Limosilactobacillus reuteri, SUBSP. REUTERI, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004644 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6310183 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CD6F3526-FFCB-2529-443B-FA90FD522566 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Limosilactobacillus reuteri |
| status |
subsp. nov. |
DESCRIPTION OF LIMOSILACTOBACILLUS REUTERI SUBSP. REUTERI SUBSP. NOV.
Limosilactobacillus reuteri subsp. reuteri (reu′ te.ri. N.L. gen. n. reuteri , of Reuter; named for G. Reuter, a German bacteriologist after whom the species L. reuteri was named).
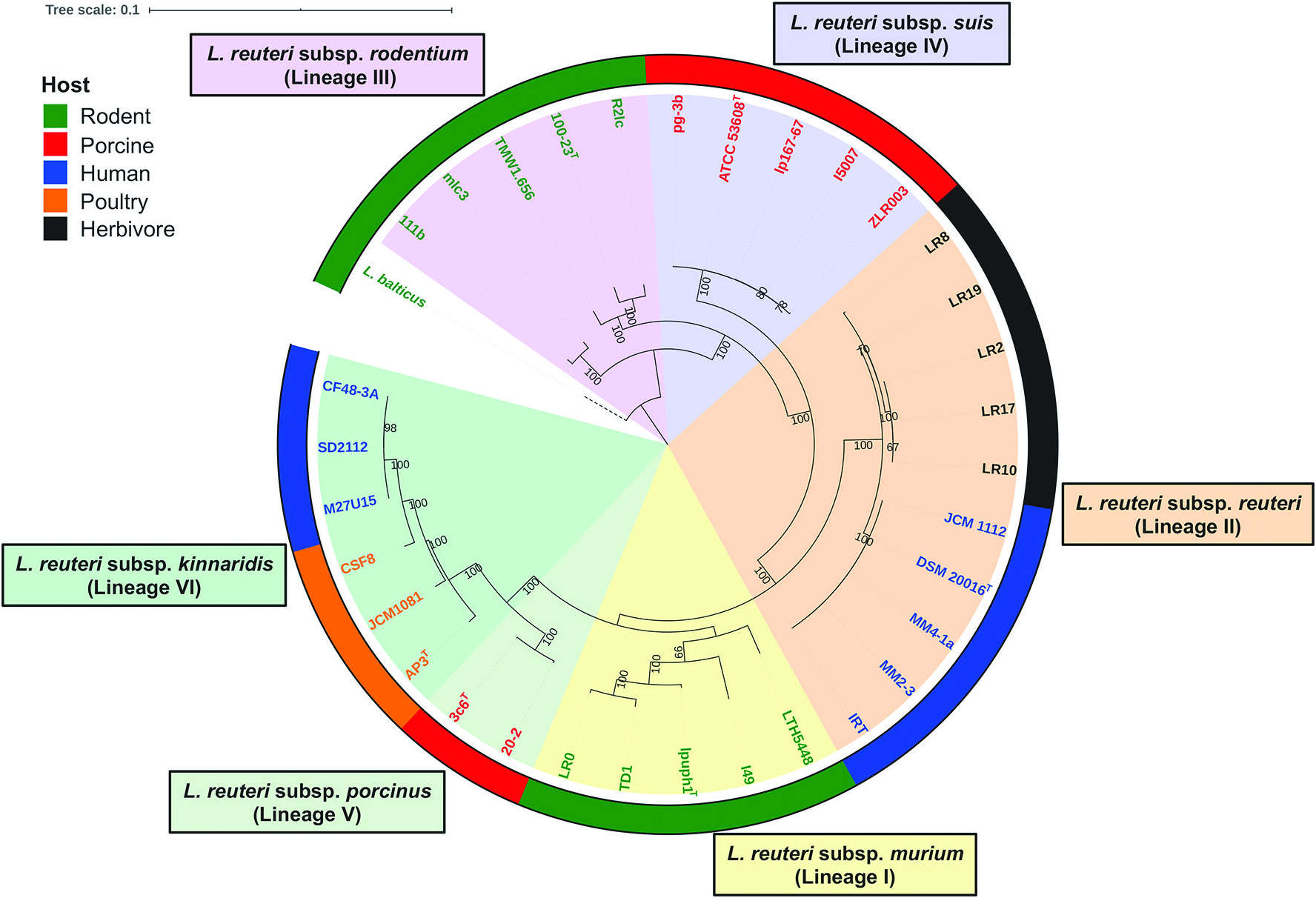
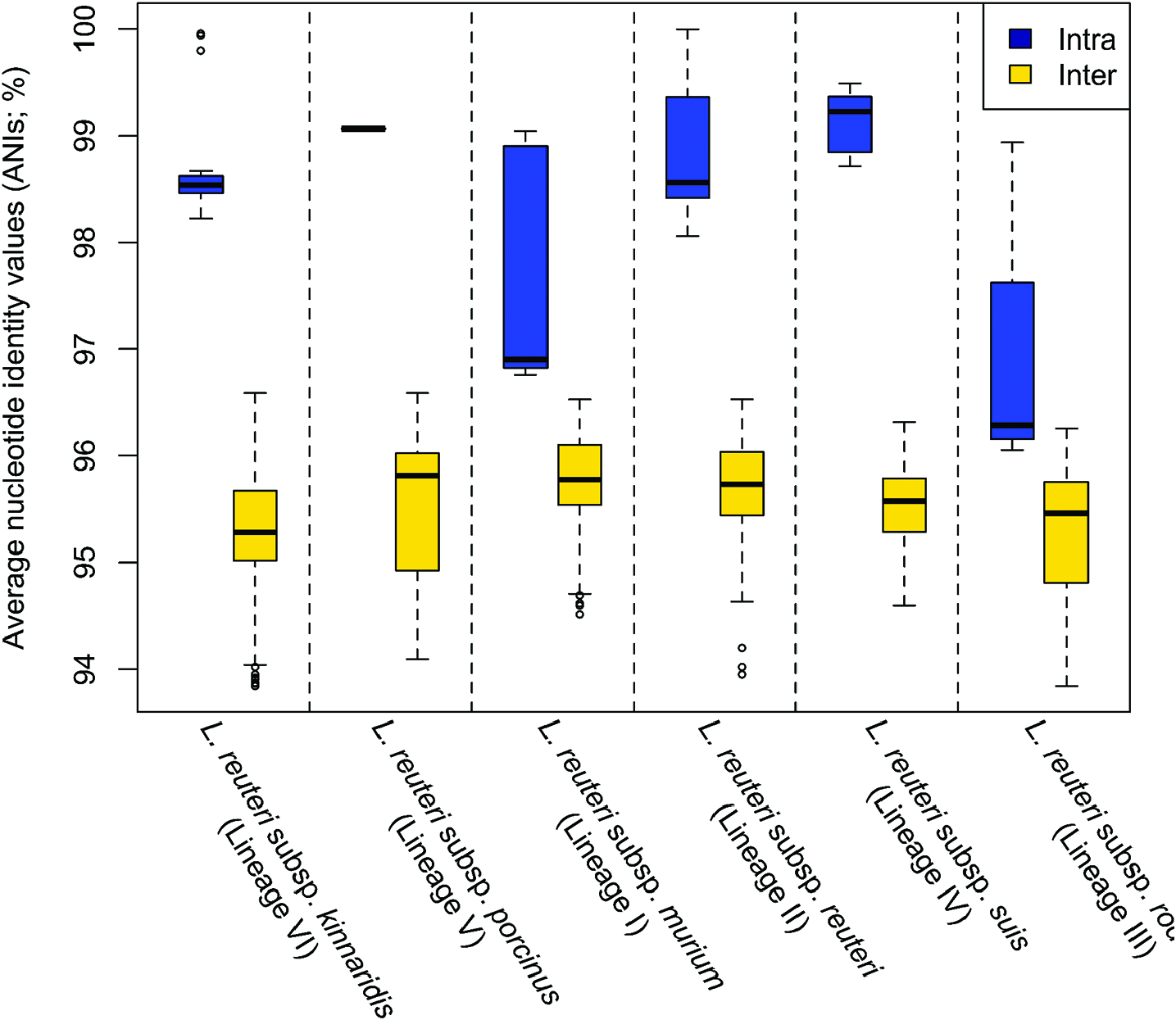
L. reuteri strains clustered in lineage II ( Fig. 3 View Fig ) belong to L. reuteri subsp. reuteri and they were isolated from humans and herbivores [ 7, 43]. Strains of this subspecies have ANI values of 98.1–100.0% with each other and ANI values of 94.0–96.5% with other L. reuteri strains belonging to different subspecies ( Fig. 4 View Fig ). Acid is produced from L-arabinose,D-ribose, D-galactose,D-glucose, maltose, lactose, melibiose, sucrose and raffinose; acid production from potassium gluconate is strain-specific; acid is not produced from D-xylose,D-fructose, D-mannose, methylα- D-glucopyranoside, aesculin, glycerol, erythritol, D-arabinose, L-xylose, D-adonitol, methyl β -Dxylopyranoside, L-sorbose, L-rhamnose, dulcitol, inositol, D-mannitol, D-sorbitol, methyl α- D-mannopyranoside, N -acetylglucosamine, amygdalin, arbutin, salicin, cellobiose, trehalose, inulin, melezitose, starch, glycogen, xylitol, gentiobiose, turanose, D-lyxose, D-tagatose, D-fucose, L-fucose, D-arabitol,L-arabitol, potassium 2-ketogluconate or potassium 5-ketogluconate. Phylogenetic analyses based on the core genes identified in this study ( Fig. 3 View Fig ) and previous studies [ 5, 43], AFLP and MLSA (using concatenated sequences of ddl, pkt, leuS, gyrB, dltA, rpoA and recA genes) [ 7], suggest that these strains are genetically homogeneous [ 8]. Strains of this subspecies possess the pdu-cbi-cob-hem cluster ( pdu cluster) [ 6, 8], which equips them with the ability to utilize 1,2-propanediol and glycerol as electron acceptors [ 16, 39, 40] and to produce the antimicrobial compound reuterin [ 8]. They also produce histamine from histidine that has been linked to their anti-inflammatory phenotype [ 34]. Strains belonging to this subspecies have been considered as immunosuppressive because they could suppress the proinflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor (TNF), monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, interleukin (IL)-1 β and IL-12, as well as suppress intestinal inflammation [ 34].
The type strain, DSM 20016 T (=ATCC 23272 T =F 275 T [original designation]), was isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of an adult human [ 6, 44, 45], with a DNA G+C content of 38.9mol%.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Limosilactobacillus reuteri
| Li, Fuyong, Cheng, Christopher C., Zheng, Jinshui, Liu, Junhong, Quevedo, Rodrigo Margain, Li, Junjie, Roos, Stefan, Gänzle, Michael G. & Walter, Jens 2021 |
L. reuteri
| SUBSP. REUTERI 2021 |
L. reuteri
| subsp. reuteri 2021 |
L. reuteri
| SUBSP. REUTERI 2021 |