Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4847.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1F8E3DED-6EA9-4D8A-8DA9-CD8C0CC9147F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4407473 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A32D87D4-1C58-5365-55DE-FC082006E166 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi |
| status |
|
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi View in CoL
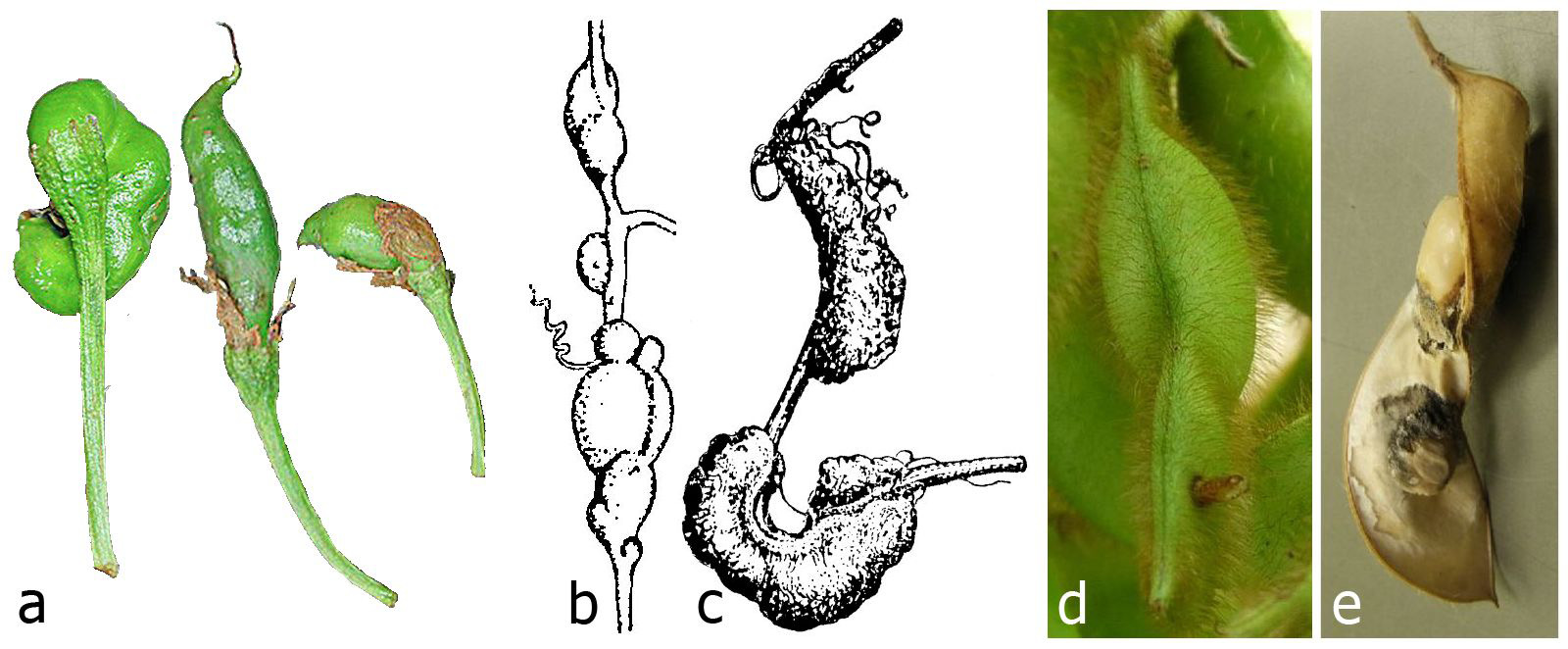
[ Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 d–e]
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi, 2003 in Yukawa et al. (2003a: 77) View in CoL , nomen nudum.
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi, 2003 in Yukawa et al. (2003b: 265) View in CoL .
Type series. Holotype male (slide Cecid. No. B 2461) from malformed pod of soybean, Glycine max (L.) Merrill ( Fabaceae ), collected at Kamifukumoto, Kagoshima City, Japan in mid x-1979, emerged 17-x-1979; paratypes: 35 males, 35 females, 14 larvae, 26 pupae, collected and reared from G. max (slides Cecid. Nos. B 2401–2413, B2417– 2436, B2451–2455, B2462–2479) and Prunus zippeliana Miquel (slides Cecid. Nos. C 0501–0514, C0521–0530, C0544–0565, C0571–0578) in Japan at various dates ( Yukawa et al. 2003a). Types are lodged in the Entomological Laboratory, Faculty of Agriculture , Kyushu University, Japan. We did not find it necessary to examine the types of this species.
DNA. Yukawa et al. (2003a) described the morphology and sequenced COI mitochondrial gene fragment from populations on G. max (GenBank accession numbers AB085776 View Materials – AB085787 View Materials , AB085856 View Materials – AB085859 View Materials , AB085863 View Materials – AB085866 View Materials , AB085868 View Materials , AB085870 View Materials , AB085871 View Materials , AB086429 View Materials ) and on P. zippeliana in Japan ( AB 085860 View Materials – AB085862 View Materials , AB085867 View Materials , AB085869 View Materials ). Uechi et al. (2005) sequenced COI from population on Osmanthus heterophyllus (G. Don) P. S. Green in Japan ( AB 194469 View Materials –AB194477). Uechi & Yukawa (2006) sequenced COI from population on G. max in Japan ( AB 197981 View Materials – AB197984 View Materials ). Uechi et al. (2018) sequenced COI from population on G. max in Japan ( LC 348697 View Materials – LC348701 View Materials ) and South Korea ( LC 348702 View Materials – LC348706 View Materials ). GenBank (accessed 15-xii-2019) currently contains 50 sequences of COI, 6 sequences of 12S ribosomal gene and 4 of other genes, with the intraspecific divergence in COI <1.59%.
Morphology. This species can be distinguished from its congeners with known larvae and pupae by the combination of the following characters ( Yukawa et al. 2003a). Larval sternal spatula with long shaft; four anterior lobes, pointed apically, outer lobes longer than inner lobes; adjacent three inner and two outer lateral papillae, all setose. Pupal antennal horn long, finely serrated on medial edge; anterior frontal horn simple, pointed; three posterior frontal horns forming a roughly equilateral triangle.
Biology. Asphondylia yushimai causes malformation of the pods of soybean, Glycine max (Fabaceae) [ Figs 4d, e View FIGURE 4 ], and fruit malformation on Prunus zippeliana (Rosaceae) and Osmanthus heterophyllus (Oleaceae) Uechi et al. (2018). This insect is one of the major pests of soybeans in Japan (see references in Yukawa et al. 2003a). It is one of several Asphondylia spp. with alternate hosts ( Uechi et al. 2004). In Japan, A. yushimai utilizes G. max as the summer host, and P. zippeliana and O. heterophyllus as the autumn-to-spring hosts ( Uechi et al. 2018).
Geographical distribution. Asphondylia yushimai was found feeding on Glycine max , Prunus zippeliana and Osmanthus heterophyllus in Japan, and on G. max in South Korea, China and Indonesia ( Nakayama 1982 [as Asphondylia sp.]; Yukawa et al. 2003a; Uechi et al. 2018). The extent of this insect’s distribution and the damage to soybean production in Indonesia have yet to be assessed.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi
| Kolesik, Peter & Gagné, Raymond J. 2020 |
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi, 2003 in Yukawa et al. (2003a: 77)
| Yukawa, J. & Uechi, N. & Horikiri, M. & Tuda, M. 2003: ) |
Asphondylia yushimai Yukawa & Uechi, 2003 in Yukawa et al. (2003b: 265)
| Yukawa, J. & Uechi, N. & Horikiri, M. & Tuda, M. 2003: ) |