Cyathoshiva amaleshi, Datta, Tridip Kumar, Miljutin, Dmitry M., Chakraborty, Susanta Kumar & Mohapatra, Anil, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4126.4.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:73B98DDB-B5EE-44BC-91E1-E2F1FE412304 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5664069 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A67687DB-FF9D-FF86-FF0D-FF2DFC9BFB60 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cyathoshiva amaleshi |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Cyathoshiva amaleshi gen. n. sp. n.
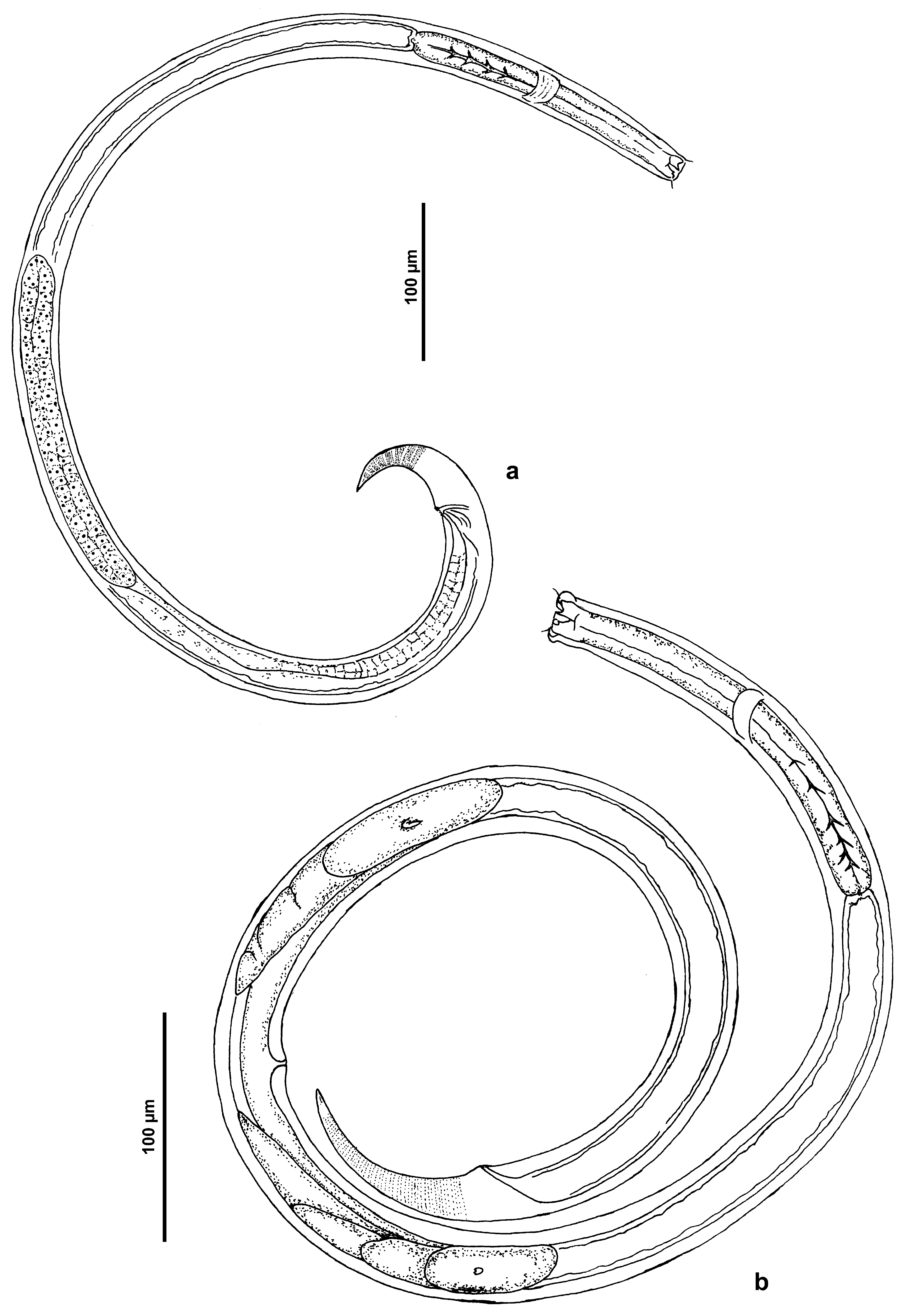
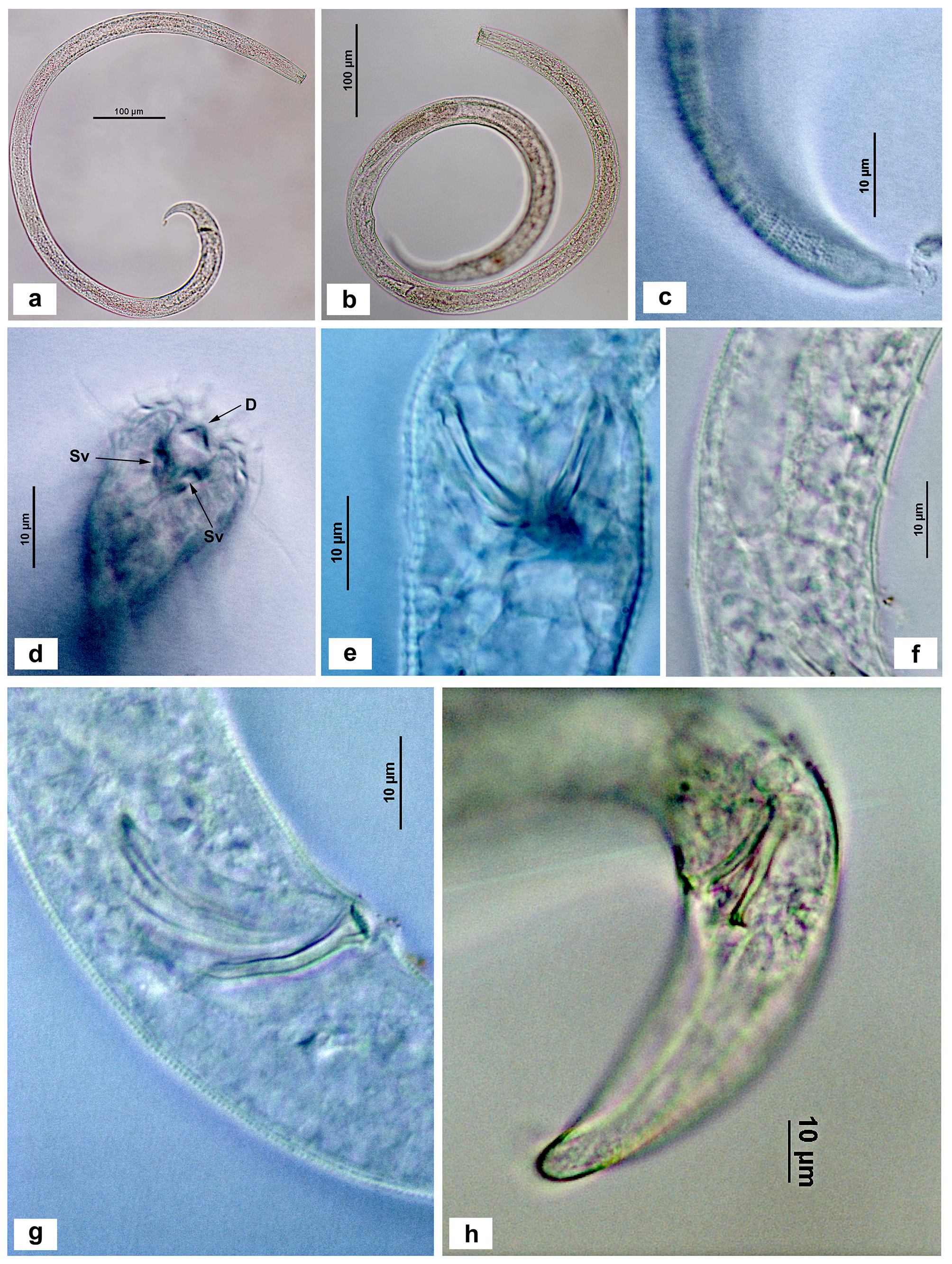
Figures 2–4 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 , Table 1 View TABLE 1
Type material. Six males (of those, two males dissected), five females. Holotype male: Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/ N4356 (Co-ordinates of the Collection Site: 21° 37.237′ N; 87° 31.048′ E). Male paratypes: Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/ N4357; Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/N4358; Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/N4359. Male body parts: Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/ N4365–N4367. Female paratypes: Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/N4360; Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/N4361; Reg. No. MARC / ZSI/N4362; Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/N4363; Reg. No. MARC /ZSI/N4364.
Etymology. The species name is given in honour of our beloved Retired Professor, Dr. Amalesh Choudhury, a renowned marine biologist and ecologist of the University of Calcutta, India.
Main measurements (males and females together): L = 814–1233 µm; a =33.6–38.3; b =5.3–6.5; c =10.8– 14.7; V =48.6–53.3
Description. Body cylindrical with truncated anterior end and conical tail. Cuticle transversely punctated. Lateral differentiation in form of slightly larger dots; hardly visible along whole body, except post-anal where it is seen more distinctly in males. Body pores arranged in longitudinal rows. Mouth opening with indistinct lips. Inner labial sensilla not clearly seen. Six outer labial sensilla and four cephalic sensilla arranged in one circle. Cephalic sensilla shorter than outer labial sensilla. Two types of somatic somatic setae differing in length. Larger somatic setae 7–12 µm long; two large somatic setae present in anterior part of pharynx; a series of larger somatic setae present at sub-dorsal part of caudal region. Smaller somatic setae 2–3µm long; sparsely distributed along the body. Amphideal fovea 6–8 µm in diameter, multispiral with 4–4.25 turns or slightly more. Cheilostoma cup-shaped, surrounded by twelve longitudinal rugae. Pharyngostoma with one large pointed cuticularised dorsal tooth 4–5 µm long and two smaller pointed subventral teeth 2–2.5 µm long. Pharynx about one sixth of total body length, muscular, lacking developed posterior bulb. Nerve ring situated at about half pharynx length. Cardia not observed. Renette cell and ampulla not seen. Tail conical, with narrow terminal spine 3–4 µm long.
Male. Reproductive system diorchic; anterior testis outstretched, posterior testis reflexed. Anterior and posterior testes lying to right and left of intestine, respectively. Vas deferens with fine and coarsely granulated regions. Spicules 28–32 µm long in arc, arcuate without vellum; capitulum, calomus and lamina are almost similar in diameter; distal end pointed and slightly upwardly directed. Gubernaculum 19–20 µm long; proximally fused, distally paired. Distal end with dilated head with serrated edges and two teeth looking like a spread bird’s foot. Three preanal supplements having basal tubular part inserted mostly within the body and distal part in shape of indistinct papilla or short seta 1–2 µm long. Supplements at similar distances (12–16 µm) from each other.
Female. Ovaries paired, opposed and reflexed. Anterior ovary larger than posterior. Anterior ovary lying on right of intestine; posterior ovary on left. Vulva located at about mid-body length. Tail length longer in female than male (de Man’s c 10.8–11.9 vs 13.3–14.7 in female and male, respectively). Cuticular punctations on tail homogenous; no lateral differentiation.
Habitat and biology. The holotype and paratypes were found in sand with medium to fine particles and with little silt and clay. Throughout the year, sea-water temperature, salinity and pH varied from 24.6°C–37.7°C, 9–34 ppt and 7.17–8.66 respectively. Available sulphate S and phosphate P of the sediment varied from 56.9–163.8 mg / kg and 15.4–35 mg /kg respectively. Organic carbon content varies up to 0.37%. The specimens were found with algal matter but no clear food particles were identified from the gut of preserved specimens. Based on the structure and arrangement of teeth in the buccal cavity it is predicted that these specimens would be classified under 2A or as epistrate feeders, according to Wieser’s (1953) terminology.
TABLE 1. Morphometric measurements of Cyathoshiva amaleshi gen. n sp. n; All the characters except ratio are taken in µm.?: Data Unknown.
| Specimen status | Holotype 1 | Paratype 1 | Paratype 2 | Paratype 3 | Paratype 4 | Paratype 5 | Paratype 6 | Paratype 7 | Paratype 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registration No. | N4356 | N4357 | N4358 | N4359 | N4360 | N4361 | N4362 | N4363 | N4364 |
| Gender | m | m | m | m | f | f | f | f | f |
| Total length | 1074 | 1138 | 1006 | 1010 | 1121 | 1233 | 1106 | 814 | 908 |
| Pharynx length | 179 | 200 | 190 | 177 | 186 | 188 | 189 | 151 | 163 |
| Tail length | 81 | 84 | 69 | 68 | 103 | 107 | 96 | 73 | 77 |
| Distance from head end to amphid | 10 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 |
| NR distance from anterior end | 9 2 | 1 1 1 | 9 3 | 8 5 | 8 6 | 8 6 | 8 5 | 7 6 | 9 5 |
| Head cbd | 1 8 | 2 2 | 1 8 | 1 7 | 1 9 | 2 1 | 1 7 | 1 7 | 1 7 |
| Amphidcbd | 2 0 | 2 3 | 1 8 | 1 8 | 2 1 | 2 3 | 2 1 | 2 2 | 2 0 |
| NR cbd | 2 6 | 2 8 | 2 3 | 2 3 | 2 3 | 3 0 | 2 2 | 2 2 | 2 4 |
| Midbodycbd | 29 | 32 | 28 | 27 | 30 | 32 | 30 | 23 | 27 |
| Anal cbd | 2 5 | 3 1 | 2 5 | 2 7 | 2 3 | 2 9 | 2 6 | 2 2 | 2 2 |
| Length of outer labial sensilla | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 10 |
| Length of cephalic sensilla | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 |
| Amphid diameter | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| NR (%) | 5 1 | 5 6 | 4 9 | 4 8 | 4 6 | 4 6 | 4 5 | 5 0 | 5 8 |
| Amphidtocbd (%) | 33 | 31 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 33 | 29 | 31 | 31 |
| Turns of amphid | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.2 5 | 4 | 4.2 5 | 4 | 4 |
| Spicule length in arc | 32 | 31 | 31 | 28 | |||||
| Gubernaculum length | 19 | 20 | 19 | 20 | |||||
| a | 36.9 | 35.3 | 35.4 | 37.6 | 37.2 | 38.3 | 36.7 | 35.6 | 33.6 |
| b | 6.0 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 5.9 | 5.4 | 5.6 |
| c | 13.3 | 13.5 | 14.6 | 14.7 | 10.8 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.2 | 11.9 |
| c' | 3.2 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 4.5 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 3.4 |
| V | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 8.6 | 5 3.3 | 4 8.8 | ? | ? |
| V' | NA | NA | NA | NA | 55.3 | 58.5 | 54.7 | ? | ? |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Cyatholaiminae |
|
Genus |