Cladolasma damingshan, Zhang, Chao & Zhang, Feng, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3691.4.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B1249CAB-0BD6-4D05-B8B9-4C1A84531737 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5661545 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1021FED9-995D-4533-BA04-380039218A0C |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:1021FED9-995D-4533-BA04-380039218A0C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cladolasma damingshan |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cladolasma damingshan sp. nov.
( Figs 1–24 View FIGURES 1 – 4 View FIGURES 5 – 6 View FIGURES 7 – 18 View FIGURES 19 – 24 )
Type material. Male holotype; CHINA, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Wuming County, Damingshan National Nature Reserve ( 23°30´N, 108°26´E), elevation 1231 m, 18. July 2012, C. Zhang leg. (MHBU-Opi- 12ZC030).
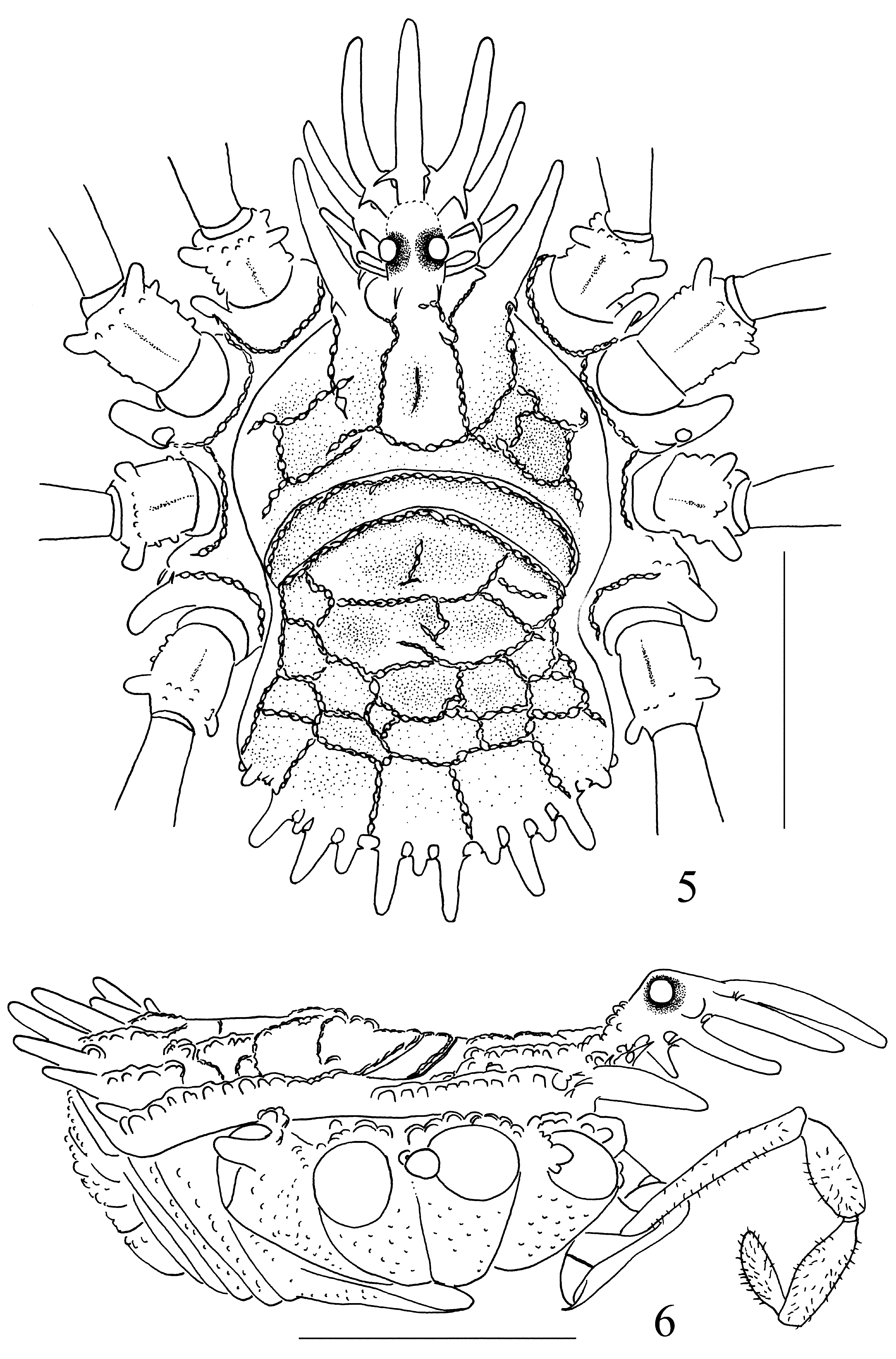
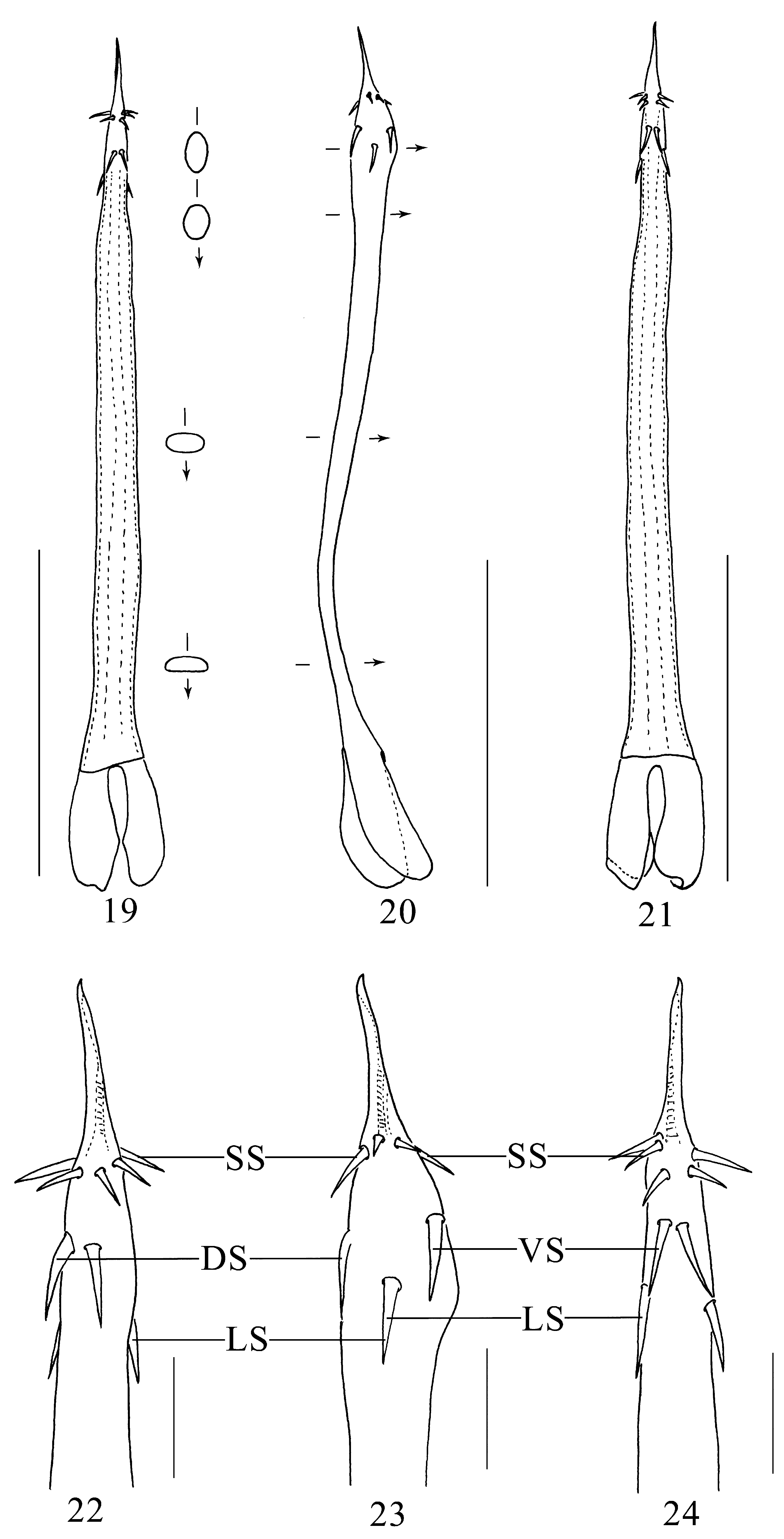
Diagnosis. Base of penis dorsoventrally compressed, truncus penis bent to ventral after proximal third ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ). Glans with eight small spines and six large spines: small ones arranged around base of stylus; large ones situated on dorsal, lateral, and ventral side at the central and basal part of the glans ( Figs 22–24 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ). Ocularium ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 5–6 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ) without circumocular keels (see Suzuki 1974: 123, fig. 1 for C. parvulum ; Schwendinger & Gruber 1992: 58, fig. 2 for C. angka ). The eyes at the highest part of the ocularium and the hood projections sloping slightly to ventral ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ; in comparison to Suzuki 1974: 123, fig. 1; Schwendinger & Gruber 1992: 58, fig. 3). Abdominal scutum ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ) without enlarged, dorsad-directed tubercles (compare Schwendinger & Gruber 1992: 58, fig. 3 for C. angka ).
Etymology. The species epithet is a noun in apposition, referring to the type locality.
Description. Male ( holotype) habitus as in Figs 1–2 and 4–6 View FIGURES 1 – 4 View FIGURES 5 – 6 . Coloration in alcohol generally dark brown with yellow background color: dorsum with yellowish brown background ( Figs 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Propeltidium with two brown lateral areas. Eye rings black, hood pale brown to yellow ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Meso- and metapeltidium with a lighter median area in the center. Most of the opisthosomal scutum brown, only area V yellowish brown posteriorly, where thinning into tubercle structures. Venter dark brown, slightly lighter in ventral midline ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Chelicerae dark brown. Pedipalpi pale brown except for dark brown trochanter. Legs yellowish brown except for dark brown trochanters, metatarsi and tarsi; femora of legs I, III and IV banded brown (base and center) and yellow.
Dorsum ( Figs 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 5 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ). Entire body strongly sclerotized. Metapeltidium clearly separated from carapace and abdominal scutum ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 5 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ). Free tergites not visible from above. Surface covered with a network of interconnected anvil-shaped tubercles. Anterior border of carapace with one lateral conical process on each side of ocularium; central portion of carapace with four longitudinal rows of anvil-shaped tubercles connected with each other by transverse bridges; lateral margin of carapace smooth, without anvil-shaped tubercles. Metapeltidium with a transverse row of anvil-shaped tubercles ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 5 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ). Abdominal scutum with intricate lattice of interconnected anvil-shaped tubercles, its posterior margin with a fence-like row of 6 enlarged, posteriad-directed digitiform tubercles. Free tergites on caudal surface of body with low keels in transverse rows ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 6 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ).
Hood ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 5–6 View FIGURES 5 – 6 ) highly arched, with one median, unpaired and 4 lateral, paired digitiform tubercles, decreasing in length toward base of the hood; these digitiform tubercles usually with small basal cross-bars and decreasing in diameter from base to tip. Basal stem of the hood very short in comparison to other species, and hood projecting ventral and not bent in central part. Eyes thus located relatively high, not below the level of the hood if seen from lateral. No circumocular keels or lace-like elevations present.
Venter ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Coxae with small wart-bearing setae on ventral surfaces and with dorso-distal rows of anvilshaped tubercles; a row of anvil-shaped tubercles along anterior and posterior margins of coxae II, III and IV; coxae I and II with distal digitiform processes retrolaterally; coxa IV with similar process prolaterally. Genital operculum short and tongue-shaped, surface with tubercles. Sternites with transverse rows of low keels, these reduced at the midline.
Chelicerae ( Figs 7–9 View FIGURES 7 – 18 ). Basal segment without glandular area and dorsomedial tooth, only ventrally and dorsally with a few setae. Second segment with one basal, prodorsal tooth ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 18 ) and many long dorsal setae, and rows of short setae at base of fixed finger ( Figs 7, 9 View FIGURES 7 – 18 ). Fingers short, with diaphanous teeth and dark subapical teeth: one dark tooth on movable finger, two dark teeth on fixed finger.
Pedipalpi ( Figs 10–12 View FIGURES 7 – 18 ). Coxae with one ventral setiferous tubercle. Trochanters with two ventral setiferous tubercles. Femora with few clavate hairs. Patellae medially with many clavate hairs and laterally with few clavate hairs. Tibiae and tarsi densely covered with clavate hairs.
Legs ( Figs 13–18 View FIGURES 7 – 18 ). All trochanters prodorsally and retrodorsally with one enlarged tubercle. Femora, patellae and tibiae without pseudoarticulations, with distinctive microsculpture as shown in Fig. 18 View FIGURES 7 – 18 , composed of broad, thick, conical, slightly inclined denticles. Metatarsi and tarsi without annulations and microsculpture, only with setae. Tarsal segments I–IV: 4 (2+2), 5 (3+2), 6 (2+2+2), 6 (2+2+2).
Penis ( Figs 19–24 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ) slender; no clear distinction between shaft, glans and stylus. Shaft with nearly parallel sides for most of its length (seen from dorsal and ventral), then tapering distally; in proximal portion dorsoventrally compressed and ventrally flattened (best seen from lateral), in median portion elliptical and wider than long in cross-section, in distal portion elliptical and longer than wide in cross-section, close to glans almost circular. Base of truncus drawn out in two large lobe-like roots, containing the muscles. Glans strongly bulged ventrally and slightly bulged dorsally ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ); distal part of glans with eight small spines at the base of the stylus and basal part with six large spines, the latter arranged as follows: two dorsal, two lateral, and two ventral ( Figs 22–24 View FIGURES 19 – 24 ). Stylus simple, straight, slightly inclined towards dorsal side, without torsion; tip of stylus slightly bent towards ventral side.
Female. Unknown.
Measurements. Male holotype: Total length (including hood and posterior tubercles) 3.15. Prosoma 0.75 long, 1.35 wide. Opisthosoma 1.23 long, 1.31 wide. Median hood process 1.00 long, 0.82 wide. Basal segment of chelicerae 0.55 long, 0.22 wide; second segment of chelicerae 0.60 long, 0.18 wide. Measurements of left pedipalpus and right legs as in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Habitat. The single specimen was collected by sieving leaf litter in a sub-tropical evergreen broad-leaved forest.
Distribution. This species is so far known only from the type locality, the Damingshan National Natural Reserve in Guangxi Province, China.
TABLE 1. Pedipalpus and legs measurements of the Cladolasma damingshan sp. nov. holotype; length / width given for femora.
| Trochanter | Femur | Patella | Tibia | Metatarsus | Tarsus | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pedipalpus | 0.37 | 0.70/0.10 | 0.38 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 2.25 | |
| Leg I | 0.34 | 1.27/0.23 | 0.55 | 0.96 | 0.33 | 0.60 | 4.05 |
| Leg II | 0.40 | 3.00/0.18 | 1.00 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 1.48 | 9.68 |
| Leg III | 0.34 | 1.40/0.23 | 0.55 | 1.03 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 4.29 |
| Leg IV | 0.34 | 1.85/0.23 | 0.65 | 1.72 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 5.66 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |