Phytomastax pentaspinula Ge, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5068.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:38C16DF3-C0C4-4713-B045-87BD693CA11B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5707049 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/991C87FF-4607-4D4B-FF12-7FAA7C394FDA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Phytomastax pentaspinula Ge |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Phytomastax pentaspinula Ge View in CoL , sp. nov.
Material examined. Holotype: 1 ♂, paratypes: 2 ♂, 3 ♀. China, Jiangda (Tibet), 3903 m, (31°63’94’’N 98°43’67’’E), August 2020. Coll. Jun-Jie Ge, Ke-Yao Zhang & Kuo Sun; deposited in the Zoological and Botanical Museum, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China. ( ZBM).
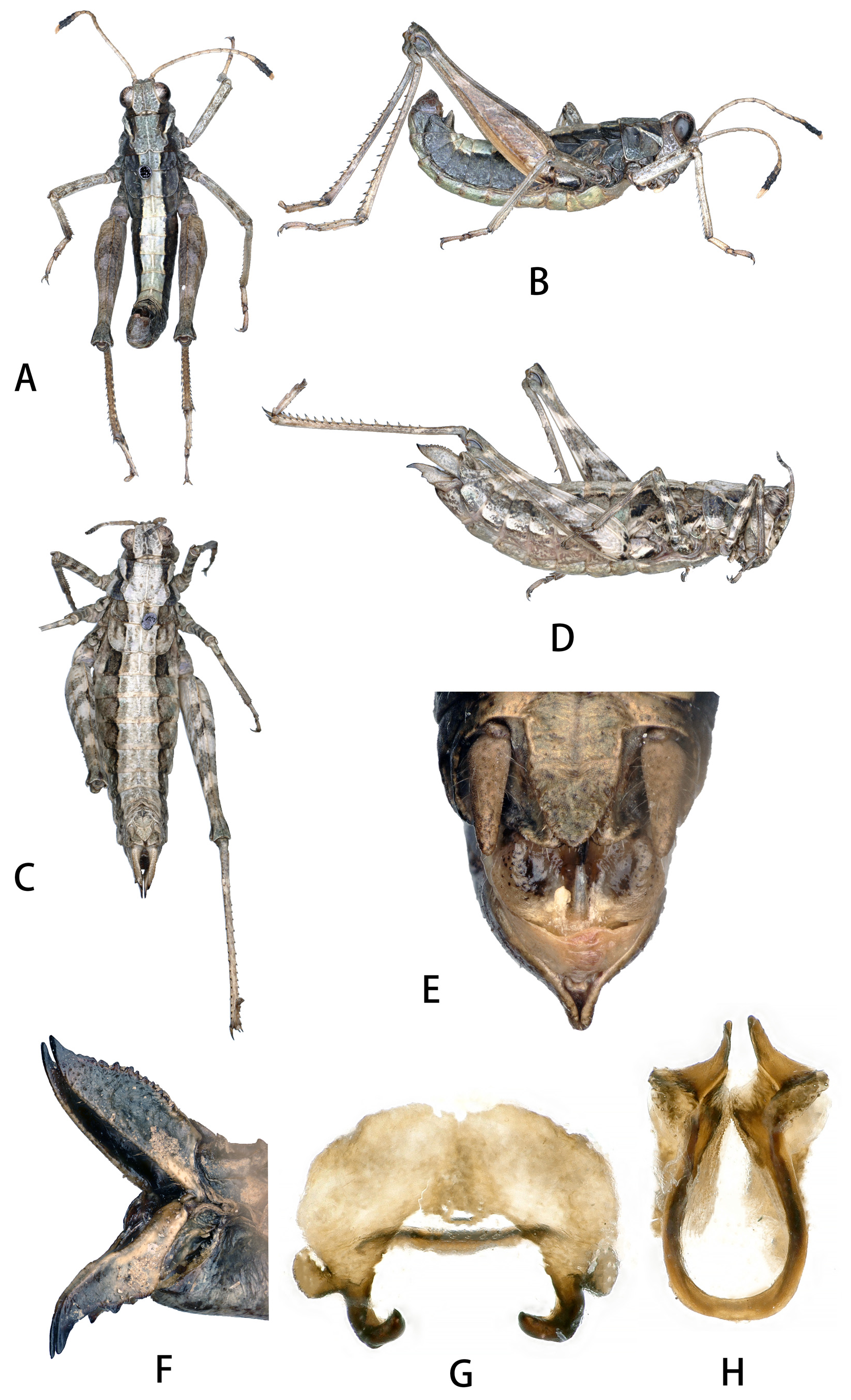
Description. Male ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Body size small, head distinctly higher than pronotum, shorter than the length of pronotum; vertex slightly prominent between the eyes, median keel distinct, anterior margin and lateral margin of vertex with distinct keels; face oblique in profile, forming a round fastigium; frontal ridge sulcate and widened margins between antennae, constricted above the lateral ocellus and below the median ocellus, prominent between antennae basal in profile; antennae clavate, with 21 segments and apical six segments distinctly wider, distinctly longer than front femur; eyes oval, longitudinal diameter is 1.4 times than the horizontal diameter and 1.3 times than the length of subocular furrow; pronotum flattened, with distinct median and lateral keels, lateral keels irregularly curved, its anterior margin incised mesally forming a triangular structure, its apex being in continuity with the median keel, mesosternal interspace almost 3 times wider than long; metasternum lobes adjacent; wings, sound producing organ and tympanum absent; hind femur 5 times longer than its width, upper median keel smooth with one apical spine; lower and upper lobes of hind knee above with short spines; hind tibia with 17 spines on outer and inner sides, external apical spine present, inner spurs length different, upper spur length 1.67 times longer than lower spur, first segment of hind tarsus above with 3 inner and 4 outer teeth; arolium tiny; tergum with distinct median and lateral keels; tympanal organ absent; epiproct small triangle, cerci long conical, slightly longer than epiproct, subgenital plate short conical ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ); epiphallus bridged, lophi slender and hook-like, lateral plate wide and short, with small flaky structure on lateral side ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ); phallic structure simple, forming a U-shaped, dorsal with two flaky structures, apical valves of penis hook-like ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ).
Female. Similar to male but larger and more robust; tergum lateral keels distinct; cerci long conical with acute apex; outer side of dorsal valves with serrate teeth, apex acute; outer side of ventral valves with big teeth, apex hooklike; the middle of posterior margin of subgenital plate with conical prominent, acute apex ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ).
Coloration. Body dark-brown; apical second to sixth segments of antennae black-brown, apical first segment antennae yellow; sternum and tergum yellowish; a yellowish-brown band running along the dorsal surface of the mesothorax and continuing to the eighth abdominal segment; anterior, median and hind femurs with gray and darkbrownish stripe; epiproct and cerci yellowish.
Habitat. Alpine brushwood.
Measurements. Body length: ♂ 13.8-14.3 mm, ♀ 17.3-17.8 mm; pronotum length: ♂ 1.6-1.8 mm, ♀ 1.9-2.0 mm; hind femur: ♂ 8.5-8.8 mm, ♀ 9.4-10.1 mm.
Diagnosis. Antennae 21 segments. Hind femur with 5 spines. Epiphallus bridged, lophi slender and hook-like, lateral plate wide and short, with small flaky structure on lateral side; phallic structure simple, forming a U-shaped, dorsal with two flaky structures, apical valves of penis hook-like. The new species Phytomastax pentaspinula sp. nov. is similar to Phytomastax tianshanensis Zheng et Xi, 1994 China, Xinjiang, Tekes. Some of the characteristic differences are shown in Table 2 View TABLE 2 .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Eumastacoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Gomphomastacinae |
|
Genus |