2.87–3.19, 2.98 [3.19] mm (n=5). Radial veins and apical half of r-m brown, other veins paler and M-stem very faint. Sc, R4, bM-Cu, M-stem and basal half of cu-stem bare; C, R1, R5 and r-m setose on both surfaces; M1, M2, apical two third of cu-stem, CuA1, CuA2 and A1 setose on dorsal surface. Costa reaches 0.30–0.36, 0.32 [0.36] from R5 to M1. Sc ending in R, slightly before the level of origin of M-stem. Anterior fork begins at the level of R4 or a little before at the level of R4. Posterior fork begins before anterior fork at level of middle of r-m. R1 2.3–2.7, 2.5 [2.3] times as long as r-m, which is 1.0–1.3, 1.1 [1.0] times as long as M-stem.
Abdomen blackish brown with sternites somewhat lighter. Terminalia ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ) brown with gonostyli lighter. The ventroapical margin of gonocoxite with flange bearing a medial bump with black spine-like blunt bristles. The gonostylus with two apical and three to four subapical black spines. Tergite 9 widening apically; apical margin slightly concave. Cercus with 10 combs of retinacula.
Female. Unknown.
Biology. Unknown.
Etymology. The species is named after the type locality—Chimgan Mountain in Tashkent Province, Uzbekistan.
Discussion. The species is close to D. selini Kurina, 2006 , which is described from Kazakhstan but also found in the Chimgan area of Uzbekistan. Docosia chimganica markedly differs from D. selini in the shape of the gonostylus. In D. chimganica , the gonostylus has six subequal spines on its apical half and medial and basal extensions. The gonostylus of D. selini , on the other hand, has three spines and only a basal extension. The cercus has 10 combs of retinacula in contrast to 11 in D. selini . Considering the overall structure of the male terminalia, both species are possibly related to the European D. montana Laštovka & Ševčík, 2006 and D. matilei Ševčík & Laštovka, 2008 but differ mainly in details of the gonostylus (cf. Laštovka & Ševčík 2006: fig. 10, Ševčík & Laštovka 2008: fig. 2).
| IZBE |
Institute of Zoology and Botany |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |