Cloeodes itajara, Massariol, Fabiana Criste & Salles, Frederico Falcão, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.202897 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6191990 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6A17C33C-FFBC-FFB8-FF05-89C6B8E2FD2E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cloeodes itajara |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cloeodes itajara View in CoL , sp. nov.
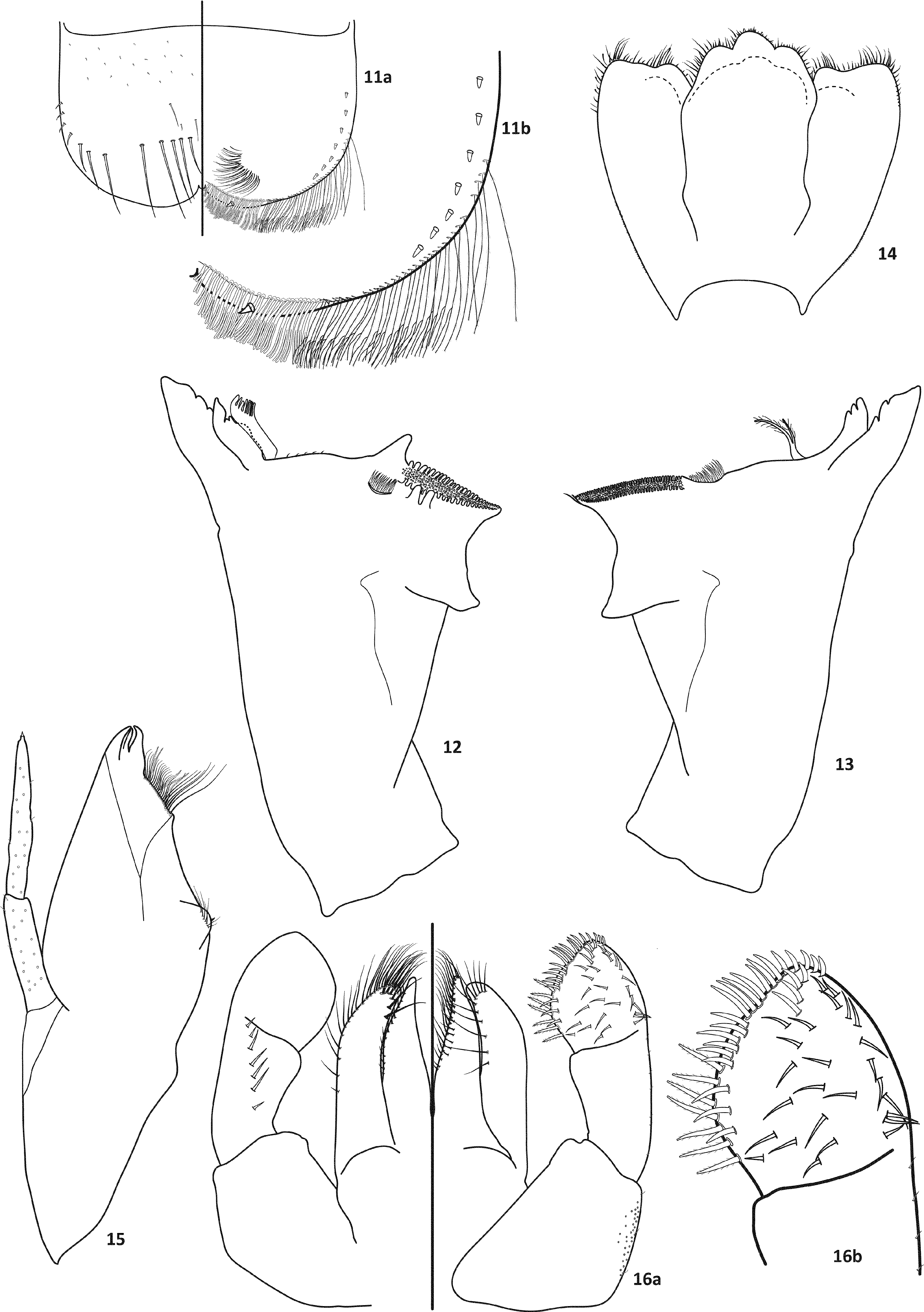
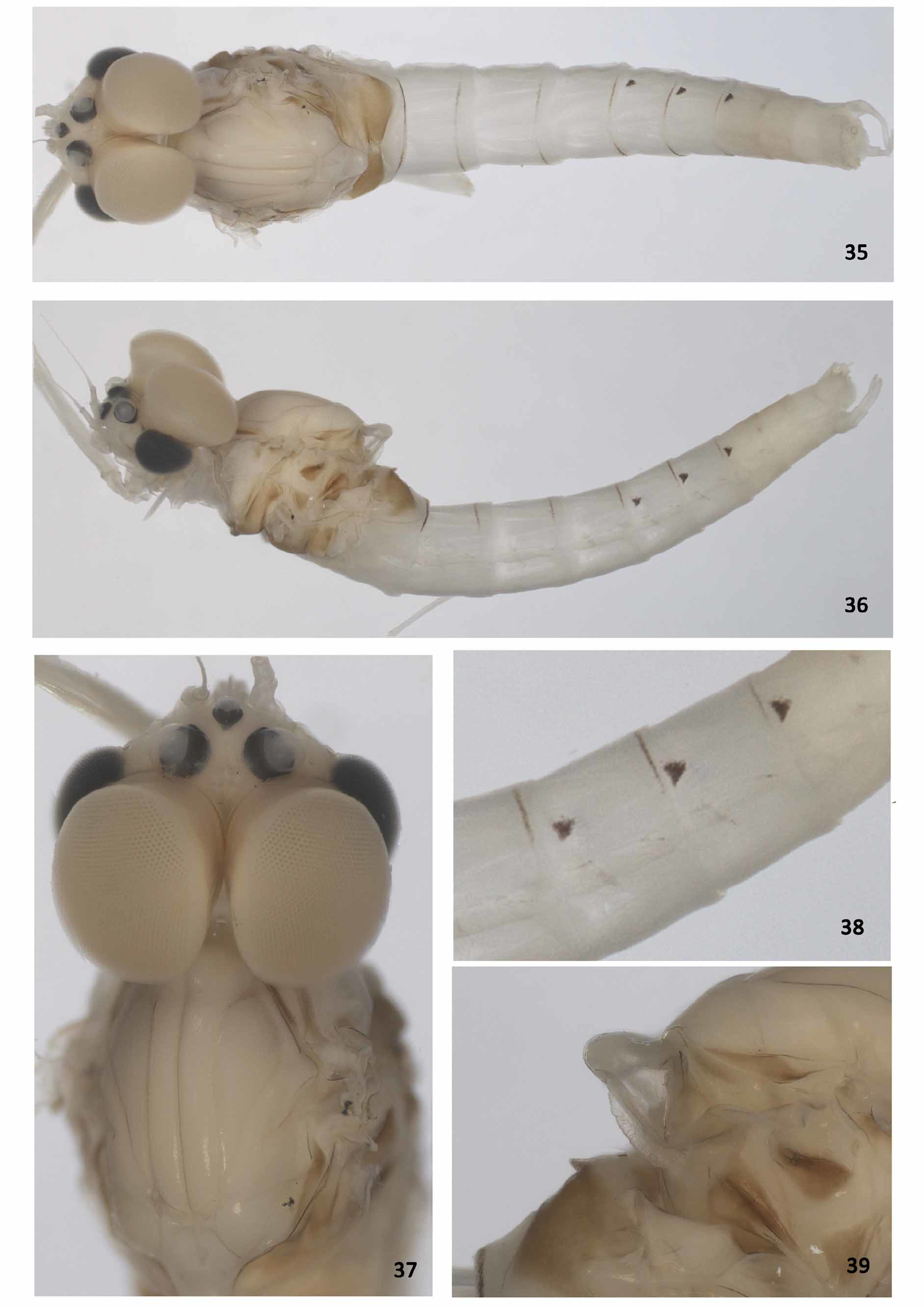
( Figs. 2 View FIGURES 2 − 3 , 4−6 View FIGURES 4 − 6 , 11−22 View FIGURES 11 − 16 View FIGURES 17 − 22 , 35−39 View FIGURES 35 − 39 , 46, 48 View FIGURES 46 − 49 , 50−52 View FIGURES 50 − 52 )
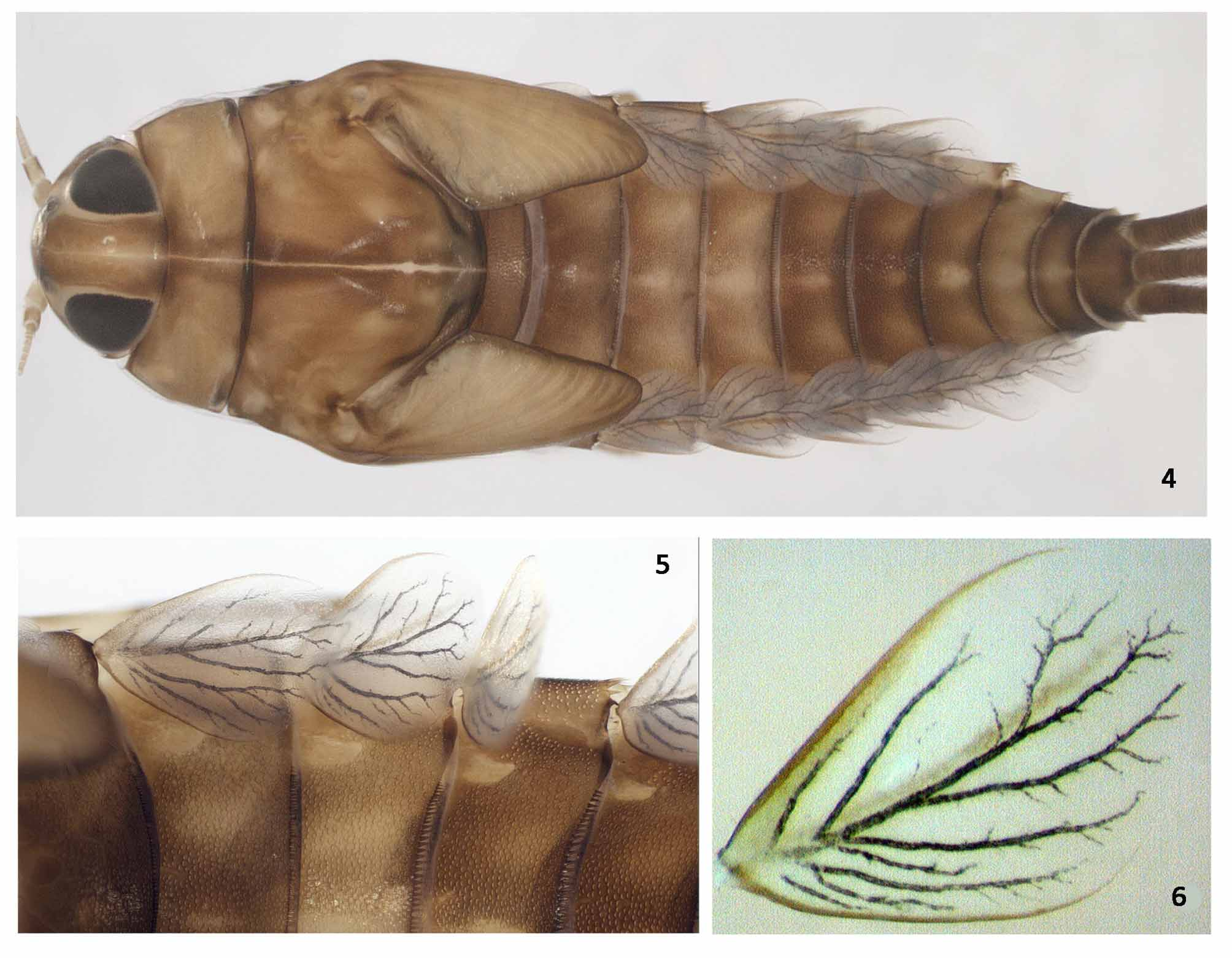
Diagnoses. Nymphs. 1) General coloration of abdominal terga yellowish brown washed with brown to dark brown with a lighter medial longitudinal stripe ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 − 6 ); 2) Labrum with dorsal arc of setae composed of 12 setae ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 − 16 a); 3) Segment III of labial palp obliquely truncate ( Figs. 16 View FIGURES 11 − 16 a, b); 4) Segment III of labial palp with robust and pectinate setae on inner margin ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 11 − 16 b); 5) Fore femur with apex projected, with 5−6 blunt setae ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 17 − 22 a); 6) Gill opaque; trachea dark greyish, inner and outer margins brown and with a light brown stripe parallel to main trunk ( Figs. 6 View FIGURES 4 − 6 , 21 View FIGURES 17 − 22 a); 7) Caudal filaments with posterior margin of segments with short spines on each segments. Adults. 1) Abdominal terga V −VII with a anterolateral triangular black mark ( Figs. 38 View FIGURES 35 − 39 , 52 View FIGURES 50 − 52 ); 2) Marginal intercalaries absent between Sc-R1 and CuP-A ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 46 − 49 a); 3) Hind wing present; costal process hooked, located on basal third ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 46 − 49 b); 4) Hind wing with 2 complete longitudinal veins and 1 incomplete ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 46 − 49 b); 5) Segment III of forceps elongated ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 46 − 49 ); 6) Posterior margin of subgenital plate rounded ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 46 − 49 ).
Description. Nymph
Length. Body: 7.5–9.0 mm; cerci: 3.0– 3.5 mm; terminal filament: 3.0– 3.5 mm; antenna: 2.3 mm.
Head ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 − 6 ). Coloration: light brown with light yellow narrow median longitudinal stripe on all length of vertex. Compound eyes and lateral ocellus surrounded yellowish. Frons with area between antennal sockets yellowish. Turbinate portion of male compound eyes reddish brown.
Antenna light brown; short, 1.3×the length of head capsule.
Labrum ( Figs. 11 View FIGURES 11 − 16 a, 11b). Rectangular, broader than long; length about 0.6× maximum width; dorsal surface flat; distal margin with medial emargination and small process. Dorsally with few short, fine, simple setae scattered over surface; dorsal arc of setae composed of 12 long spine-like setae, 5 restricted to medial group; lateral margin bare. Ventrally with submarginal row of setae decreasing in length toward medial region, composed of lateral setae pectinate; anterolateral setae bifid, pectinate; medial setae bifurcated at middle ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 − 16 b); ventral surface with 7 short, blunt setae near lateral and anterolateral margin.
Left mandible ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 − 16 ). Inner and outer set of incisors respectively with apparently 3 + 4 denticles. Prostheca robust, apically denticulate and with comb-shape structure at apex. Margin between prostheca and mola slightly convex, with spine-like setae on entire length; tuft of setae absent; tuft of spine-like setae at base of mola present; subtriangular process wide, above level of area between prostheca and mola; denticles of mola not constricted; tuft of setae at apex of mola absent. Lateral margins almost straight; bare. Basal half with few short, fine, simple setae scattered over dorsal surface.
Right mandible ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11 − 16 ). Inner and outer set of incisors respectively with apparently 3 + 3 denticles. Prostheca slender, bifurcated at middle, inner lobe long, outer short and both pectinate. Margin between prostheca and mola straight, without setae; tuft of setae absent; tuft of spine-like setae at base of mola present; tuft of setae at apex of mola present, reduced to a bifid setae. Lateral margins almost straight; bare. Basal half with few short, fine, simple setae scattered over dorsal surface.
Hypopharynx ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 11 − 16 ). Lingua subequal in length to superlingua; apex with anteromedial lobe rounded; with short, fine, simple setae; distal half not expanded. Superlingua not expanded; fine, simple setae scattered over lateral and distal margin; basal half of lateral margin with short, spine-like setae.
Maxilla ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 11 − 16 ). Crown of galea-lacinia with 4 denticles, inner denticle opposed to outer denticles; inner dorsal row of setae with 2 denti-setae, pectinate and bifurcated at base. Medial protuberance of galea with 1 short, spine-like setae + 7 long setae. Maxillary palp subequal in length of galea-lacinia; two segmented; setae on maxillary palp few short, fine and simple setae, micropore scattered over surface and one spine-like setae on the apex of segment II; palp segment II 1.4× length of segment I; apex of last segment constricted.
Labium ( Figs. 16 View FIGURES 11 − 16 a, 16b). Glossa basally broad, narrowing apically and subequal in length to paraglossa; inner margin with 20 long, spine-like setae increasing in length apically; outer margin with 12–13 long, spine-like setae increasing in length distally; ventral surface with one row of 8 simple setae near inner margin. Paraglossa sub-rectangular or straight, curved only at apex; apex with 2 rows of spine-like setae; outer margin with row of 13 long, spine-like setae; dorsally with a curved row of 6 long setae near inner margin; ventrally with a curved row of 12 spine-like setae near inner margin. Labial palp with segment I 0.8× length of segments II and III combined; segment I covered with few short, simple setae and micropore near to outer margin; segment II without distomedial protuberance; inner margin bare; outer margin with few, short, simple setae; dorsally with row of 7 spine-like, simple setae; segment III obliquely truncate; length 1.1× width; covered with robust, simple setae on distal margin, robust and pectinate setae on inner margin ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 11 − 16 b); long, spine-like setae scattered over ventral surface, but forming a row near outer margin.
Thorax ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 − 6 ). Yellowish brown with brownish marks. Fore wing pads yellowish brown.
Hind wing pads present.
Fore leg ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 17 − 22 ). Coxa brown. Trocanter light brown. Femur yellowish washed with brown, except at base and apex of anterior surface. Tibia light brown. Tarsus brown. Ratio of fore leg 1.3:0.8:0.8: 0.2 mm.
Fore femur. Length about 3.5× maximum width; dorsally with a row of 11 blunt setae (in lateral view they look like spine-like setae); length of setae about 0.1× maximum width of femur; apex projected; with 5–6 blunt setae ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 17 − 22 a); ventrally with row of short, spine-like setae restricted to posterior lobe; anterior surface with abundant micropore (restrict to anterior lobe), scale-bases and scales.
Tibia. Dorsally with a row of abundant, fine, simple setae; ventrally with row of 10 short, spine-like setae, with a lanceolate setae subapically; anterior surface with abundant scale-base and micropore; tibio-patelar suture present. Subtending bristle present ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 17 − 22 ).
Tarsus. Dorsally with abundant, long, simple setae; ventrally with a row of 15 spine-like setae and one long lanceolate setae near the apex; tarsal claw bare.
Mid and hind legs. Similar to fore leg, except for: hind femur dorsally with a row of 9 blunt setae (in lateral view look spine-like setae); subapical projections of femur less developed on mid leg and practically absent on hind leg ( Figs. 18 View FIGURES 17 − 22 a, b, c).
Abdomen ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 − 6 ). Yellowish brown washed with brown to dark brown with one lighter medial longitudinal stripe. Segments VIII and IX eventually lighter; segments II −VIII with yellowish smooth antero-sublateral area ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 4 − 6 ). Sterna yellowish.
Terga. S urface with abundant scale-bases and micropore; posterior margin with regular spines, 2.3× as long as wide ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 17 − 22 ); spines present in posterior margin of segments: II −X.
Sterna . Spines present in posterior margin of segments: V − IX.
Gill ( Figs. 6 View FIGURES 4 − 6 , 21 View FIGURES 17 − 22 a, b). Opaque; trachea dark greyish, inner and outer margins brown and with a light brown stripe parallel to main trunk. Margin with broad spines and short, fine, simple setae ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 17 − 22 b). Tracheae extending from main trunk to inner and outer margins. Gill I about 0.5 length of segment II; oval. Gill IV as long as length of segments V to half VI combined; oval. Gill VII about 1.5 length of segment VIII; oblong and obliquely truncate.
Paraproct ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 17 − 22 ). With 19–21 marginal spines; surface with abundant scale-bases and micropores; posterolateral extension with blunt marginal spines and scale-bases scattered on surface.
Caudal filaments. Brown with a yellowish band subdistally. Posterior margin of segments with short spines on each segment. Inner margin of cercus and inner and outer margin of terminal filament with tufts of long, flat setae.
Male imago
Length. Body: 7.0 mm; fore wing: 8.0 mm; hind wing: 1.2 mm; antenna: 1.2 mm; tibia I: 2.1 mm; tibia II: 1.6 mm; tibia III: 1.4 mm; caudal filament: broken.
Head ( Figs. 35−37 View FIGURES 35 − 39 , 50−52 View FIGURES 50 − 52 ). Coloration yellowish white. Antenna yellowish white.
Turbinate portion of compound eyes orangishdorsally (yellowish in alcohol), stalk yellowish brown. Dorsal portion of turbinate eyes oblong; length 1.8× width; stalk height 0.4× width of dorsal portion; inner margins parallel, close to eacher other.
Thorax ( Figs. 37, 39 View FIGURES 35 − 39 , 50−52 View FIGURES 50 − 52 ) Pronotum light brown (yellowish in alcohol) and mesonotum light brown (yellowish white in alcohol), except anterolateral scutal costa and area between posterior scutal protuberance whitish, metanotum brown.
Anteronotal protuberance rounded.
Metascutellar protuberance posteriorly pointed ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 35 − 39 ).
Legs. Whitish with orange band on apex of femur and black mark on apex of tibia and tarsomeres. (yellowish white in alcohol). Leg I: tibia 1.6× length of femur; tarsus 1.8× length of femur; and with 4 segments decreasing on length apically. Leg II: tibia 1.4× length of femur; tarsus 0.2× length of femur. Leg III: tibia 1.3× length of femur; tarsus 0.3× length of femur.
Fore wing ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 46 − 49 a). Hyaline, except between C and R1 opaque; longitudinal and cross veins light yellowish brown. Stigmatic area with 3 cross veins touching or almost touching subcostal vein and 2 veins not touching subcostal vein; marginal intercalary veins paired, except between veins R1-R2, ICu2-CuP single and between veins Sc-R1, CuP-A absent; length of each intercalary vein between IMA and IMA2 0.6× distance between adjacent longitudinal veins; length of fore wing about 2.6× width.
Hind wing present ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 46 − 49 b). Hyaline; veins light yellowish brown; with 2 complete longitudinal veins and 1 incomplete, not reaching apex of hind wing. Costal process hooked; located on basal third.
Abdomen ( Figs. 35, 36, 38 View FIGURES 35 − 39 , 50−52 View FIGURES 50 − 52 ). Terga. Segments I −VI white, VII −X orangish (yellowish white in alcohol); segments I −VI with a dark brown narrow line on posterior margin; segments V −VII with anterolateral triangular black mark ( Figs. 51, 52 View FIGURES 50 − 52 ); segments I −V with lateral orange band. Tracheation not pigmented. Sterna . Segments I −VI white, VII −X yellowish white.
Genitalia ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 46 − 49 ). Coloration yellowish white. Forceps segment I sub-rectangular; 0.3× length of segment II; distance between base of forceps 1.3× distance between lateral margins of forceps. Forceps segment II medially with constriction. Forceps segment III elongated, 2.0× as long as wide; 0.1× length of segment II. Posterior margin of subgenital plate rounded.
Female imago. Unknown.
Etymology. The specific epithet is a combination derived from the tupi-guarani ita (=stone) and jara (=lord), "Lord of the stones".
Distribution ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 2 − 3 ). Brazil - Espírito Santo (Ibitirama), Minas Gerais (Alto Caparaó, Espera Feliz).
Material examined. Holotype. Male imago with corresponding nymphal exuvia, Brazil, Espírito Santo, Parque Nacional do Caparaó, Ibitirama, Pedra Roxa River, 20/iv/2008, 20°23'48.1''S / 41°44'08.1''W, Salles, F.F., Massariol, F.C., Boldrini, R., Lima, M.M. and Britto, P.V.A. col. ( INPA). Paratypes. Ten nymphs, Brazil, Minas Gerais, Parque Nacional do Caparaó, Espera Feliz, São Domingos River, Sete Pilões Waterfall, 22/iv/2008, rock, low current, Salles, F.F., Massariol, F.C., Boldrini, R., Lima, M.M. and Britto, P.V.A. col. (six at CEUNES, two at DZRJ, two at IML).
Additional material. PT 02: (12N) 23/iv/2008, PT 03: (60N) 23/iv/2008, PT 03: (37N) 25/iii/2009, PT 04: (51N) 23/iii/2009, PT 08: (3N) 27/iii/2009, PT 09: (24N) 22/iv/2008, PT 11: (67N) 22/iv/2008, PT 11: (13N) 25/ iii/2009, PT 13: (32N) 21/iv/2008, PT 15: (12N) 20/iv/2008, PT 16: (19N) 20/iv/2008 (CEUNES).
Life cycle association. Rearing.
Biology. Most of the nymphs of the new species were found on rocky substrates, such as slab and stones, preferable in areas with low or no current, as in other species of the genus ( Salles & Lugo-Ortiz 2003; Salles et al. 2004b). They were also collected in leaf litter and marginal vegetation.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |