Crocidura huangshanensis Yang, BW Zhang & Li, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11865/zs.202001 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F4A3BC83-CD57-4B9D-BA03-86FA3D868AE2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5104879 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C834AE56-FFDB-FFF0-FF77-0CAA8E80FBC4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Crocidura huangshanensis Yang, BW Zhang & Li |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Crocidura huangshanensis Yang, BW Zhang & Li , sp. nov.
Diagnosis. The new species has the size of the head and body easily distinguished from other known Crocidura species in the Southeast Asia region ( Table 7 View Table 7 ). It is smaller than C. hikmiya , C. sokolovi , C. cranbrooki , C. ninoyi , C. gathornei , C. absconditus, C. anhuiensis , C. tanakae , C. attenuata and C. fuliginosa , but larger than C. kegoensis , C. zaitsevi , C. annamitensis and C. guy . Additionally, the new species has the body size similar to C. sapaensis (HBL±SD 57.4±3.91, TL±SD 41.6± 2.48 in mean); and skull size similar to C. phanluongi (UTRL±SD 7.7±0.3, BH±SD 4.4± 0.19 in mean), C. varax (UTRL±SD 7.77±0.39, BB±SD 8.40±0.48, BH±SD 4.75± 0.22 in mean) and C. umbra (UTRL±SD 7.63±0.12, BB±SD 8.27± 0.19 in mean).
Description. A middle-sized Crocidura . Weight approximately 4.35–7.77 g; length of head and body approximately 50.45–61.97 mm; length of tail ranging 39.64–45.03 mm ( n = 5).
Head small, with a long elephant-like nose, long mustache back to the base of the ear, small eyes, round ears, and an obvious undercoat on ear shells; pelage slightly metallic, gray-brown, slightly darker in dorsal; limbs slender, composed of five toes on each hind foot; small, fleshy protuberances and palmate rings present on foot, with moderate color; dorsal side of palm and sole pink, semi-naked, and ankles with hairs sparse and brown; tail with length about 76% of head and similar color as pelage, nearly naked, with sparse and long bristle hairs ( Fig. 4 View Figure 4 ).
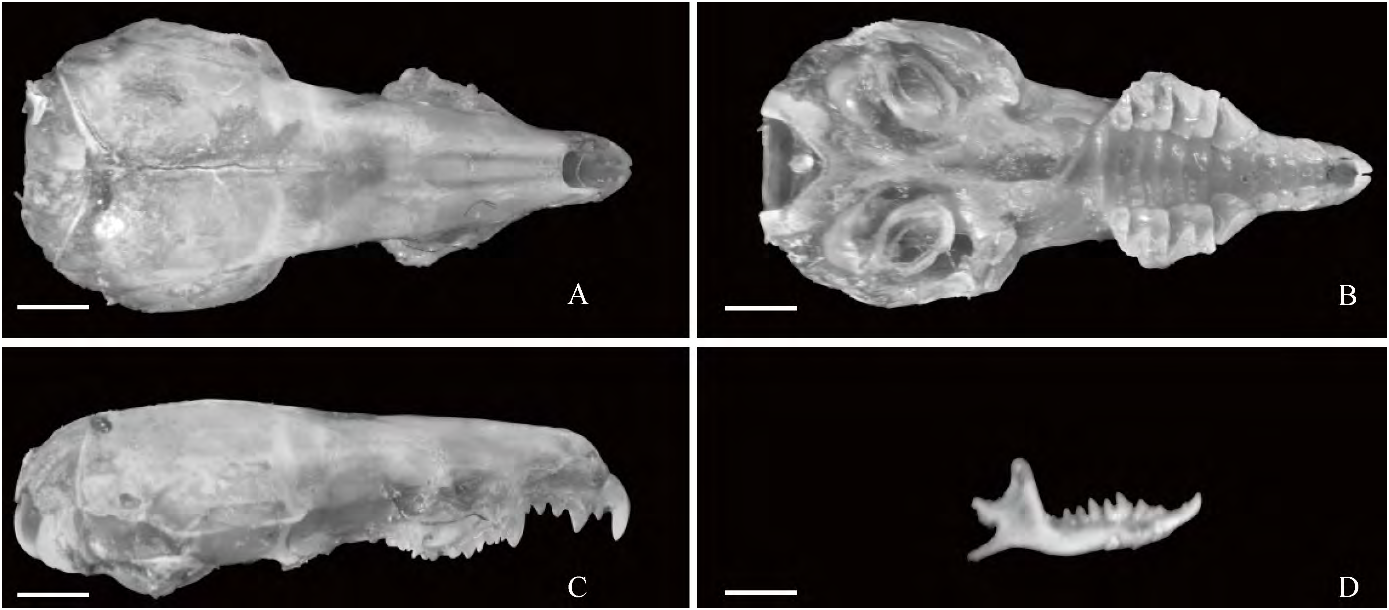
Skull long and flat, without zygomatic arch, and with distinct ridges. First incisor of maxillary strong and curved; second single cusps with similar size as third, with a large and triangular premolar and a front cusp. Molar cusp sharp. First incisor teeth of mandibular extended forward, end of mandibular slightly bended upward; tip of premolar and molar teeth sharper than other tips. Suture line between occipital ande parietal bones extended downward, at prominent position front of herringbone ( Fig. 5 View Figure 5 ).
Measurements of holotype (AhuHS10). WT 5.77; HL 23.49; HBL 61.97; TL 41.28; FFL 7.73; HFL 11.84; LAL 9.63; TBL 15.05; EH 8.03; GL 16.52; BL 14.82; BSL 13.9; CIL 17.24; PL 6.99; PAL 6.15; PPL 7.66; LR 6.55; BB 8.18; LIOB 4.08; PW1 5.48; PW2 2.37; BR1 1.91; BR2 5.52; BPM 1.25; HB 4.53; I-UN3 3.63; UTRL 7.83; ML 8.67; LDI 10.98; LDT1 4.71; LDT2 6.61; DD 4.47; MH 4.04.
Holotype. AhuHS10, female, ( Fig. 2 View Figure 2 ), coll. Liu Yang, 15 June 2017, Fuxi , Mt. Huang, Anhui Province, China ( 30.0828°N, 118.1506°E; elev. 616 m), dissected. The skin and skull tissues were preserved in dry, and the muscle tissues were kept in ethanol. GoogleMaps
Paratypes. AhuHS04 (male, 50.45 mm HBL), AhuHS05 (female, 59.29 mm HBL), AhuHS06 (female, 55.75 mm HBL), AhuHS07 (female, 55.27 mm HBL), May to July, 2017, other data same as holotype GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The specific name, huangshanensis , refers to its locality, Mt. Huang, Anhui Province, China.
Common names. We suggest “Huangshan white-toothed shrew” as the English common name of the species, and “ · ±+•× ” as the Chinese common name.
Distribution. Only found in the type locality.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.