Assamacris bidentata, Mao, Ben-Yong, Ren, Guo-Dong & Ou, Xiao-Hong, 2007
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.177303 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6250459 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9C5587AD-D30D-1A19-FF49-87A4608AFB78 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Assamacris bidentata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Assamacris bidentata sp. nov.
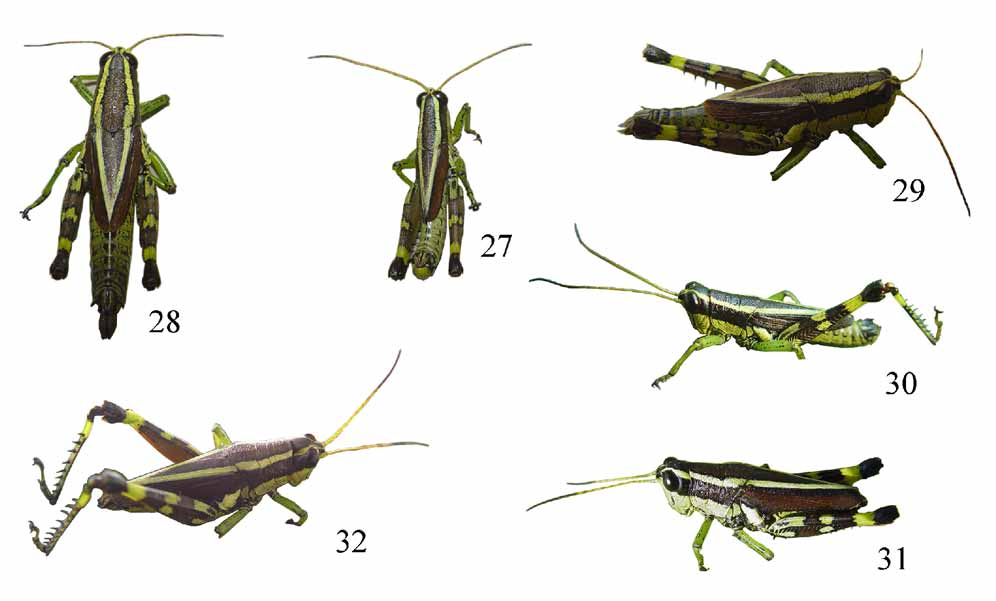
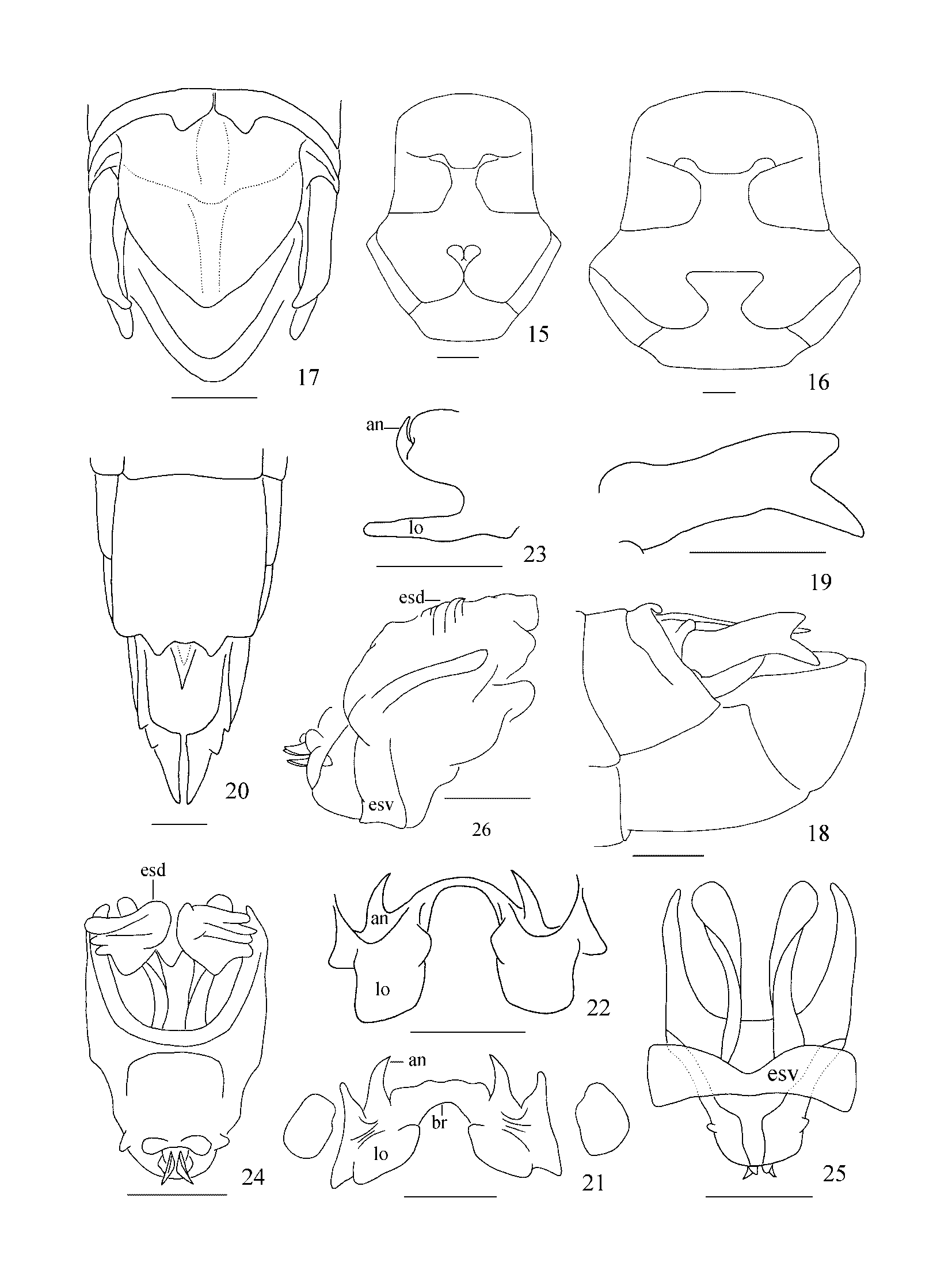
( Figs 15–26 View FIGURES 15 – 26 , 30–32 View FIGURES 27 – 32 )
Type material. Holotype: male, CHINA: Yunnan, Maguan, 22°49'N, 103º58'E, 1400m, 21 Jul. 2006, collected by Ben-yong Mao ( CLDU). Paratypes: 5 males, 6 females, same data as holotype but collected by Zizhong Yang ( CLDU), Ji-shan Xu ( CLDU), Yu-long Wang, Qi-qi Wu, Hao-yu Liu and Yu-xia Yang.
Diagnosis. The new species is closely related to A. trimaculata sp. nov. (as demonstrated by similar coloration pattern), but differs from the latter by longer tegmina that nearly reaching 8th–10th abdominal tergite or three-fifths of hind femur in male, 6th–10th tergite or seven-tenths of hind femur in female (figs 30–32); by narrower cerci of male; by posterior margin of subgenital plate with two obtuse teeth in female (fig. 20). The male of the new species also differs from A. spinipicta and A. trimaculata sp. nov. by details of the phallic complex.
Etymology. The name refers to the posterior margin of subgenital plate with two obtuse teeth in female.
Description. Head almost as long as prozona in male, slightly shorter than prozona in female. Fastigium prominent forwards and downwards. Vertex with an indistinct median longitudinal carina. Face foveolate, in profile remarkably oblique in male or weakly oblique in female; frontal ridge prominent between antennae with margins somewhat parallel and raised; subobsolete below transverse facial sulcus; width between antennae 0.7–1.0 (male) or 0.7–0.8 (female) times as wide as interocular distance; lateral facial carinae interrupted in middle by foveolae. Antennae narrow, reaching middle (male) or base (female) of hind femur, any middle segment 3.6–4.1 (male) or 3.3–3.8 (female) times longer than wide. Eyes long oval, longitudinal diameter 1.3–1.4 (male) or 1.1–1.3 (female) times as long as horizontal one, and 1.4–1.6 (male) or 1.2–1.4 (female) times as long as subocular furrow. Pronotum cylindrical; surface dotted and rugose; anterior margin broadly rounded, with a shallow emargination in middle; posterior margin roundly angular; median carina faint, distinctly intersected by three sulci; lateral carinae absent; prozona 1.3–1.5 (male) or 1.2–1.3 (female) times as long as metazona. Prosternal spine conical with apex subacute. Tegmina developmental, nearly reaching 8th– 10th abdominal tergite or three-fifths of hind femur in male, 6th–10th tergite or seven-tenths of hind femur in female (figs 30–32). Mesosternal lobes nearly as long as wide in both sexes; mesosternal interspace 1.6–1.8 (male) or 1.2–1.4 (female) times as long as minimum width; lateral lobes of metasterum contiguous in male, separate in female (figs 15–16). Hind femur 4.4–5.0 (male) or 4.7–5.1 (female) times longer than wide; upper carina weakly serrate, terminating in a short spine; lower knee lobes roundly angular. Hind tibia with 8–9 spines on both dorsal margins; inner spines longer than outer spines, outer apical spur absent. Hind tarsi with 1st and 2nd segments nearly as long as 3rd segment; arolium a little shorter than length of claw. Tympana opening oval.
Male genitalia. 10th abdominal tergite excised but contiguous in middle, with distinct small furculae (fig. 17). Supra-anal plate tongue-shaped with median area somewhat raised and shallowly furrowed from base to apex; with a weak, transverse, median fold; lateral margins somewhat raised with base constricted; posterior margin roundly rectangular (fig. 17). Cerci stout, reaching beyond apex of supra-anal plate; apex bilobate, ventral branch decurved, slightly narrower but strongly longer than dorsal one (figs 17–19). Subgenital plate short conical, apex obtuse. Epiphallus with quadrangular lophi projecting in a 90° angle from bridge, width as large as length; anchorae hooked, narrow, pointing entad and apicad (figs 21–23). Ectophallic membrane with extra sclerites: paired dorsal sclerites lying on phallus and a band-shaped ventral sclerite surrounding phallic complex ventrally and laterally (figs 24–26).
Female genitalia. Supra-anal plate almost triangular with lateral areas sloping; with a broad and shallow median longitudinal furrow, interrupted by a transverse fold in middle. Cerci conical; apex obtuse. Valves of ovipositor narrow, without teeth along margins; apices hooked. Posterior margin of subgenital plate sinuate with two obtuse teeth and a short angular flap in middle (fig. 20).
Coloration (figs 30–32). The following notes according to fresh specimens. Olivaceous brown. Vertex with two light greenish-yellow bands along lateral margins, contiguous between eyes, separating backwards to occiput, continuing as lateral bands on disc of pronotum and dorsal area of tegmina; vertex and occiput with a black band between light ones, continuing as olivaceous brown median band on pronotum and dorsal area of tegmina; postocular bands olivaceous brown (male) or brown (female), continuing along dorsal area of lateral lobes of pronotum and lateral areas of tegmina; all three brown bands black-marginated. Antennae with scape greenish yellow; apical six segments black; others yellowish brown. Fore and middle legs greenish yellow; femora with three series of dark spots. Hind femur olivaceous brown but lower side red, with three irregularly black-margined greenish yellow maculas (including ring-like one before knee) on outer and upper sides, basal one on upper side with a black spot in middle; knee black. Hind tibia greenish yellow, black at base, in middle third and at apex; spines black. Abdominal tergits yellowish green, with some irregular black spots; supra-anal plate with median longitudinal furrow black, lateral area and apical half black; cerci black. Color of dried specimens is similar to that of fresh ones.
Measurements (mm). Length of body: male 24.0–25.0, female 36.5–39.0; length of pronotum: male 6.1– 6.4, female 8.4–9.2; length of tegmen: male 13.0–14.5, female 18.0–20.0; length of hind femur: male 14.4– 15.0, female 18.2–20.0; length of antenna: male 16.0–18.0, female 17.4–20.0; length of eye: male 2.7–2.8, female 2.8–3.2; interocular distance: male 0.5–0.6, female 1.0–1.1.
Distribution. China: Yunnan (Maguan).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Catantopinae |
|
Genus |