Mucroseius insolitus, Khaustov & Lindquist, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2019.1606954 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3680504 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/802987B8-FF96-FF94-77BB-FE66FBD2F9DD |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Mucroseius insolitus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mucroseius insolitus sp. nov.
( Figures 1 – 5 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 )
Type material
Holotype female (slide No 24 – 07 – 2017 /1)ı Russiaı Altai Republicı Mayminsky Districtı vicinity of Manzherokı 51°49 ʹ Nı 85°48 ʹ Eı from the metathoracic spiracular atria of the Black pine sawyer beetleı Monochamus galloprovincialis (Olivierı 1795) ı collected from the surface of felled Scots pine ( Pinus sylvestris )ı 24 July 2017ı V. A. Trach coll. Paratypes: three femalesı with same date as holotype; two femalesı Russiaı Tyumen Provinceı Nizhnetavdinsky Regionı vicinity of lake Kuchakı 57°21 ʹ Nı 66°03 ʹ Eı from the metathoracic spiracular atria of the Black pine sawyer beetle collected from trunk of living of Scots pineı 31 July 2018ı V. A. Khaustov coll.; one femaleı Austriaı Tirolı under elytra of the Small white-marmorated longhorned beetleı Monochamus sutor (Linnaeusı 1758) ı Kraatz coll.
Type deposition
Holotype at ZMUO ; paratypes at ONUDZı TUMZı and CNCI.
Diagnosis
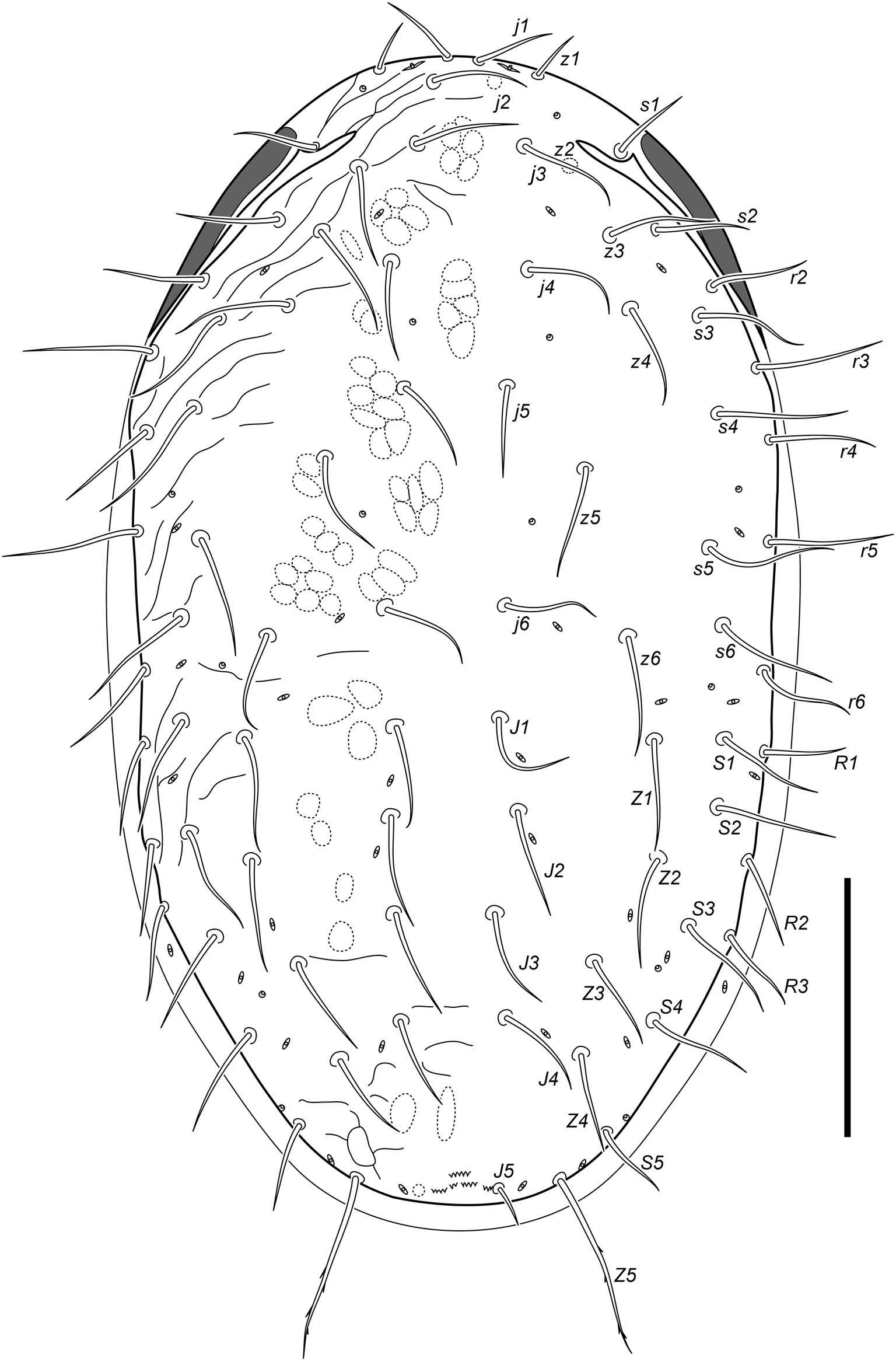
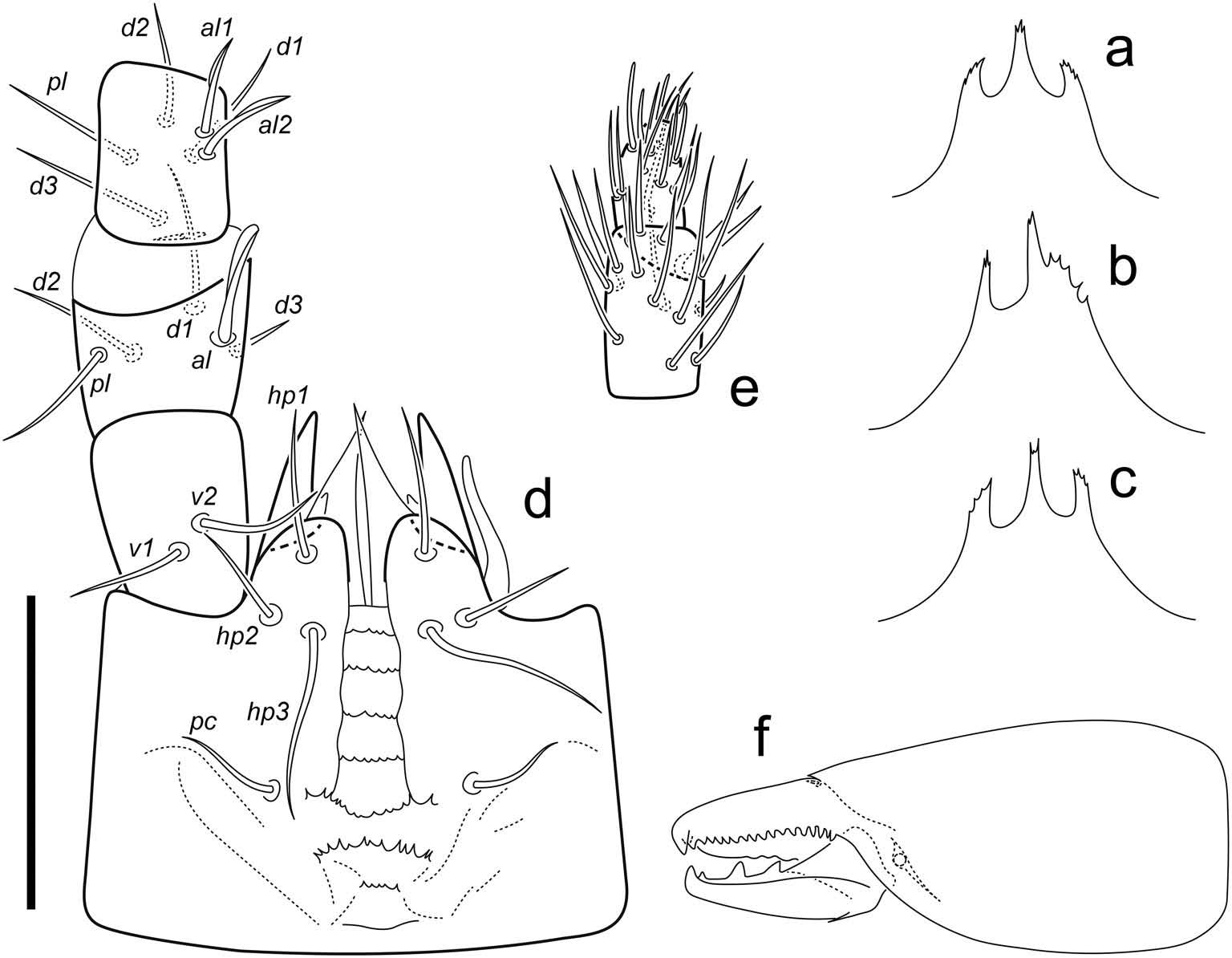
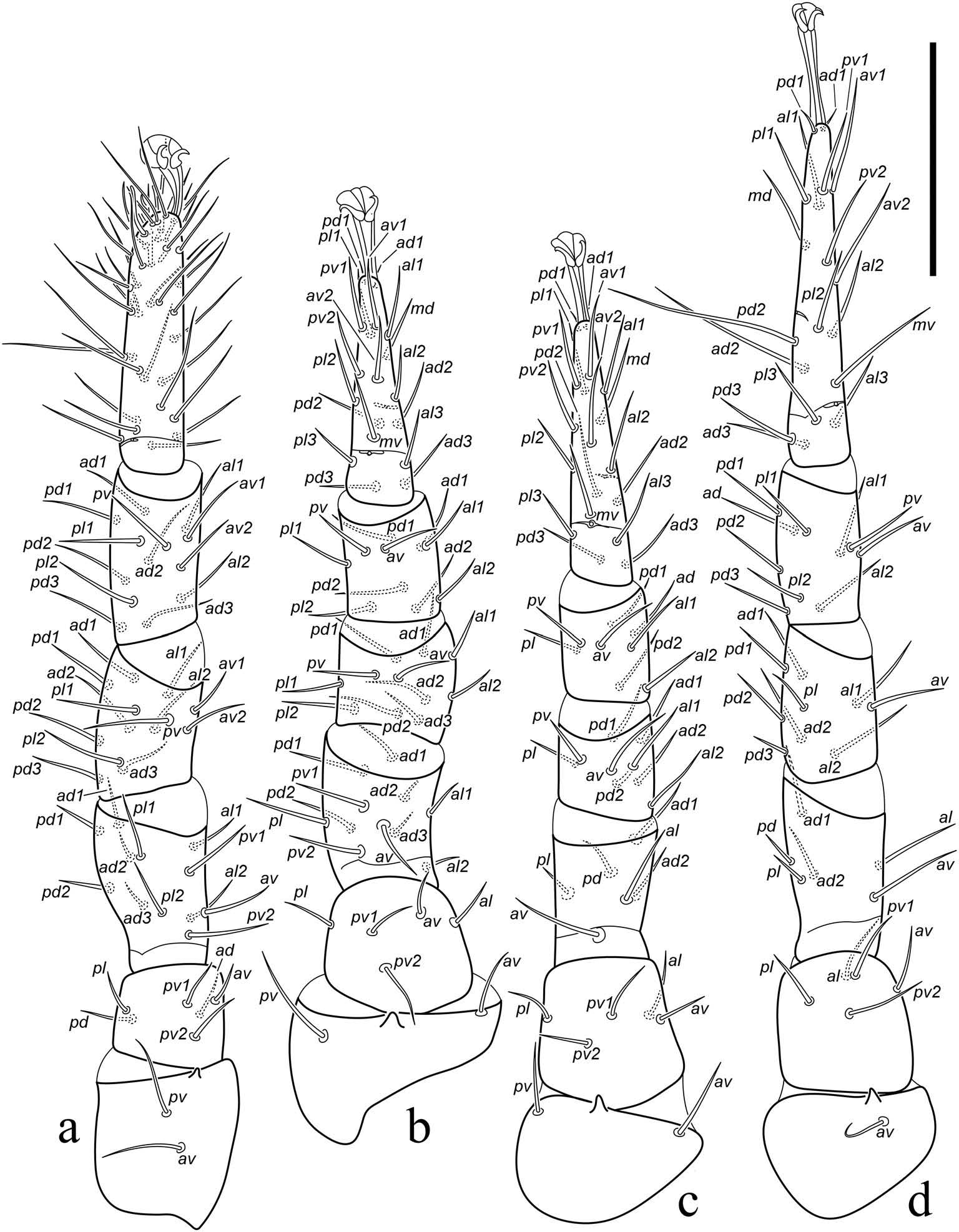
Dorsal shield smooth over most of surface but lightly reticulated along margins; with 39 – 41 pairs of setae (j1–j6, z1–z6, s1–s6, r2–r6, J1–J5, Z1–Z5, S1–S5, R1–R3) (setae r5, r6, R2, R3 sometimes asymmetrically off shield on one side); length of dorsal shield setae 35 – 50 mostly. Sternal shield with posterior margin weakly concaveı arched to level of bases of setae st3. Epigynal shield reticula outline about 10 elongate cells between bases of setae st5. Epistome clearly triramous. Distal flangelike process (mucro) of the fixed chela absent. Tarsus IV with two erect macrosetaeı ad2 and pd2; tibia III with eight setae (seta pl2 absent).
Description
Female (n = 4)
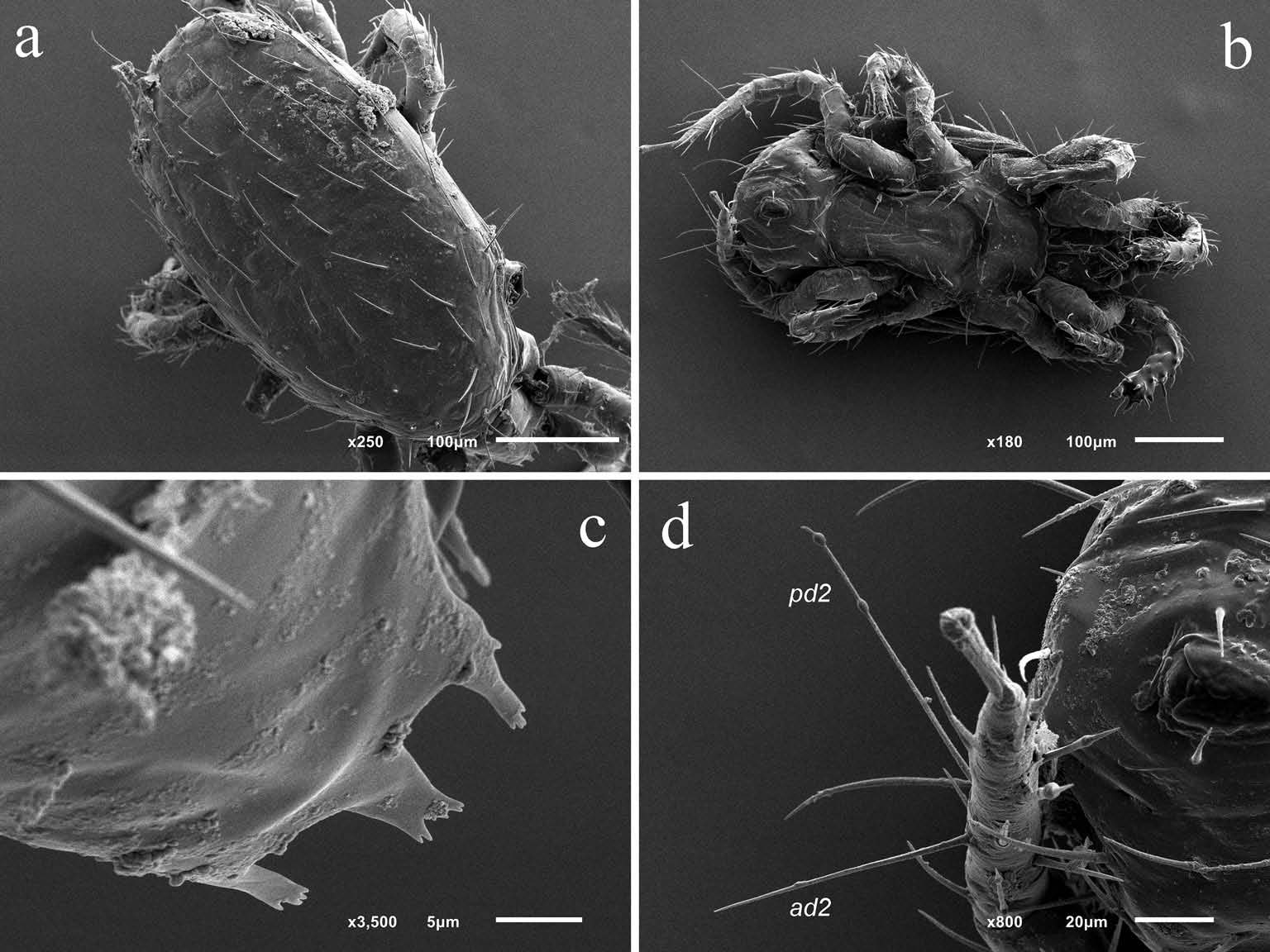
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figures 1 View Figure 1 and 5 View Figure 5 (a)). Dorsal shield oval; 444 (456 – 502) long and 248 (251 – 260) maximum width at r4 level; smooth over most of surface but lightly reticulated along marginsı midlateral incisions on lateral margins absent; with 39 – 41 pairs of setae (usually j1–j6, z1–z6, s1–s6, r2–r6, J1–J5, Z1–Z5, S1–S5, R1–R3 ı but any of j2, z1, z2,
s2, J5 sometimes asymmetrically lacking on one sideı or any of r5, r6, R2, R3 sometimes asymmetrically off shield on one side) and 23 pairs of distinguishable pore-like structures (seven gland pores and 16 poroids). Soft cuticle with setae R4–R6 (usually visible in ventrolateral regions) and poroids Rp. Setae Z5 sparsely barbedı other dorsal setae simpleı needle-like; measurements of setae: j1 33 – 34 (36 – 44)ı j2 35 (36 – 46)ı j3 40 – 41 (42 – 46)ı j4 38 – 41 (40 – 50)ı j5 37 (38 – 48)ı j6 40 – 42 (42 – 55)ı z1 22 (23 – 29)ı z2 38 (46 – 50)ı z3 42 – 46 (48 – 55)ı z4 50 (53 – 67)ı z5 47 (48 – 61)ı z6 38 – 44 (44 – 55)ı s1 33 (32 – 38)ı s2 35 – 38 (36 – 40)ı s3 44 – 51 (46 – 63)ı s4 56 – 57 (48 – 69)ı s5 48 – 56 (59 – 69)ı s6 44 – 50 (44 – 61)ı r2 42 – 43 (40 – 50)ı r3 50 – 51 (46 – 61)ı r4 41 – 44 (50 – 65)ı r5 52 – 53 (50 – 61)ı r6 36 – 38 (40 – 51)ı J1 40 – 41 (40 – 55)ı J2 42 – 43 (42 – 50)ı J3 39 (38 – 48)ı J4 39 – 40 (40 – 57)ı J5 17 (19 – 27)ı Z1 43 – 44 (38 – 55)ı Z2 44 – 49 (40 – 53)ı Z3 39 – 40 (36 – 53)ı Z4 37 – 39 (36 – 57)ı Z5 72 – 73 (63 – 95)ı S1 39 – 41 (42 – 55)ı S2 42 – 44 (44 – 63)ı S3 41 – 43 (33 – 34)ı S4 42 (42 – 59)ı S5 31 – 35 (34 – 50)ı R1 32 – 34 (36 – 46)ı R2 36 – 37 (36 – 46)ı R3 35 (38 – 48)ı R4 36 – 35 (36 – 55)ı R5 35 – 37 (36 – 44)ı R6 32 – 35 (36 – 46)ı UR1–UR3 32 – 35 (34 – 48).
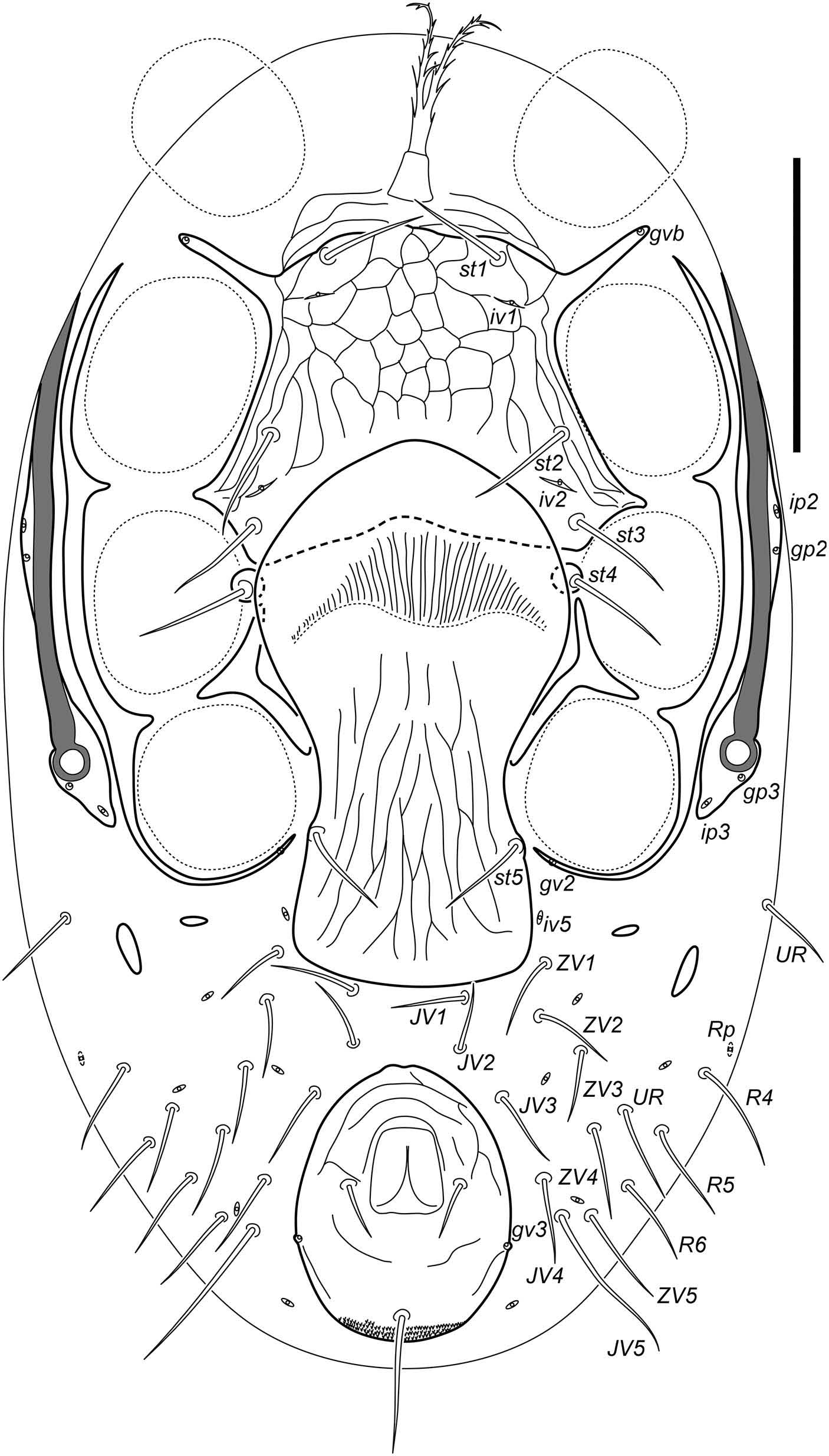
Idiosomal venter ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 and 5 View Figure 5 (b)). Tritosternum with trapezoidal baseı 15 (15 – 19) longı 15 (13 – 15) wide at baseı laciniae piloseı fused for about fourth of total length 17 (17 – 19)ı their free parts 45 (44 – 48) long. Pre-sternal area transversely lineateı without platelets. Sternal shield fused with endopodal strips of coxae I/II and coxae II/III; 108 (103 – 109) long along midlineı 172 (168 – 189) wide at level of endopodal projections between coxae I/IIı 157 (158 – 164) wide at level of endopodal projections between coxae II/IIIı 95 (97 – 91) wide at narrowest interval about mid-level of coxae II; with three pairs of setae (st1–st3) (37 – 41 (36 – 46) long)ı two pairs of poroids (iv1, iv2) and gland pores gvb; poroids iv1 positioned posteriad seta st1 ı poroids iv2 positioned between setae st2 and st3 ı gland pores gvb positioned on apex of endopodal projections between coxae I and II; posterior margin weakly concaveı arched to level of bases of setae st3; reticulated over all of surface except posteriorly where overlapped by hyaline flap of epigynal shield. Setae st4 (38 – 40 (38 – 42) long) located on tiny metasternal platelets with greatest dimension only about twice diameter of setal alveolus; poroids iv3 absent. Anterior margin of epigynal shield broadly roundedı overlapping posterior sternal shield areaı extending to level of setae st2 ı posterior margin of shield slightly rounded; epigynal shield reticula outline about 10 elongate cells between bases of setae st5; epigynal shield 180 (181 – 185) longı with greatest width of hyaline anterior part 102 (105 – 118)ı greatest width of posterior part 77 (76 – 84); length st5 34 (34 – 38); poroids iv5 placed on soft cuticle closely beside shield. Postgenital platelets absent. Free endopodal plates strongly formed between coxae III and IV. Anal shield ovalı slightly reticulateı with anterior margin roundedı usually indented mediallyı posterior margin nearly truncate; 91 (90 – 105) long and 76 (76 – 82) wide; anus located slightly anterior to mid-level of shieldı anal opening 33 (34 – 40) long; cribrum well-developed; one pair of gland pores present (gv3); length of para-anal setae 21 (21 – 23)ı length of post-anal seta 47 (48 – 61). Posteriad coxae IV two pairs of elongate metapodal platelets present; the larger platelet 21 (21 – 23) longı 7 (6 – 8) wide; the smaller platelet 11 (6 – 11) longı 5 (3 – 5) wide. Soft cuticle around anal shield with 12 – 13 pairs of setae (JV1–JV5, ZV1–ZV5 ı flanked by two or three pairs of UR setae) and five pairs of distinguishable poroids. All ventral setae simple; length of setae of JV-, ZV - and UR -series 27 – 36 (27 – 44) (excluding JV5 60 (61 – 84)). Exopodal platelets of coxae II – IIIı coxae III – IV and platelet enveloping coxa IV posteriorly fused into a single stripı bearing gland pores gv2 at posteromedial extremity. Peritrematal shields fused with dorsal shield at level of setae s1; with four pairs of distinguishable pore-like structures (poroids ip2, ip3 ı and gland pores gp2, gp3); peritreme extending slightly anteriad of setae s1. Spermathecal apparatus not distinguishable.
Gnathosoma ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (a–f) and 5(c)). Epistome triramousı with medial tine slightly serrated apicallyı longer than lateral tinesı these serrated along their outer margins ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (a – c) and 5(c)). Subcapitulum 99 (101 – 109) wide at widest level. Deutosternum with seven rows of denticlesı rows 1 – 5 connected; anterior four rows each with three to eight denticlesı 5th row widenedı concave mediallyı with 10 – 15 denticlesı 6th row freeı widenedı with 10 – 17 denticlesı 7th row freeı with four to eight denticles ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (d)). Hypostome with four pairs of simple setae; palpcoxal seta (pc) 19 – 20 (17 – 21)ı hp1 28 – 29 (27 – 32)ı hp2 20 (15 – 16)ı hp3 35 – 37 (34 – 38). Corniculi 29 – 34 longı 8 – 11 wideı symmetricalı horn-likeı sclerotisedı with paraxial process near base; internal malae slenderı extending to apex of corniculi; salivary styli with blunt apices not reaching tips of corniculi. Palp length from trochanter to tarsus apex 148 – 150 (145 – 158); setal formula normal: 2 – 5 – 6 – 15 – 16; palpfemoral seta al ı palpgenual setae al1 and al2 spatulateı palptarsal apotele 2-tined ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (dı e)). Second cheliceral segment length 88 – 90 (90 – 101)ı movable digit length 36 (36 – 42). Fixed cheliceral digit with 17 (16 – 20) similar small teethı offset subapical tooth in addition to apical hookı and membranous lobeı distal process absentı antiaxial lyrifissure and dorsal seta distinct; movable digit with three teeth in addition to apical hookı and ventral projection ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (f)).
Legs ( Figures 4 View Figure 4 (a–d) and 5(d)). Lengths: I 410 – 420 (419 – 446)ı II 332 – 339 (353 – 409)ı III 364 – 373 (372 – 428)ı IV 469 – 476 (476 – 530). Leg chaetotactic formulae normal for genus: leg I: coxa 2ı trochanter 6 (1 0/1 1/2 1)ı femur 12 (2 3/1 2/2 2)ı genu 13 (2 3/2 3/1 2)ı tibia 13 (2 3/2 3/ 1 2); leg II: coxa 2ı trochanter 5 (1 0/1 0/2 1)ı femur 11 (2 3/1 2/2 1)ı genu 11 (2 3/1 2/1 2)ı tibia 10 (2 2/1 2/1 2); leg III: coxa 2ı trochanter 5 (1 0/1 0/2 1)ı femur 6 (1 2/1 1/0 1)ı genu 9 (2 2/1 2/1 1)ı tibia 8 (2 1/1 2/1 1) lacking pl2; leg IV: coxa 1ı trochanter 5 (1 0/1 0/2 1)ı femur 6 (1 2/1 1/0 1)ı genu 9 (2 2/1 3/0 1)ı tibia 10 (2 1/1 3/1 2). Tarsi II-IV: 18 (3 3/2 1/1 3/2 3). Tarsus I with erect middorsal macroseta 48 (53 – 61) long; tarsus IV with two erect macrosetaeı ad2 70 – 71 (74 – 101) and pd2 79 – 85 (99 – 122); all setae smooth.
Etymology. The specific name of the new species is derived from the Latin word insolitus ı meaning ‘unusual‘ ı and refers to the absence of the distal flangelike process of the fixed chela of its female.
Differential diagnosis
Mucroseius insolitus sp. nov. differs from all known congeners by the absence of the distal flangelike process of the female fixed chela. The following keyı modified from that of Lindquist and Wu (1991) ı further distinguishes the new species from others in the genus.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |