Adoncholaimus chinensis, Huang & Zhang, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222930902777945 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/DE6B075D-FFED-837D-3DFE-FD43FBF5E065 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Adoncholaimus chinensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Adoncholaimus chinensis sp. nov.
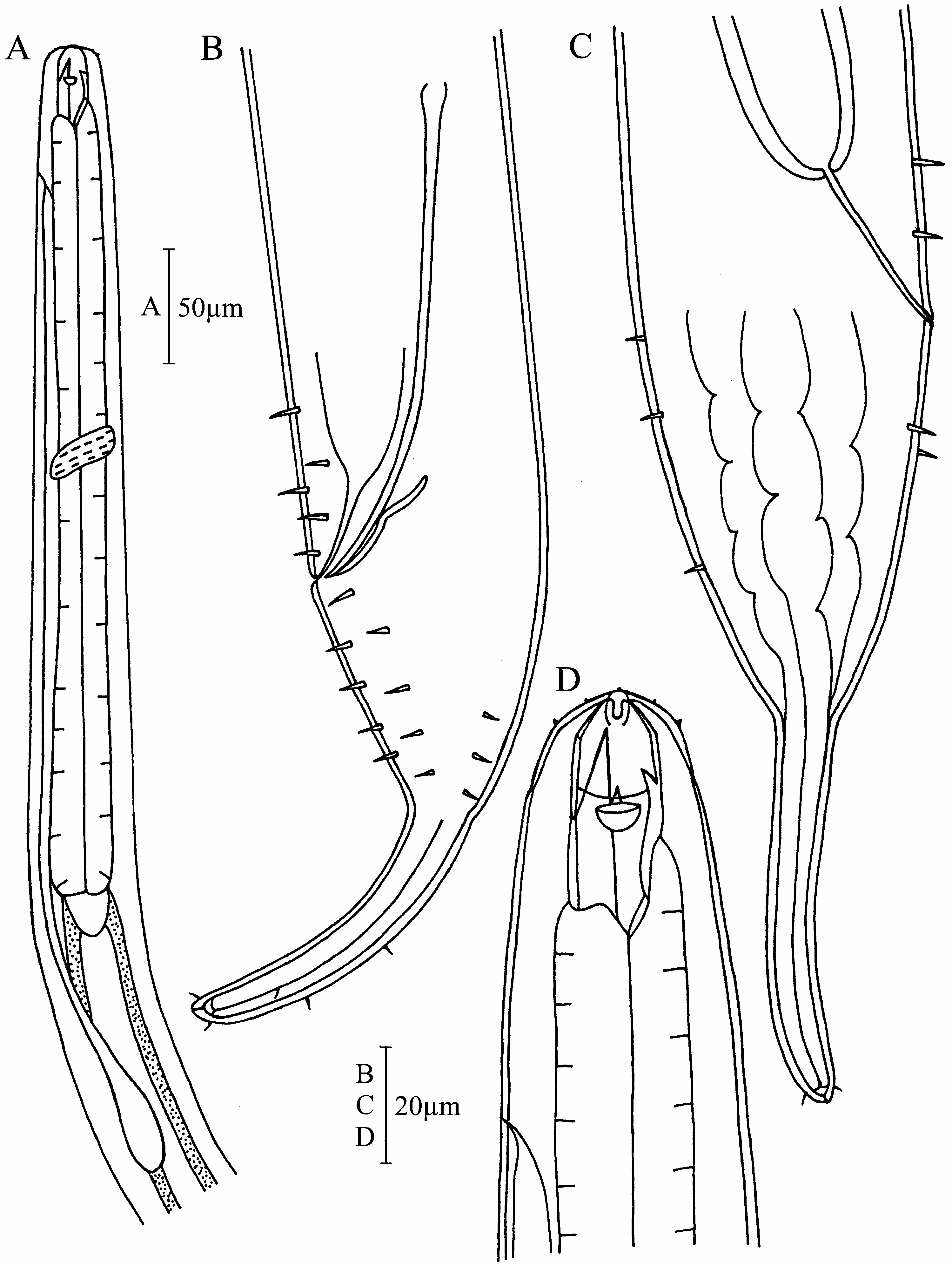
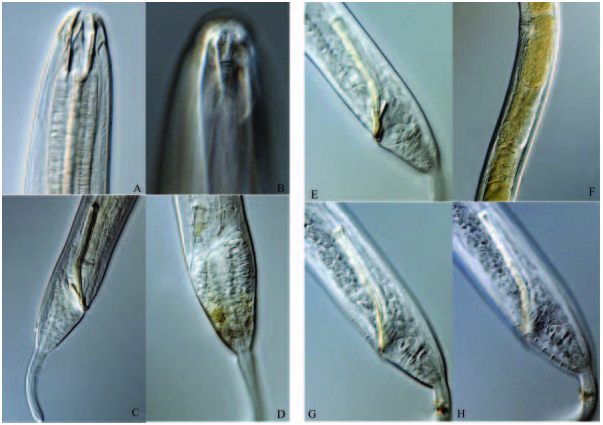
( Figures 1 View Figure 1 and 2 View Figure 2 )
Type material
Holotype: „ 1, Specimen number of new species: LUH001 View Materials (Slide number: LUL 08801); paratypes: „ 2, „ 3, „ 4, „ 5, ♀ 1, ♀ 2, ♀ 3 LUH002-008 View Materials ( LUL08802-004 , LUR 08901).
Type locality and habitat
Intertidal muddy-sand sediment in the Yellow Sea, from Lianyungang to Rizhao: 119 ° 30 9 E, 34 ° 42 9 N – 119 ° 34 9 E, 35 ° 26 9 N.
Etymology
This species is named with reference to the country of the type locality.
Measurements ( Table 1)
{455 W 2350
Holotype „ 1: 2460mm; a~43:9, b~5:4, c~22:4, Sc~93
25 55 56 39
{459 V 2684
Paratype ♀ 1: 2826mm; a~40:4, b~6:2, c~19:9, V %~46:5%
27 68 70 49
Description
Males. Body length 2540 mm (2412–2644 mm). Maximum diameter 60 mm (56– 61 mm). Six rounded lips with small rounded labial papillae. Ten small rounded cephalic papillae. Buccal cavity large with three teeth. Right subventral tooth larger than remaining two (32 mm vs. 26 mm), which are equal and prominent. Buccal cavity divided by a groove at the level of the tips of the smaller buccal teeth. Amphids pocket-like, 8.5 mm wide, situated at level of half buccal cavity length from the anterior end. Pharynx 0.18 times body length, swollen towards posterior end, but no definite bulb. Excretory pore about two times the buccal cavity length from the anterior. Nerve ring about 0.5 times pharynx length from anterior. A few short papillae setae over the body surface of the anterior pharyngeal region. A few longer setae on the tail. Tail 2.8 a.b.d. long, anterior half conical and posterior half cylindrical.
Spicules slender and curved, 97 mm (2.4 a.b.d., 95 mm as chord) long, with a proximal cephalated and a distal tip pointed. Two files of seven to eight circumcloacal setae (3–4 mm long) on each subventral side of body. Several short setae and three terminal setae on the tail. Gubernaculum slender curving parallel to spicules and with a slender apophysis free from the spicules.
Females. Body larger than the males. Body length 2825 mm (2817–2832 mm). Maximum diameter 68 mm (63–70 mm). Ovaries paired, opposed, reflexed. Demanian system is not observed. Vulva at 48% (47%–51%) of body length.
Differential diagnosis
Adoncholaimus chinensis sp. nov. is similar to Adoncholaimus fuscus Bastian differing in the following characters. Small body, length 2650 mm vs. 4300 mm; maximum
diameter 65 mm vs. 123 mm. Spicules short, 95 mm vs. 185 mm, without dorsal spines. Gubernaculum of this new species with a distinct apophysis.
Remarks
The genus Adoncholaimus was established by Filipjev (1918) with the type species Oncholaimus fuscus Bastian (1865) designated by Filipjev in 1918 ( Gerlach and Riemann 1974). This genus can be distinguished from the closest genus Viscosia by long slender spicules and a much more complex and well-developed demanian system in the female. But the demanian system of this new species is not observed. So far, 20 species have been described ( Platt and Warwick 1983; Gerlach and Riemann 1974; Electronic database: http://nemys.ugent.be) in the world. All of these species are closely related to each other and can be separated by the structure of the spicules, the presence or absence of gubernaculums and the structure of demanian system.
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.