Bacharaboilus lii, Gu, Jun-Jie, Qiao, Ge-Xia & Ren, Dong, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.277797 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6187055 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CBF825-FF91-B144-FF5A-904AFB52724D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bacharaboilus lii |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bacharaboilus lii View in CoL sp.nov.
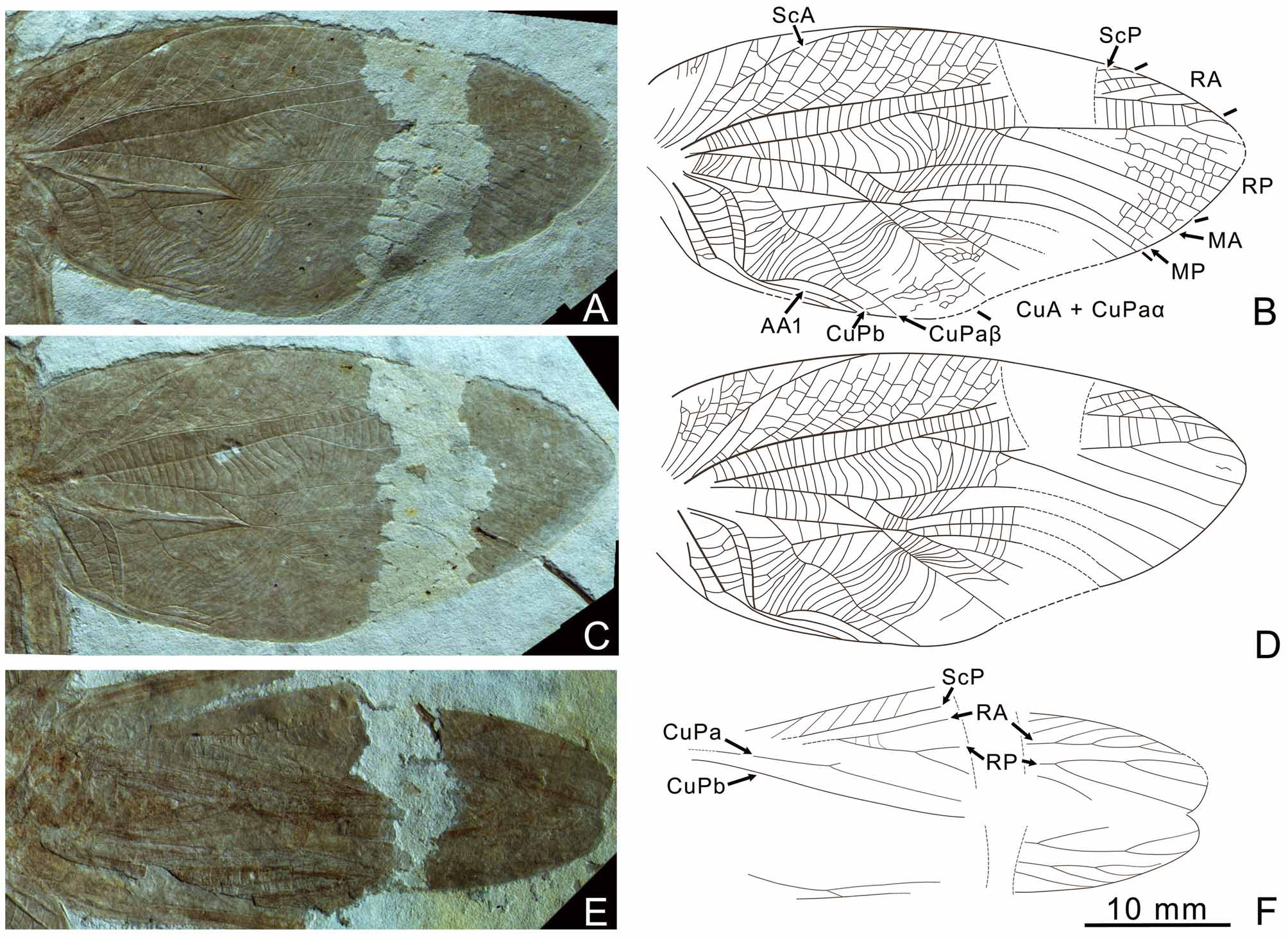
Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2
Diagnosis. RP branching earlier, basal of the first branch of RA; CuPaβ between ‘handle’ and posterior wing margin undulate; AA1 fusing with CuPb for a moderate distance; CuPb between handle and CuPaα short.
Etymology. The specific name is dedicated to Mr. Li Yuezhuo, Director of Sanya Palaeontological Museum, for providing this specimen for this study.
Holotype. CNU-ORT-NN2011001PC.
Horizon and locality. Jiulongshan Formation, Middle Jurassic; Daohugou Village, Ningcheng County, Chifeng City, Inner Mongolia, China.
Description. Head is hypognathous, about 5.2 mm wide; antennae inserted between the eyes, space between sockets of antennae about 2.3 mm; antennae typical of Ensifera, about 80 mm (much longer than the body), scapus cylindrical; mandibles stout, bearing strong molars and dentition, the dentition of the left and right mandibles is not very asymmetrical ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 , A). Forewing ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 , A–D: about 42 mm long, maximal width 20 mm; ScA slightly curved and reaching anterior wing margin close to mid-length of wing, at the level of the divergence of R; ScP basally bowed towards anterior margin, branches of ScP numerous, with a network of cells between them; R long and straight, simple for 18 mm, then forking into RA and RP close to the mid-length of wing, area between ScP and R broader than area between R and M + CuA in basal part; RA pectinate with 6 branches; RP branched earlier, basal of the first branch of RA, pectinate with 5 branches; areas between the branches of RP with regular reticulated cross-veins in most part; area between ScP and R broader than area between R and M + CuA in basal part, a series of straight cross-veins regularly arranged between RA and RP; M forks into MA and MP before the divergence of R, MP basally curved; area between base of RP and MA broad, with some gently curved cross-veins; free part of CuA straight, 4 mm, slightly longer than free part of M; CuA + CuPaα ramified at its origin, with 5 terminal branches reaching posterior wing margin; ‘handle’ straight, CuPaβ between its base and ‘handle’ straight, CuPaβ between ‘handle’ and posterior wing margin undulate; area between CuPaβ and last posterior branch of CuA + CuPaα apparently broad and filled with straight or curved cross-veins in most basal part, cross-veins near posterior margin formed into network; CuPb sharply curved and long, area between CuPb and CuPaβ narrower than area between CuPaβ and last posterior branch of CuA + CuPaα, filled with straight or gently curved cross-veins; stridulatory vein located on CuPb; AA1 similar to CuPb in shape and fused with CuPb for a moderate distance near wing margin, then running to posterior margin; 2 anal veins straight, cross-veins between AA1 and AA2 straight. Hind wing strongly overlapped and damaged; RA and RP have numerous branches ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E–F).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Aboilinae |
|
Genus |