Chlorionidea apenninica, Guglielmino & Bückle, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2010.512399 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9314C160-7446-377B-FE31-7A8FFCF9222F |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Chlorionidea apenninica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chlorionidea apenninica View in CoL sp. nov.
Description
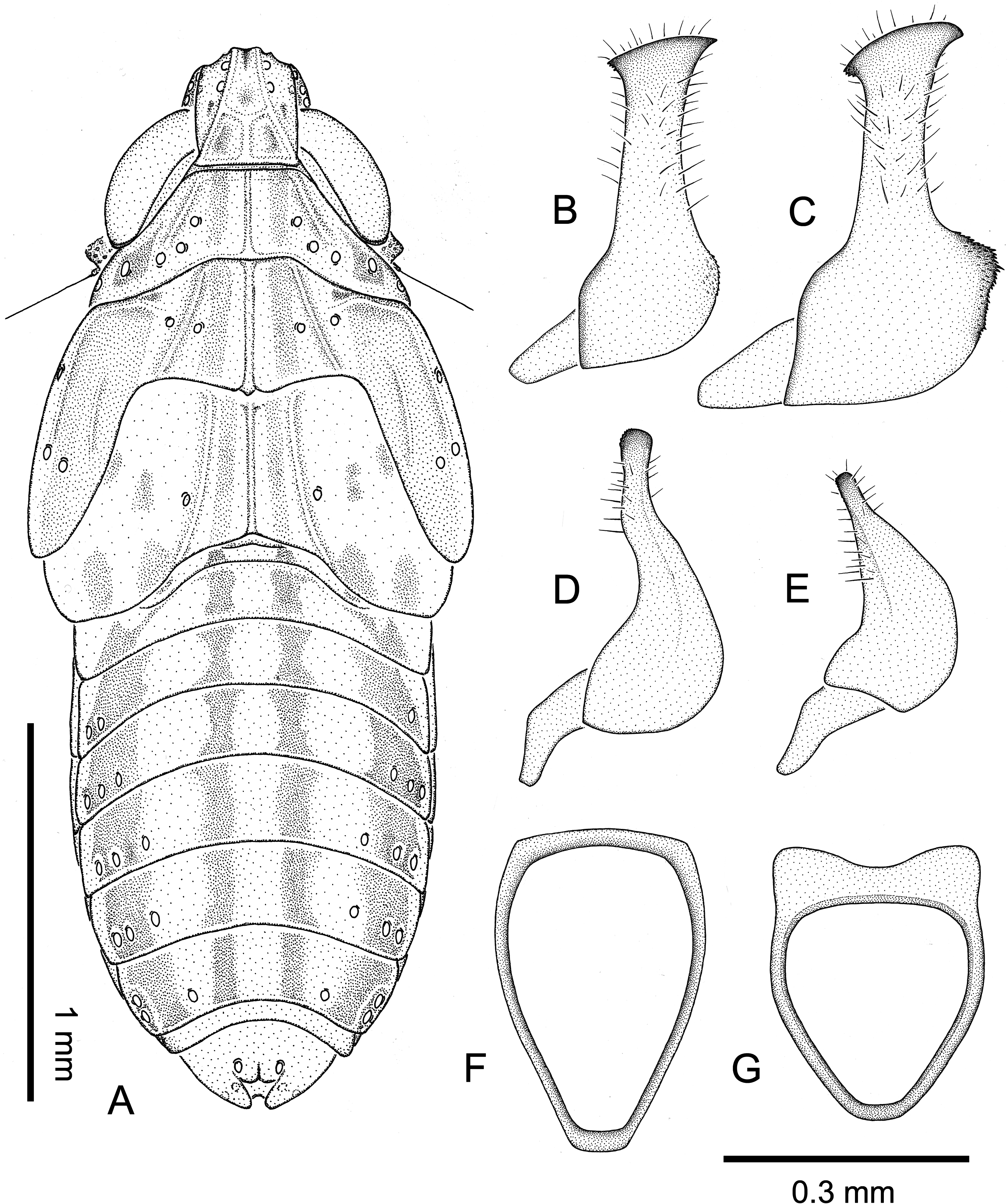
Head, pronotum, mesonotum ( Figure 3A,B View Figure 3 ) as in C. flava . In shape, proportions, size, colour and markings very similar to C. flava . The differences from that species are the
characters of the male and female genitalia. Until now only brachypterous specimens are known.
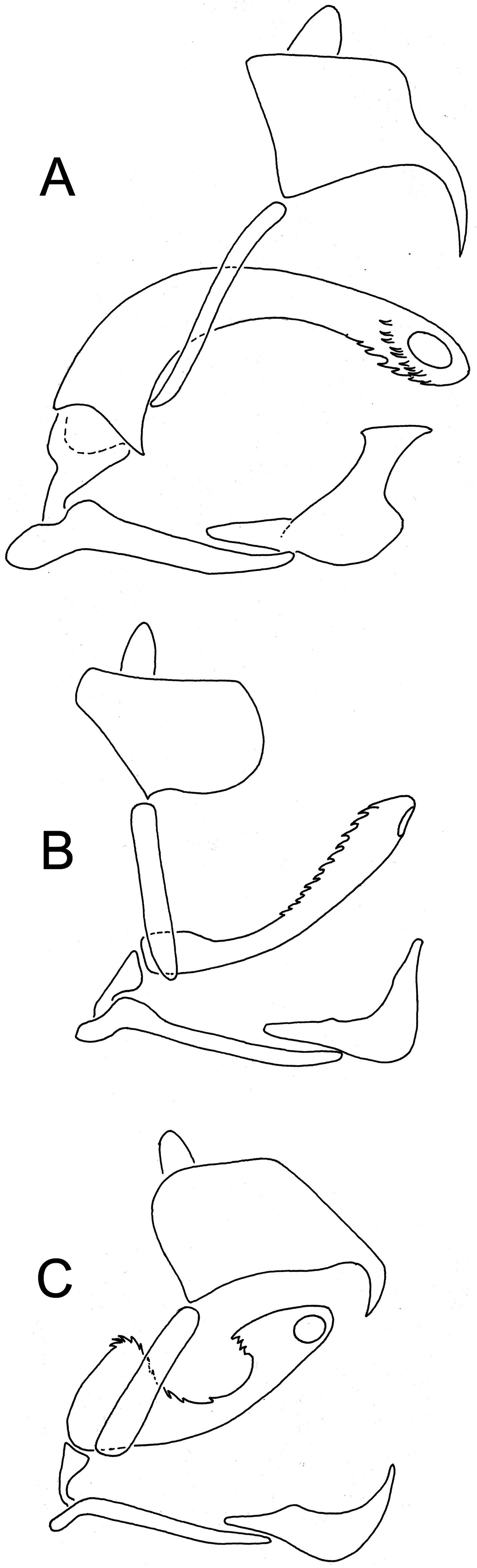
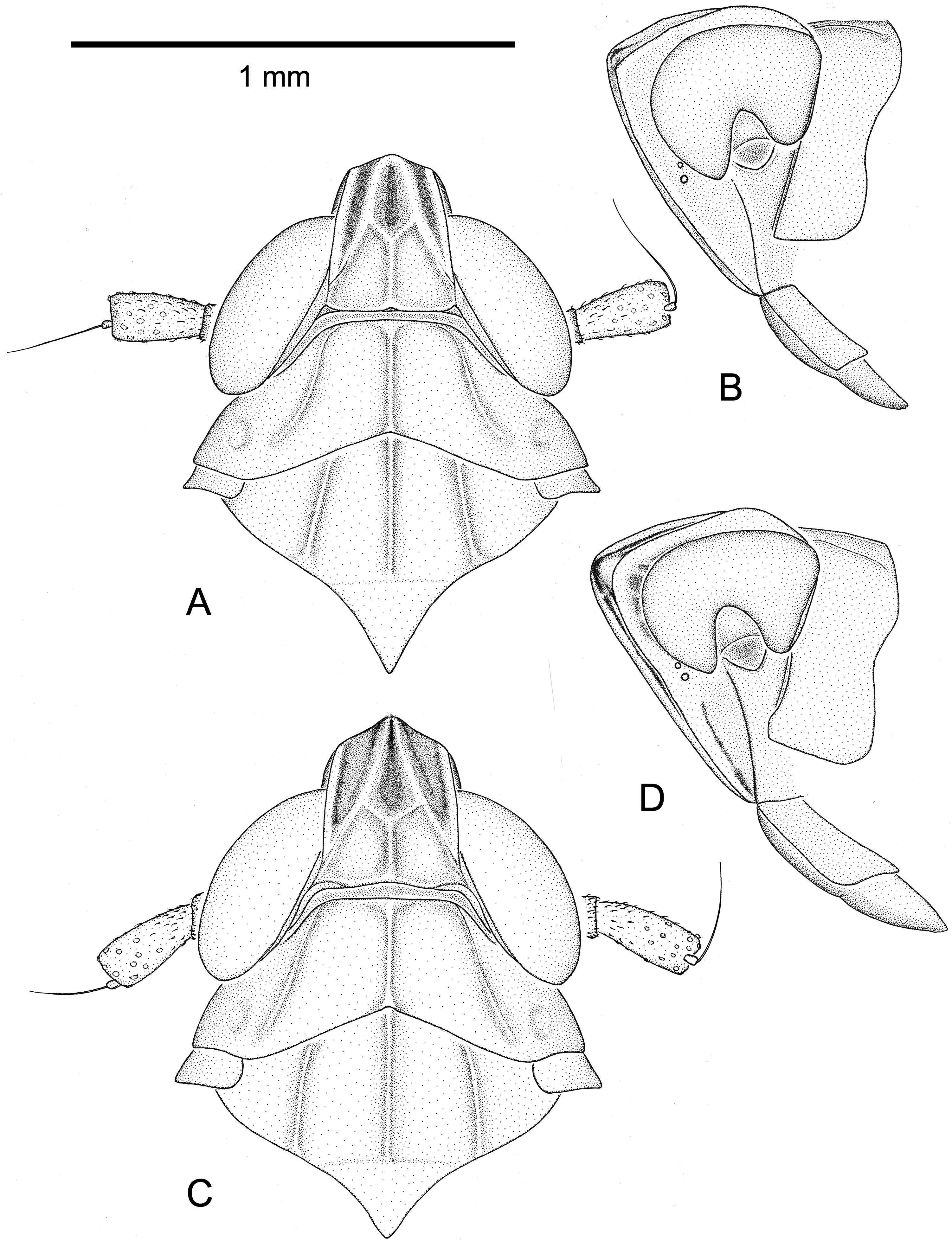
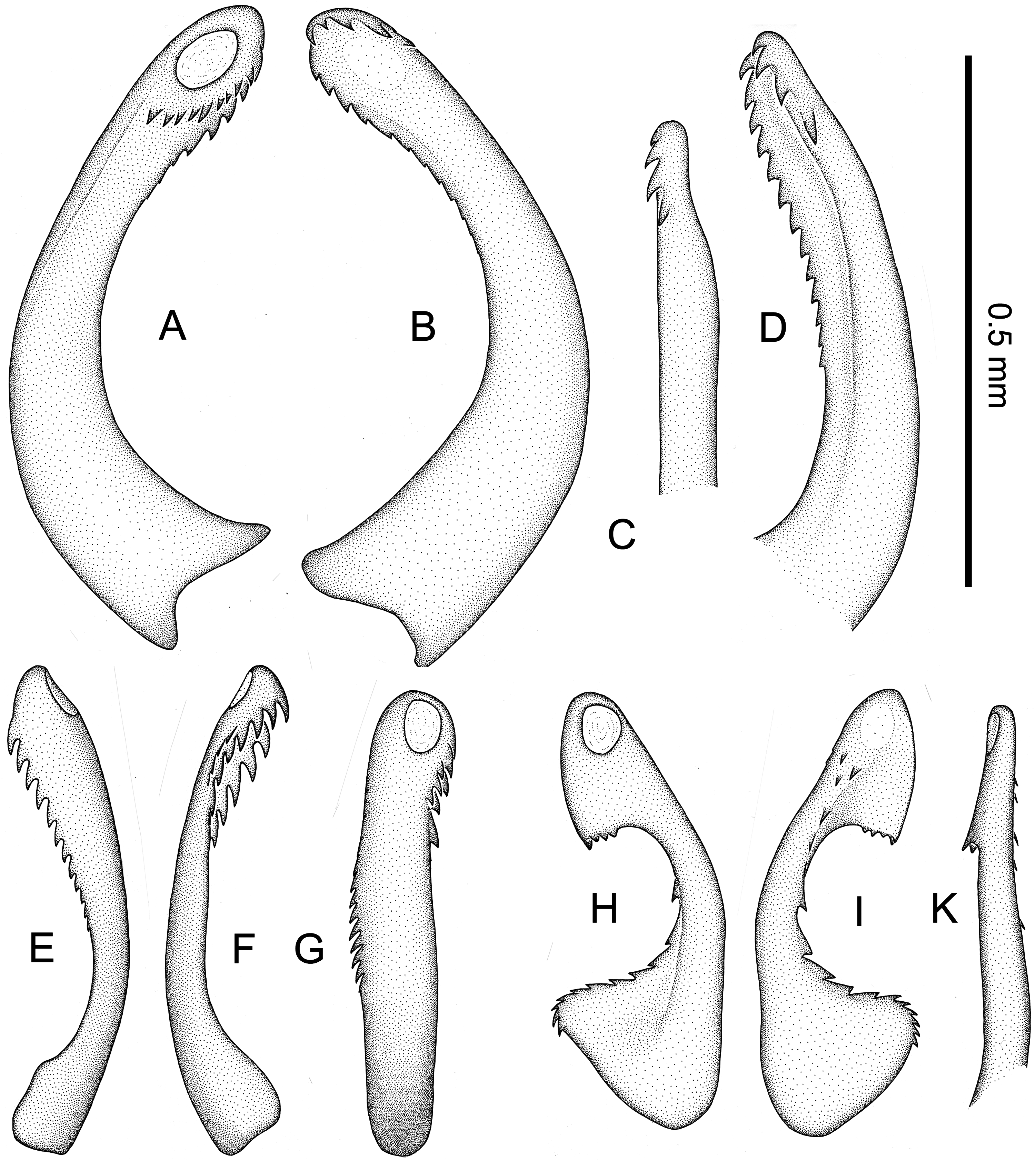
Male genitalia ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 ). Pygofer ( Figure 4B,F View Figure 4 ) very similar to that of C. flava . In lateral view with barely perceptible angle above inferior third of hind margin; in posterior view Y-shaped sclerotized thickening reduced to small sclerotized central part of hind margin of aedeagus opening and short median carina in ventral direction. Main difference from C. flava visible in the anal tube ( Figure 5B,G View Figure 5 ), which is distinctly larger and armoured with two long curved, ventrally directed processes. Styles ( Figure 6C View Figure 6 ) as in C. flava , their inner margin often more scabrous and darker. Suspensorium ( Figure 6F View Figure 6 ) as in C. flava . Aedeagus ( Figure 8A–D View Figure 8 ) similar to that of C. flava , somewhat longer and stouter, with phallotreme on its left side. Length of aedeagus, shape of apex and shape and number of teeth to some degree variable.
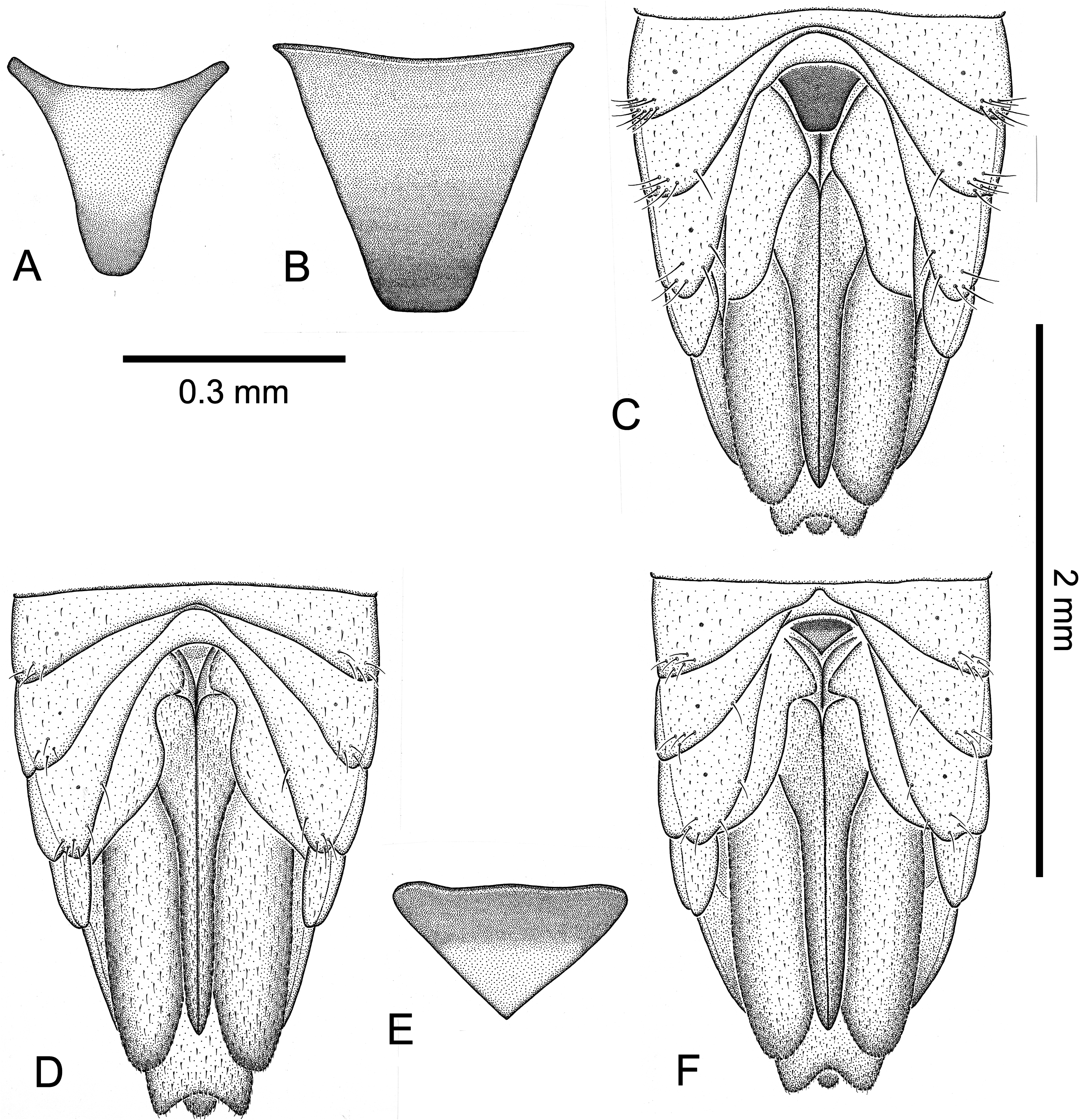
Female genitalia. Genital scale ( Figure 9B View Figure 9 ) distinctly larger than in C. flava , approximately triangular, with straight sides and truncated tip. Gonocoxae VIII ( Figure 9C View Figure 9 ) as in C. flava .
Fifth instar nymph (one specimen). In shape, colour, number and distribution of sensory pits very similar to fifth instar of C. sibillinica sp. nov. (see below).
Measurements
Males (brachypterous). Total length: 2.9–3.2 mm; width at level of wings: 1.22– 1.3 mm; width of head including eyes: 0.75–0.83 mm; length of vertex: 0.33–0.36 mm; width of vertex at base: 0.27–0.31 mm; length of pronotum: 0.24–0.25 mm; length of mesonotum from hind margin of pronotum to tip of scutellum: 0.42–0.55 mm; length of forewing: 1.16–1.36 mm; width of forewing: 0.74–0.8 mm; length of hind tibia: 0.82–0.9 mm; length of aedeagus: 0.63–0.71 mm.
Females (brachypterous). Total length: 3.6–3.9 mm; width at level of the wings: 1.42– 1.44 mm; width of head including eyes: 0.84–0.88 mm; length of vertex: 0.39–0.4 mm; width of vertex at base: 0.3–0.33 mm; length of pronotum: 0.26–0.27 mm; length of mesonotum from hind margin of pronotum to tip of scutellum: 0.51–0.55 mm; length of forewing: 1.34–1.46 mm; width of forewing: 0.84–0.89 mm; length of hind tibia: 0.92–0.95 mm.
Fifth instar nymph. Total length: 2.95 mm; width: 1.15 mm; width of head including eyes: 0.74 mm; length of vertex: 0.33 mm; width of vertex at base: 0.29 mm; length of pronotum: 0.25 mm; length of forewing pads: 0.8 mm; length of hindwing pads: 0.55 mm; length of hind tibia: 0.72 mm.
Type series
Holotype. Male: Italy, Emilia-Romagna (Modena); Monte Cimone, Sestola , 1 km north of Pian del Falco ; ∼ 1300 m; 3 June 2007; herbaceous vegetation on forest margin; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 375).
Paratypes. Same data as holotype; 14 males, 7 females . Same data as holotype; 27 June 2005 (loc. 183), 3 females . Same data as holotype; 3 September 2007 (loc. 404); 1 female . Liguria ( Genova ); M. Maggiorasca, Passo Tomarlo, road to Foresta Penna about 1 km south of fork from SP81; ∼ 1400 m; 9 June 2007; meadows between beechwood; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 383); one male . Emilia-Romagna (Piacenza); M. Lesima, road Cima della Colletta – Passo di Giove 900 m east of the pass; ∼ 1400 m; 10 June 2007; undergrowth of beechwood; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 387); 5 males, 3 females . Emilia-Romagna ( Parma ); M. Maggiorasca, SP 81 3.9km east (direction Bedonia) of Passo Tomarlo (11.4 km); ∼ 1200 m; 22 August 2008; dry meadow near beechwood; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 444); 2 females . Toscana ( Lucca ); Alpi Apuane , Terrinca , Monte Corchia, Passo di Croce; ∼ 1200 m; 16 August 2008; meadows near forest; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 433); 1 female . Abruzzo (L’Aquila); Monte Velino, Rocca di Mezzo , mountain ridge north of Piano di Pezza between Punta dell’Azocchio and Colle del Nibbio; ∼ 1850 m; 14 June 2007; mountain pasture; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 393); 2 males, 2 females . Marche ( Ascoli ); Monti Sibillini , between rifugio Monte Sibilla and Montemonaco, 4.3 km above (west of) fork to Isola di S. Biagio; ∼ 1400 m; 9 June 2008; dry meadows; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 425); 1 male . Marche (Ascoli); Monti Sibillini, Montemonaco, road to Foce near Rocca, 2.3 km from fork from road Montemonaco – Montegallo; ∼ 800 m; 9 June 2008; dry meadows; Guglielmino and Bückle leg. (loc. 426); 2 males.
The numbers in parentheses coincide with the locality number system used in our faunistic and zoogeographical papers.
Type material deposited in Dipartimento di Protezione delle Piante , Università della Tuscia, Viterbo, Italy (Guglielmino’s collection) ( CG) .
Geographical distribution
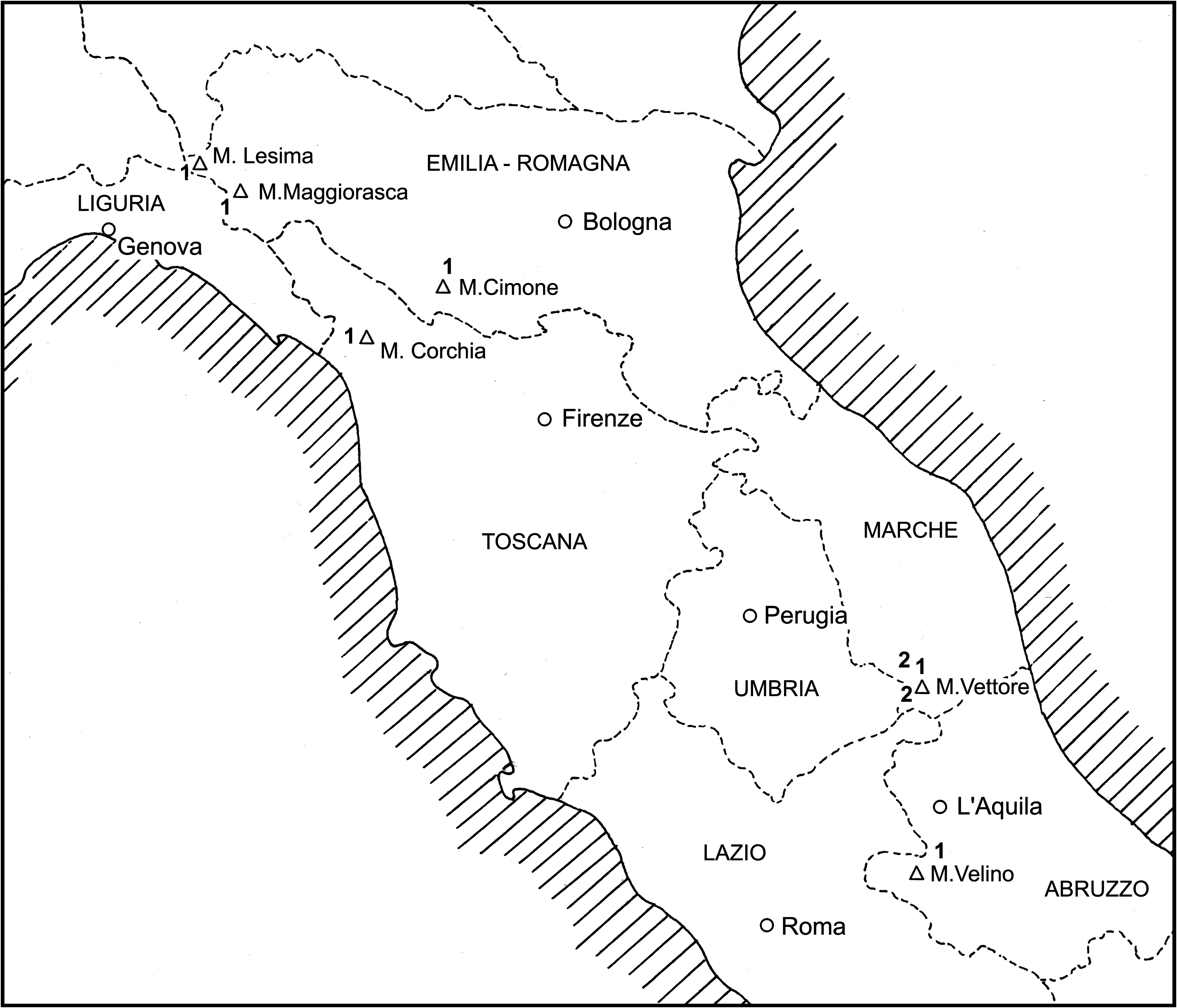
At present C. apenninica is known from Northern (M. Cimone, M. Maggiorasca, M. Lesima) and Central Apennines (Monti Sibillini, M. Velino-region) ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 : 1), at an altitude between 800–1850 m.
Biology
Adults were collected in June, four females also in August and September, respectively, in mountain meadows, on forest margins and in grass vegetation within beech forest. Chlorionidea apenninica feeds on species of the Sesleria albicans group such as S. nitida Ten. and S. autumnalis (Scop.) Schultz. Probably univoltine.
| CG |
Embrapa Collection of Fungi of Invertebrates |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.