Culex, Linnaeus, 1758
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5016.2.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:38A6AB65-BC1E-461F-8851-8648B6EBBED5 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9D45878E-FFE6-FF9C-FF69-15AAFC14FB81 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Culex |
| status |
|
Culex ekaterinae is the seventh extinct species of the genus Culex described to date. Three of the seven species are known from inclusions in amber ( Cx. erikae , Cx. ekaterinae and Cx. malariager ) and four are known from compressions/impressions in sedimentary rock ( Cx. damnatorum , Cx. protorhinus , Cx. vectensis and Cx. winchesteri ). The geological ages of the six previously described species are given in Table 1. Three of the fossils are known from North America: Cx. damnatorum from deposits in Wyoming, Cx. malariager from Dominican amber ( Dominican Republic) and Cx. winchesteri from deposits in Colorado. The other four species are known from Europe: Cx. pro- torhinus and Cx. vectensis from deposits in England, Cx. erikae from Baltic amber (Gulf of Gdańsk) and Cx. ekaterinae from Rovno amber of Ukraine. The four compression fossils and the inclusion fossil Cx. malariager are all females, all of which are morphologically distinct from and obviously not conspecific with the males of Cx. erikae and Cx. ekaterinae .
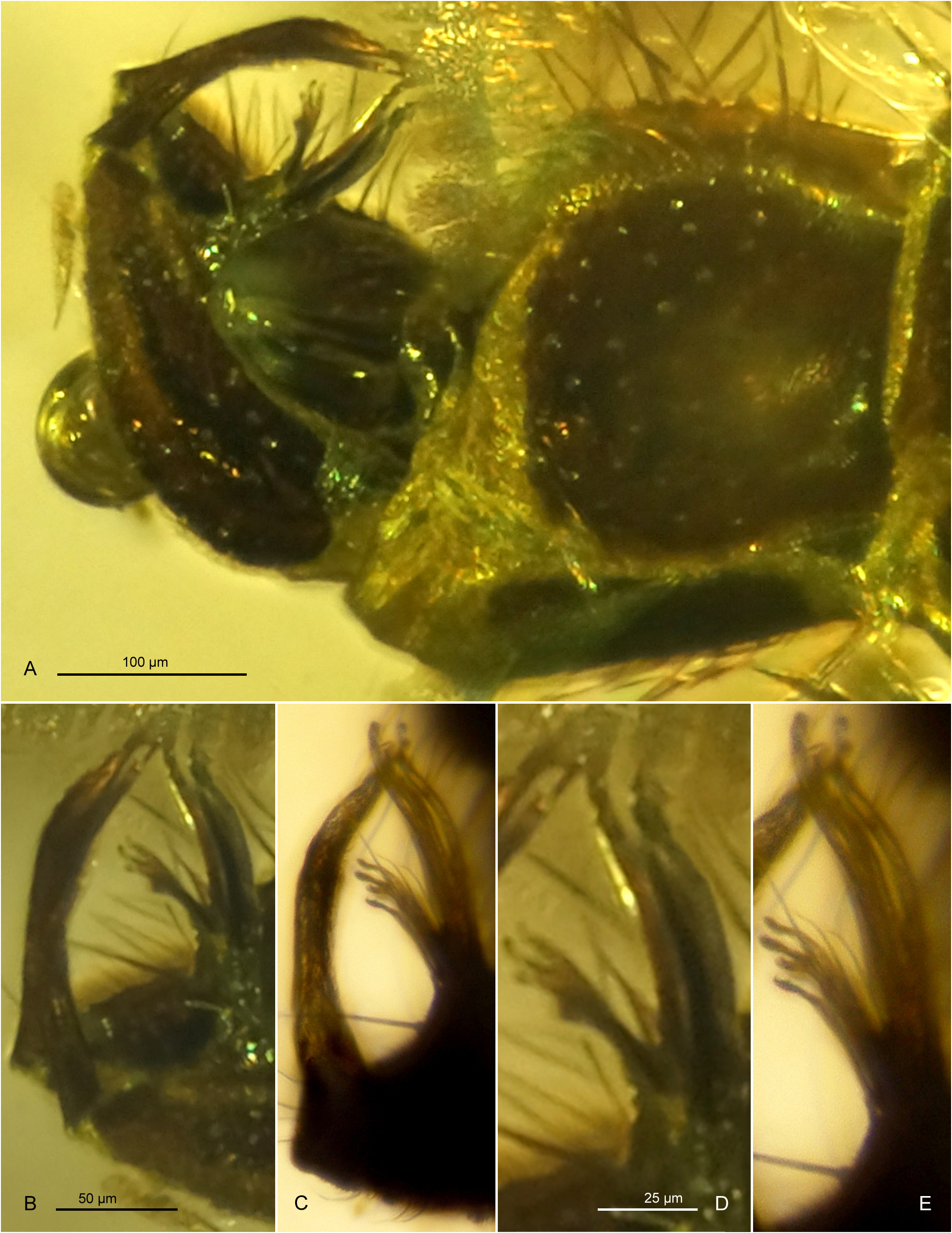
Szadziewski & Szadziewska (1985) described Cx. erikae as a species of the nominate subgenus. However, the placement of Cx. ekaterinae , and also Cx. erikae due to close similarity, in the subgenus Culex is doubtful in view of the following unique anatomical features: the distinct constriction beyond mid-length of the proboscis, the very short mediocubital crossvein with the adjoining veins distinctly indented and the strongly developed posterior cubitus. It is also noted that the agglutination of setae on the subapical lobe of the male gonocoxite is unusual, and seta g, which is most often foliform in species of the subgenus Culex , is not leaf-like in Cx. ekaterinae . These features may justify the recognition of a new subgenus, but until the phylogenetic relationships among extant species of the subgenus Culex are better understood, we refrain from introducing a new genus-group taxon at this time.
The adult males of Cx. ekaterinae and Cx. erikae , compared here, are presumably the most closely related fossil species known so far. They distinctly differ, however, in characters of the head, wing, legs and genitalia. Detailed character comparisons are shown in Figs 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 and listed in Table 4.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.