Kronomyrmecolax fushunicus, Wang & Kathirithamby & Engel, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2015.1114166 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/FB2B87DC-FFCE-D72D-FE03-FDA23585FACF |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Kronomyrmecolax fushunicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Kronomyrmecolax fushunicus View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figures 1–2 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 )
Diagnosis
As for the genus ( vide supra).
Description
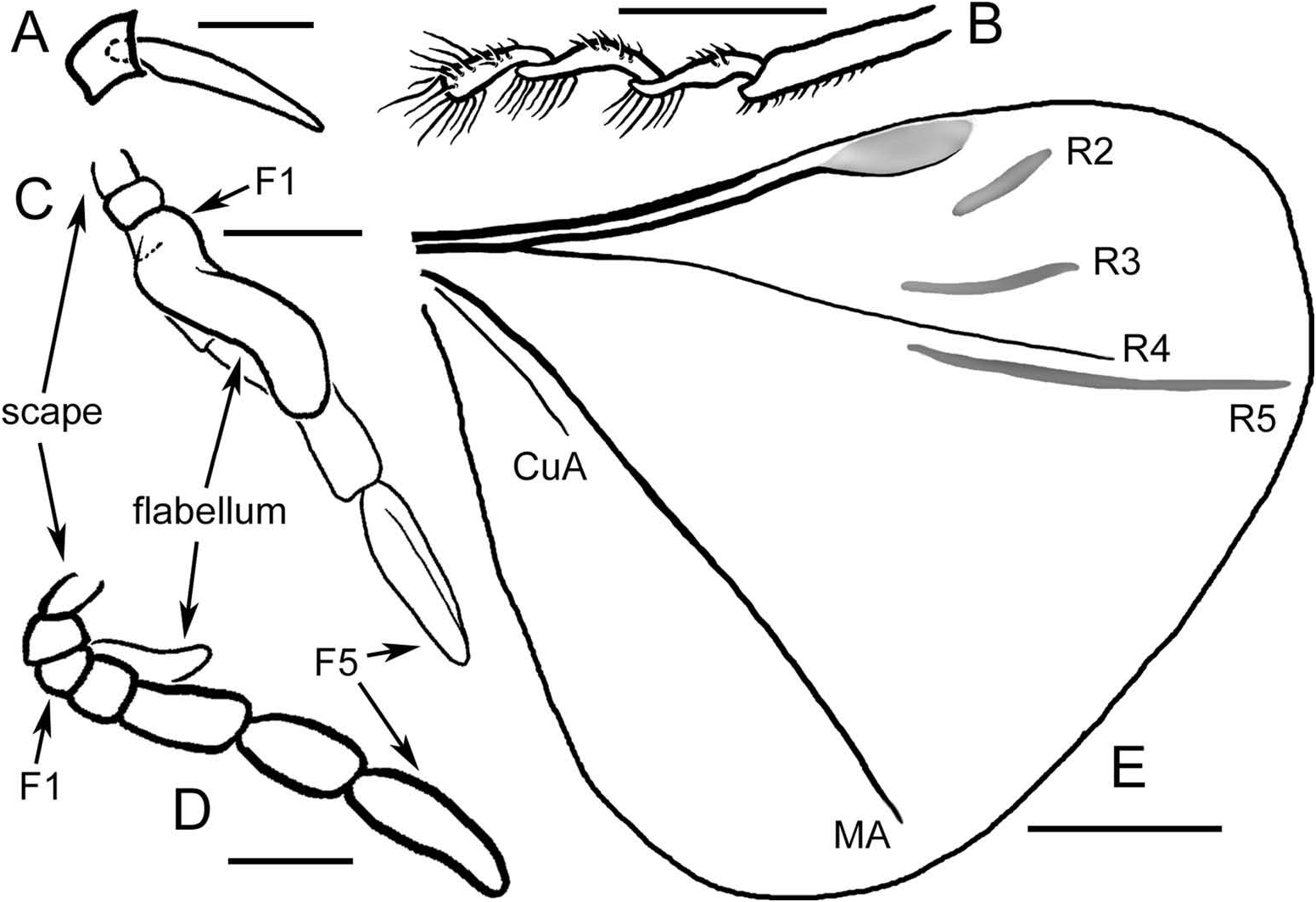
♂: Total length (as preserved) 1.1 mm; integument generally black (taphonomically darkened), except dark brown on antenna, maxilla and legs, and mandibles cleared; wings faintly infumate, with lightly pigmented veins except for C+Sc, R1, R4, MA and CuA1 more distinctly indicated and attached (remaining veins detached); integument generally with abundant, minute setae that are suberect to subappressed. Head broad, width across compound eyes 0.31 mm, medial length (in dorsal view) 0.13 mm; compound eyes large, bulging, circular, diameter 0.14 mm, with fewer than 50 ommatidia. Antenna length 0.51 mm (from base of scape to apex of flagellum; ca. 46% of hind wing length), with seven antennomeres (five flagellomeres), elongate flabellum present on flagellomere I, flabellum length 0.24 mm, flagellomeres I and II short, about as long as wide or slightly shorter; flagellomeres III and IV longer than wide, each with length of ca. 0.10 mm; flagellomere V longer than wide, length ca. 0.175 mm, apex narrowly rounded; antennomeres with abundant subappressed to suberect short setae. Mandibles thin, projected forward, simple, with an acutely pointed apex, length 0.14 mm, maximum width 0.017 mm. Maxillary palpus elongate, length 0.23 mm, with numerous, short, subappressed setae throughout length, intermingled with a few longer setae, particularly at apex; maxillary base with a series of moderately long setae along upper apical rim. Legs with abundant short setae throughout except stiff, erect, long setae present apically on coxae, ventrally on femora and ventrally on tibiae; basitarsus elongate, cylindrical, with distinct patch of setae ventroapically; remaining tarsomeres flat, broad, with scattered erect setae on dorsal surface and distinct patches of longer setae apically on ventral surfaces, apicalmost tarsomere (tarsomere IV) with dorsal setae longer, and patch of ventral setae extending to and along broad apical margin, apical margin bluntly rounded; pretarsus absent. Pseudohaltere broad, club-shaped, with pigmentation of vein running in anterior half to base of apical club, length 0.25 mm, apical width 0.10 mm, club portion more strongly pigmented; radial length of hind wing 1.10 mm, hind wing venation as in Figure 2E View Figure 2 . Thorax partly compressed laterally (rendering width measurements impossible), with abundant short setae; pronotum short, posterior border broadly concave, medial length 0.09 mm; metapostnotum elongate, length ca. 0.37 mm, projecting over base of abdomen. Length of abdomen (as preserved) 0.56 mm.
♀: Unknown.
Holotype
♂, NIGP 156972 View Materials ( Figure 1A–C View Figure 1 ); Fushun amber, Early Eocene (Ypresian), Guchengzi Formation , Fushun Coalfield , Fushun City , Liaoning, China; deposited in the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology , Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing, China.
Etymology
The specific epithet refers to the city of Fushun and whence the amber originates.
Key to genera of Myrmecolacidae
The following key is for adult males only.
1. Hind wing with R2 and R3 present, or with R2 bifurcated ............................................. 2 – Hind wing with only R2 present or without R2 and R3.................................................... 4
2(1). Length of antenna less than 50% of wing length [Eocene] ........................................... 3 – Length of antenna 75% or more of wing length [Miocene–present].............................. ....................................................................................................................... Myrmecolax Westwood
3(2). Antennomere VII 3 or more times length of antennomere VI; flabellum reaching to about half length of antennomere VII; CuP present [Baltic amber]................................. ................................................................................................................. Palaeomyrmecolax Kulicka
– Antennomere VII at most 1.8 times length of antennomere VI; flabellum not reaching to antennomere VII; CuP absent [Fushun amber]................................................. .............................................................................................................. Kronomyrmecolax gen. nov.
4(1). Aedeagus with shield-shaped plate with or without lateral spines [Eocene–present] ............................................................................................................................... Caenocholax Pierce – Aedeagus without lateral spines [Eocene–present]................ Stichotrema Hofeneder
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.