Eustenogaster agilis ( Smith, 1860 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.178242 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6251936 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4E55E763-FFD1-FFD9-FF53-FA59FDAD0324 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Eustenogaster agilis ( Smith, 1860 ) |
| status |
|
Eustenogaster agilis ( Smith, 1860) View in CoL
Ischnogaster agilis Smith, 1860: 89 .
Eustenogaster agilis View in CoL is endemic to Sulawesi Island, but the species has not so far been recorded from the northern part of the island. Showing various features unique to the species, we do not recognize any species similar to E. agilis View in CoL . Below both female and male characteristics of E. agilis View in CoL are described in detail for the first time.
Female. Body length (head + mesosoma + first two terga) about 18 mm; forewing length about 14.5 mm.
Head in frontal view about as wide as high ( Fig. 57 View FIGURE 57 A). Clypeus convex, with apex sharply pointed and having median impunctate ridge; supraclypeal area densely covered with long hairs, irregularly but not clathrately punctate in area below anterior ocelli; suture demarcating clypeus and supraclypeal area indistinct. Ocelli close to each other (Fig. 2); distance between anterior and posterior ocelli shorter than diameter of posterior ocellus; distance between posterior ocelli as long as their diameter; anterior ocellus 0.30–0.32 mm wide, 0.26 mm long, about 1.3 times as wide as posterior ocellus (diameter 0.22–0.24 mm); distance between inner eye margin and posterior ocellus 1.4 times longer than width of anterior ocellus.
FIGURES 17–25. 17–18, Eustenogaster nigra . 19–20, E. scitula . 21–25, E. calyptodoma . 17, 19, 21–24, female. 18, 20, 25, male. 17–20, 24, second metasomal tergum in lateral view. 21, apical part of clypeus. 22 and 25, mandible. 23, dorsolateral furrows on pronotum in lateral view. Scale bars show 1 mm.
Lateral furrow of pronotum deep, distinctly striate. Scutum with dense, long hairs, sparsely punctuate medially; interspace between punctures larger than puncture. Scutellum strongly convex, hairly, and densely punctate. Metanotum rather strongly convex, hairly, and sparsely punctate. Posterolateral part of pronotum and dorsal part of mesepisternum densely punctate. Propodeum hairly, covered with shallow, small punctures.
FIGURES 32–38. 32–33 Eustenogaster gibbosa , 34–36, E. hauxwellii , 37–38, E. micans . 32–35, 37, female. 36 and 38, male. 32 and 35, apical part of clypeus. 33, second metasomal tergum in lateral view. 34, mandible. 36, head in lateral view. 37, scutellum (SCL) and metanotum (MN) in lateral view. 38, lateral margin of pennies valve. Scale bars show 1 mm except for fig. 38.
First metasomal tergum thick and shortened, 6.9–7.0 mm long, about 5.0 times as long as its maximum width, and about 5.3 times longer than the maximum height; second tergum rather convex dorsally (Fig. 3); sixth metasomal tergum with stout spine (Fig. 4).
Color: Black; first tergum dark reddish-brown except for black posterior one-third of the ventral surface; following parts yellow: three longitudinal bands on clypeus ( Fig. 57 View FIGURE 57 ), large square spot below each antennal socket, narrow band in each posterodorsal margin of pronotum, scrobal spot, inverted L-shaped mark below scrobal spot, paired lateral spots on disk of scutellum, anterior band on metanotum, paired posterodorsal lines on propodeum, anterior band on second tergum, paired anterolateral spots on third tergum, and paired spots on second and third sterna. Legs brown, with following parts yellow: lateral sides of all femora, lateral spot on fore tibia, lateral sides of all coxae. Wings semihyaline, pale brown, slightly darker along anterior margin of forewing; veins brown.
Male. Body length (head + mesosoma + first two terga) 16.5–18.0 mm; forewing length about 15 mm. Structure and coloration similar to female, but head in frontal view more transverse, about 1.1 times wider than high ( Fig. 57 View FIGURE 57 ); clypeus less convex, with apex bluntly angled, and colored yellow except for black margins and some small black spots ( Fig. 57 View FIGURE 57 ); mandible with three teeth, of which proximal one is very small (Fig. 5); paired yellow spots on second sternum sometimes absent.
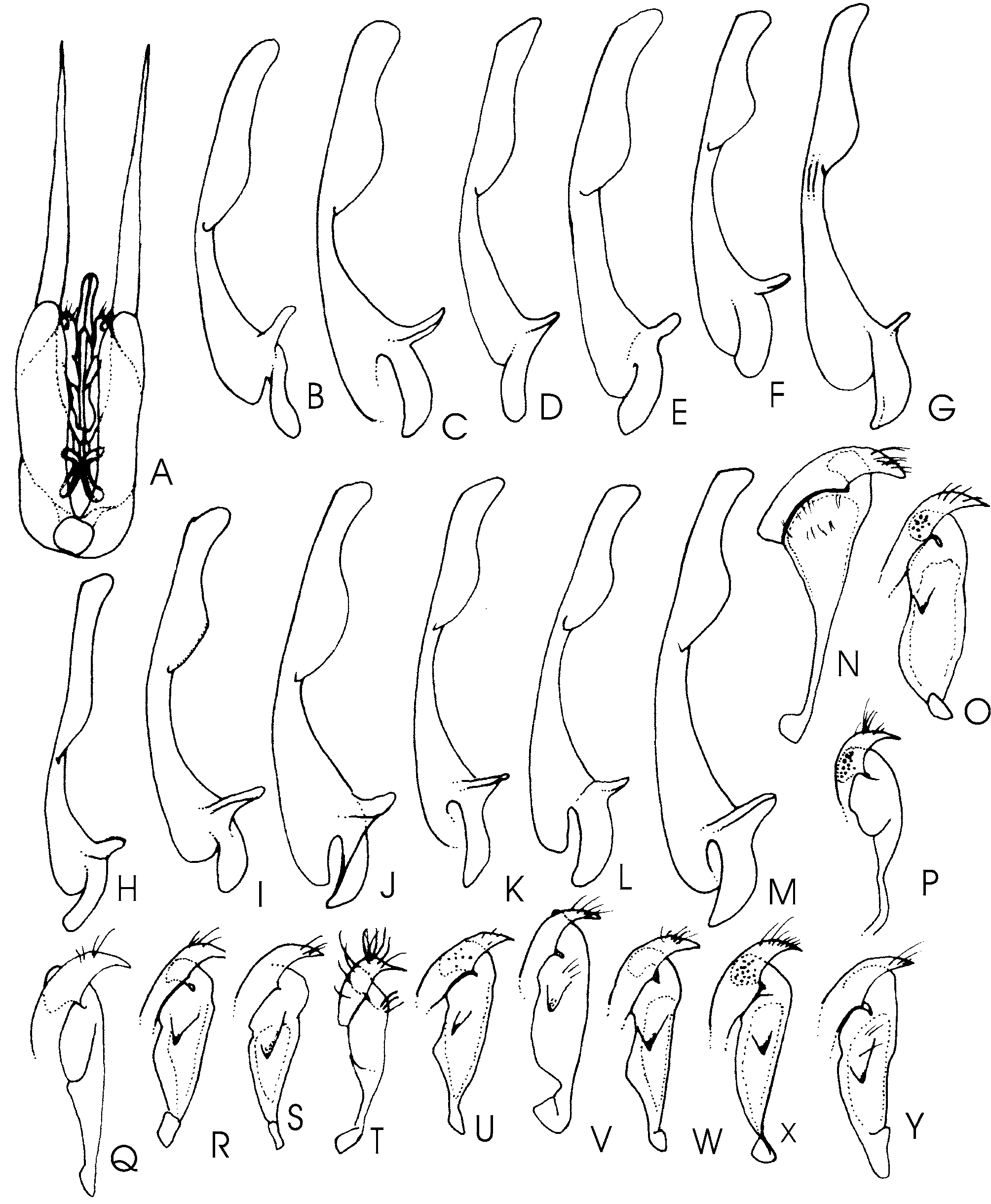
Genitalia: Aedeagus in lateral view barely swollen apically ( Fig. 59 View FIGURE 59 B); volsella elongate ( Fig. 59 View FIGURE 59 N).
Material examined. Indonesia: South Sulawesi: 1 female (holotype of Ischnogaster agilis ; OUM) labeled “Mak.” [circular] “ Ischnogaster agilis Smith ” [blue paper], “ Stenogaster agilis (Sm.) Holotype Ψ [J.v.d. Vecht 1958]” and “ Type 0 65 Hope Dept. Oxford”. 1ɗ ( RMNH), Makassar, “Gribodo collection”; 1ɗ ( RMNH), Bantimurung [near Makassar], vii.1949, C. Franssen; 2Ψ4ɗ ( IUNH), 02°58’S, 120°05’E, 800m alt., Battang, Warateluwanua, Luwu, JK [1Ψ, 29.x.2000; 1Ψ4ɗ, 30.x.2000]; South East Sulawesi, 2ɗ ( MZB), Watu Wila (± 300 m), 10.x.1989, S. Kahono; 2ɗ ( MZB), Maluhu, Wowotobi, Kendari, viii.1994, Kustoto et al.; 1ɗ ( SKYC), 23.xi.2000, IKT Ginarsa; Central Sulawesi, 1ɗ ( SKYC), W[est] of Lore Lindu, n[ea]r Palu, 300–700m, 15.viii.1992, SkY.
Distribution: Indonesia: Sulawesi.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Eustenogaster agilis ( Smith, 1860 )
| Saito, Fuki & Kojima, Jun-Ichi 2007 |
Ischnogaster agilis
| Smith 1860: 89 |