Cryptotendipes medialis, Mukherjee & Mukherjee & Hazra, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4896.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6086982F-AA93-43F0-91F0-983918696FB1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4382767 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F878651D-6561-4A41-9E56-C2D9787577D5 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:F878651D-6561-4A41-9E56-C2D9787577D5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cryptotendipes medialis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cryptotendipes medialis View in CoL sp. n. (n=2)
Material examined. Holotype male, labelled ‘ Holotype Cryptotendipes medialis sp. n., India, West Bengal, Purba Bardhaman, Burdwan [23˚22ʹN, 87˚85ʹE], 06.ii.2020, Coll. N. Hazra’ . Paratype 1 male, same data as holotype, labelled ‘ Paratype Cryptotendipes medialis sp. n., India, West Bengal, Purba Bardhaman, Burdwan [23˚22ʹN, 87˚85ʹE], 16.ii.2020, Coll. N. Hazra’ .
Diagnostic characters. The adult male is distinguished from other Cryptotendipes by the presence of small digitiform setose lobe nearly the middle of anal point, little basal expansion in gonostylus, inner margin of gonostylus bearing moderately long setae arranged in proximal half and distally broadened gonostylus with pointed tip.
Etymology. The name “ medialis ”, Latin word, derived from “ medius” (close to middle), refers to tiny digitiform lobe situated nearer the middle of the anal point.
Male (n=2)
Total length 3.03–3.1, 3.06 mm. Wing length 1.83–1.9, 1.87 mm. Costal length 1.75–1.78, 1.76 mm. Antennal length 0.94–0.95 mm.
Colouration. Thorax yellowish brown with dark brown marking, leg colour light brown, abdomen olive green.
Head. Head width 0.35–0.37 mm. Temporal setae 9–11 (IV 1–2, OV 4, Po 4). Clypeal setae 8–10. Frontal tubercle absent. Eyes bare with dorsomedial extension of 100 µm. Antenna with 11 flagellomeres, ultimate flagellomere 660–680, 670 µm long; AR 2.35–2.5, 2.42. Length of palpomeres (I–III) (µm): 30: 70–80: 110–120; palpomeres IV and V missing. CA 0.38–0.4, 0.39.
Thorax. Acrostichals 2–4; dorsocentrals 7–8; prealars 2–3; scutellars 4.
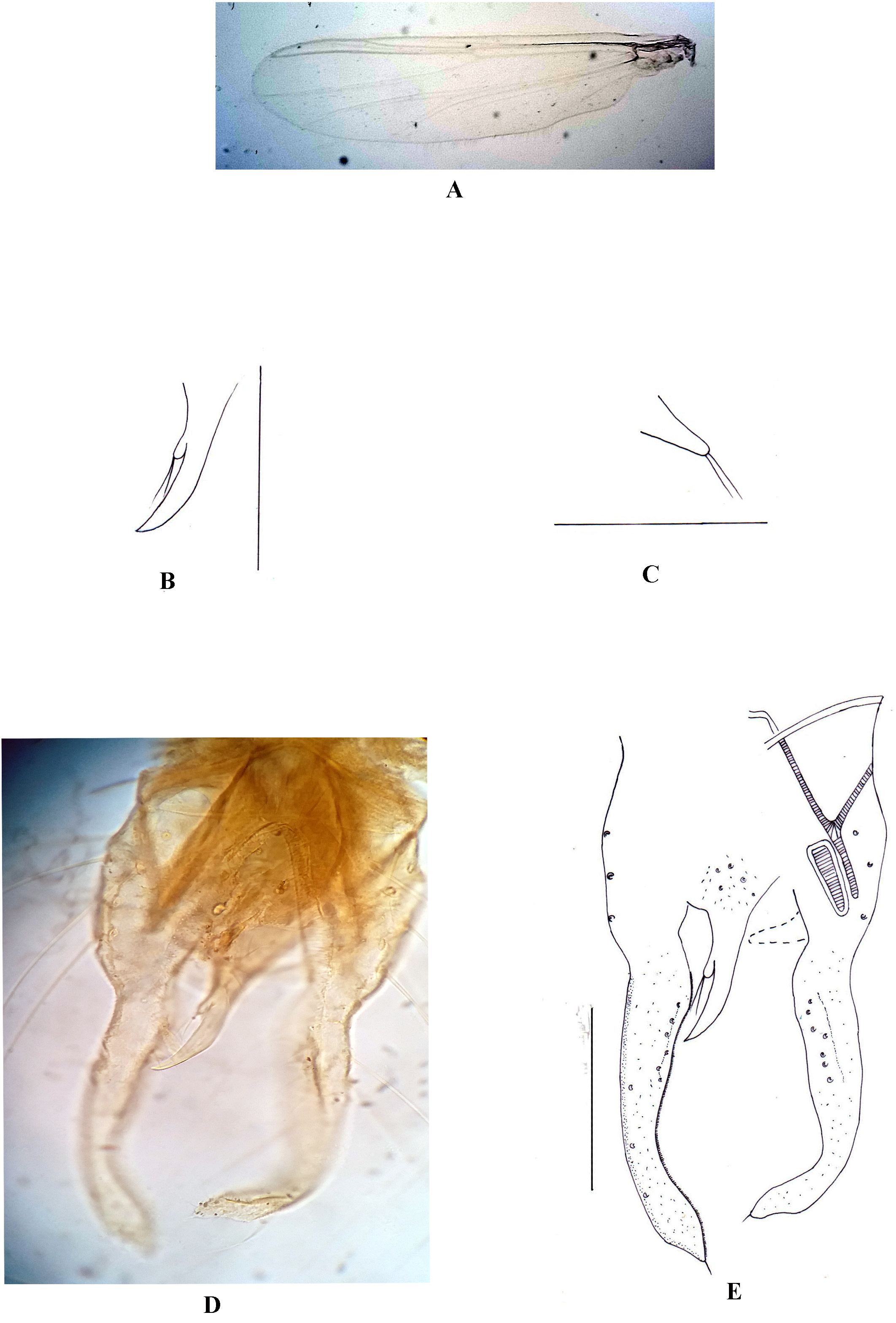
Wing ( Fig. 1A View FIGURES 1 ). VR 1.1–1.3. R with 1 seta. R 1 and R 4+5 bare. Brachiolum with 2 setae. Squama with 6–8 fringed setae. Anal lobe well developed.
Legs. Fore tibial scale bare. Mid legs with 2 tibial spurs, 13.8–13.9 µm and 16.1–16.4 µm long, comb with 14 teeth. Hind leg with two tibial spurs, 13.8–14.1 µm and 17.1–17.2 µm long, comb with 22 teeth. Lengths and proportions of leg segments shown in table 1.
Abdomen. T IX with 6–8 setae.
Hypopygium ( Figs. 1 View FIGURES 1 B–E). Anal tergite band V shaped. Anal point 69–71.3 µm long, 11.5–13.8 µm wide at base. A minute digitiform lobe of 13.8–16.1 µm long, 4.6 µm wide with 2–3 apical setae located more or less medially at anal point ( Fig 1B View FIGURES 1 ). Gonocoxite 92–96.6, 94.3 µm long; gonostylus 131–135.7, 133.4 µm long with distally pointed tip bearing 1 apical seta. ^aOn anterior half of gonostylus bearing 13.8–18.4 μm long 6–8 inner setae. Superior volsella 27.6–29.9 µm long, 9.2–11.5 µm wide ( Fig 1C View FIGURES 1 ). Inferior volsella absent. Transverse sternapodeme 23–25.3 µm long; lateral sternapodeme 85.1–87.4 µm long. HR 0.7–0.71, HV 2.25–2.29.
Distribution. India (present record).
Remarks. The new species differs from all known Oriental species of the genus Cryptotendipes by the presence of minute digitiform setose lobe nearly middle of the anal point. Cryptotendipes nodus is similar with the new species in having long setae located on inner margin of the gonostylus, number of seta on R vein (1), and number of scutellars (4) but differs in AR, HR, wing length, shape of the anal point and superior volsella. The new species shows affinities with C. aculeatus Pal et Hazra, 2018 in the number of apical setae of superior volsella and number of squamal setae, but differs in the number of setae on R and M veins, HR, shape of the gonostylus, and superior volsella. The present species disagrees with C. disparilis Pal et Hazra, 2018 in shape of the superior volsella, number of anal tergite setae and acrostichals. The new species shows closeness with C. holsatus Lenz, 1959 in having similar AR, shape of the gonostylus and apical seta on the gonostylus but differs in the presence of setae in distal half of the gonostylus, shape of the anal point, number of anal tergite setae and apical seta on the superior volsella. Cryptotendipes lyalichi Zorina, 2006 shows similarities with the new species in having anal process, finger shaped superior volsella but differs in AR, Acs, length of the gonocoxite and gonostylus, shape of the anal point and presence of dorsal hump on T IX.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |