Iguana iguana ( Linnaeus, 1758 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3983.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B8075AD6-C79A-4115-980D-D30BA8325039 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5668033 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7B70CD37-F930-FF81-FF10-FEABD64AFE3D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Iguana iguana ( Linnaeus, 1758 ) |
| status |
|
Iguana iguana ( Linnaeus, 1758) View in CoL
Type-locality. Indiis, restricted by Hoogmoed (1973) to the confluence of the Cottica River and the Perica Creek, Suriname.
Pertinent taxonomic references. Linnaeus (1758), Laurenti (1768), Daudin (1802a), Link (1806), Merrem (1820), Spix (1825), Wagler (1828a; 1830), Wiegmann (1834), Duméril & Bibron (1937), Fitzinger (1843), Jan (1857), Boulenger (1885), Cope (1886), Smith (1935), Smith & Taylor (1950), Cunha (1961), Hoogmoed (1973), Lazel (1973), Trajano & Guiringuello (1978), Hoogmoed & Gruber (1983), O’Shea (1989), Schwartz & Henderson (1991), Ávila-Pires (1995), de Queiroz (1995), Hollingsworth (2004), Malone & Davis (2004), Stephen et al. (2013).
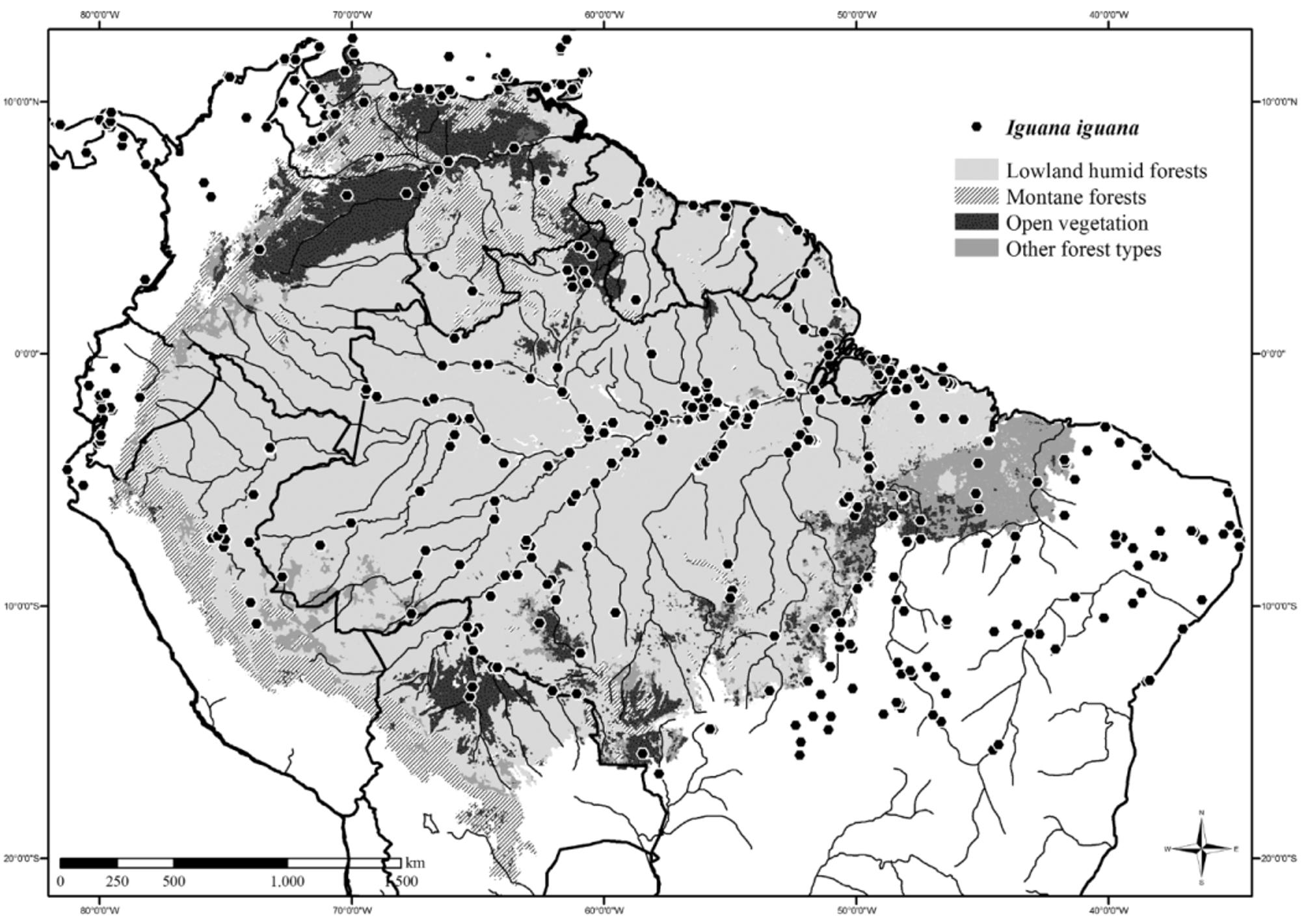
Distribution and habitat. Iguana iguana is distributed from south of North America, through Central America, part of the Caribbean islands, to center-north of South America, occurring in Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, British Virgin Islands, United States Virgin Islands, Netherlands Antilles, Montserrat, Guadaloupe, Aruba, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and Grenadines, Grenada, Brazil, French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, Venezuela, Trinidad and Tobago, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 —restricted to Panama, some Caribbean Islands and South America). Two specimens are reported from Paraguay (USNM 12202, 12295), but without exact location. In Brazil it is widespread in Amazonia and Caatinga, occurring also in northern Cerrado ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 ), where it is known from the states of Amapá, Pará, Tocantins, Amazonas, Roraima, Acre, Rondônia, Maranhão, Piauí, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Goiás, and Mato Grosso. Iguana iguana is arboreal and diurnal. In Amazonia, it inhabits primary and secondary terra firme forests, isolated patches of forest in open vegetation enclaves, and perianthropic areas, where it is found mainly along rivers, from the ground to the upper canopy (adults found higher in vegetation than juveniles—Crump 1971; Cunha 1961; Cunha et al. 1985; Zimmerman & Rodrigues 1990; Martins 1991; Ávila-Pires, 1995; Ribeiro-Júnior et al. 2008; Vitt et al. 2008a; Ortega-Andrade et al. 2010; Pantoja & Fraga 2012). In transition areas of Amazonia with other biomes the presence of water seems not to be necessary to find the species ( Hoogmoed 1973; Cunha 1981a; Vitt & Carvalho 1995). The same is observed in the Brazilian Caatinga, where Iguana iguana is very common ( Vanzolini 1972; Vanzolini et al. 1980; Vitt 1995; Freire 1996; Arzabe et al. 2005; Borges-Nojosa & Santos 2005; Loebmann & Haddad 2010).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.