Corynoneura petitspectabilis Fu, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4890.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DF8187AD-1391-4884-A33A-8B79D130DA4C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4330077 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A887DB-1662-FF90-FF1F-FE50FC4FFB66 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Corynoneura petitspectabilis Fu |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Corynoneura petitspectabilis Fu View in CoL , sp. n.
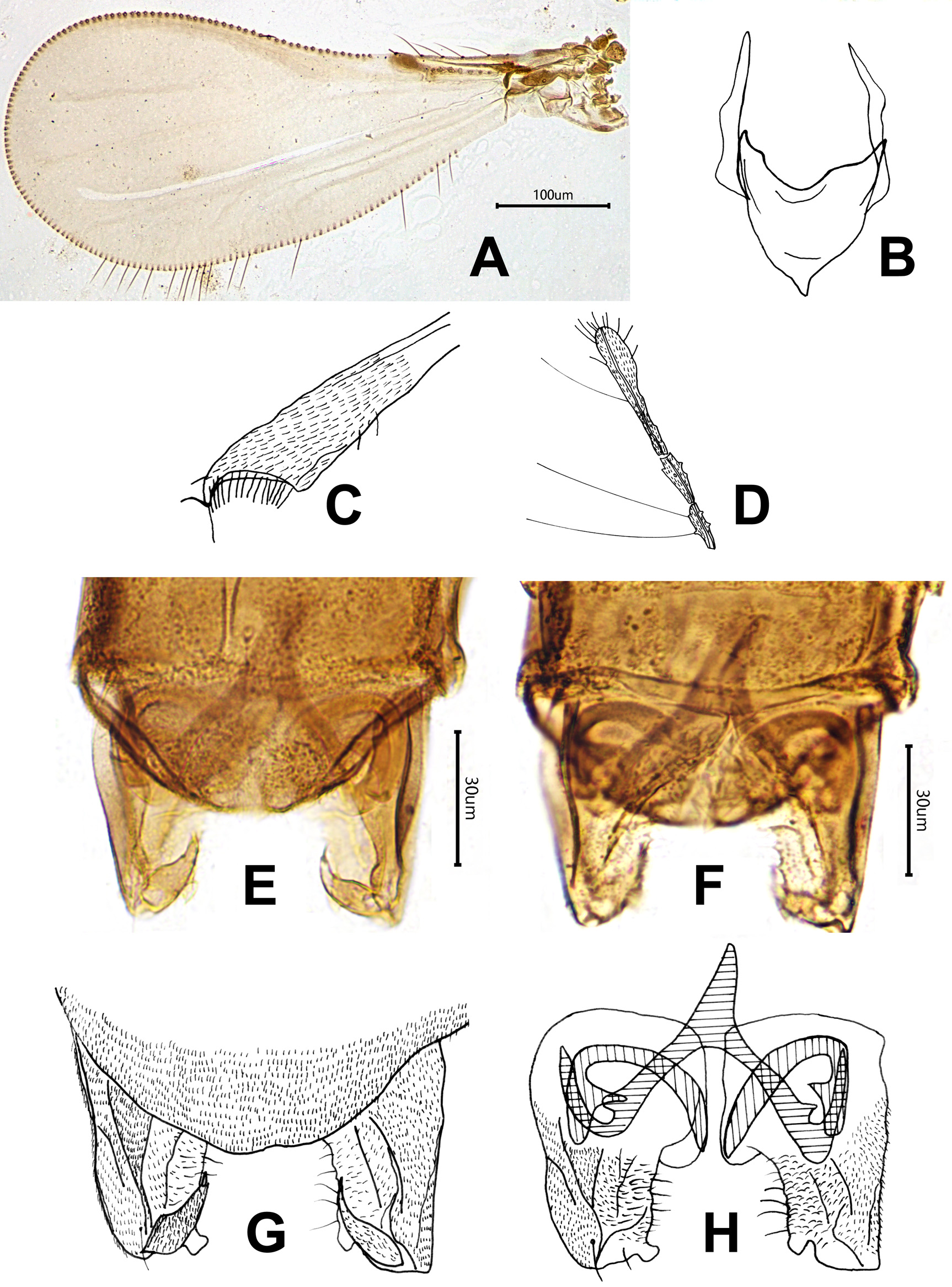
Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4
Type material. Holotype male (NKU: G5A39), CHINA: Zhejiang Province, Jinhua City, Pan’an County, Dapanshan Mountains , 120°31′30″E, 28°47′30″N, a.s.l. 800 m, 17–21.VII.2012, light trap, leg. Xiao-Long Lin. GoogleMaps
Etymology. From Latin, petit, small, referring to total length of the species only 0.75 mm; spectabilis, remarkable, referring to superior volsella being rounded and developed, as well as the phallapodeme and sternapodeme well developed.
Diagnostic characters. The male imago is characterized by having small total length of 0.75 mm; antenna with eight flagellomeres, AR 0.35; anterior margin of cibarial pump strongly concave; superior volsella developed and rounded; inferior volsella small and digitiform, placed caudally of gonocoxite; transverse sternapodeme curved into V-shape; lateral sternapodeme with very large and developed attachment point, and attachment point placed and directed lateral.
Description. Ault male (n = 1).
Total length 0.75 mm. Wing length 0.47mm. Total length/wing length 1.60.
Coloration. Head and thorax dark brown. Anterior part of eyes black, and others brown. Legs pale yellow. Abdomen: tergites I-IV yellow, tergites V-IX yellow brown.
Head. Antenna with eight flagellomeres, AR 0.35, ultimate flagellomere 70 µm long, ultimate flagellomere slightly expanded apically, with about 9–11 apical sensilla chaetica ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ). Tentorium and cibarial pump as in Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 , tentorium 83 µm long; 10 µm wide. Anterior margin of cibarial pump strongly concave. Length of palpomeres (in µm): 7; 10; 15; 15; 33. Palpomere 5/3 ratio: 2.2.
Thorax. Dorsocentrals 5. Scutellum with 2 setae.
Wing ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ). VR 3.3. Cu/wing length 0.53; C 180 µm long; Cu 250 µm long; wing width/wing length: 0.50. Costa with 5 setae.
Legs. Dehydrate and contractive, hard to measure. Hind tibia expanded, with comb of 15 setae, with hooked spur ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ).
Hypopygium ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 E-H). Tergite IX medially slightly incurved. Superior volsella rounded and developed, and anteromedially separated. Inferior volsella small and digitiform, and placed caudally of gonocoxite. Phallapodeme developed, strongly curved, 58 µm long, with obvious projection, and joint with sternapodeme placed lateral. Transverse sternapodeme absent, curved into V-shape. Lateral sternapodeme with very large and developed attachment point, placed and directed laterally. Gonostylus apical slender and slightly curved tapering, 23 µm long, with 1 subapical seta; megaseta 4 µm long. HR 2.6; HV 3.3.
Remarks. The legs of the type material were difficult to measure; however, most of the observable characters of the male separate the species from all other members of the genus.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Orthocladiinae |
|
Genus |