Spilopteron mucronatus Lee, 2008
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2017.356 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A7ED0BAC-2637-433D-9BD2-8A9E2C59B2CA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3851932 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3D6F7173-5373-3E02-1836-48E1FCDBFD01 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Spilopteron mucronatus Lee, 2008 |
| status |
|
Spilopteron mucronatus Lee, 2008
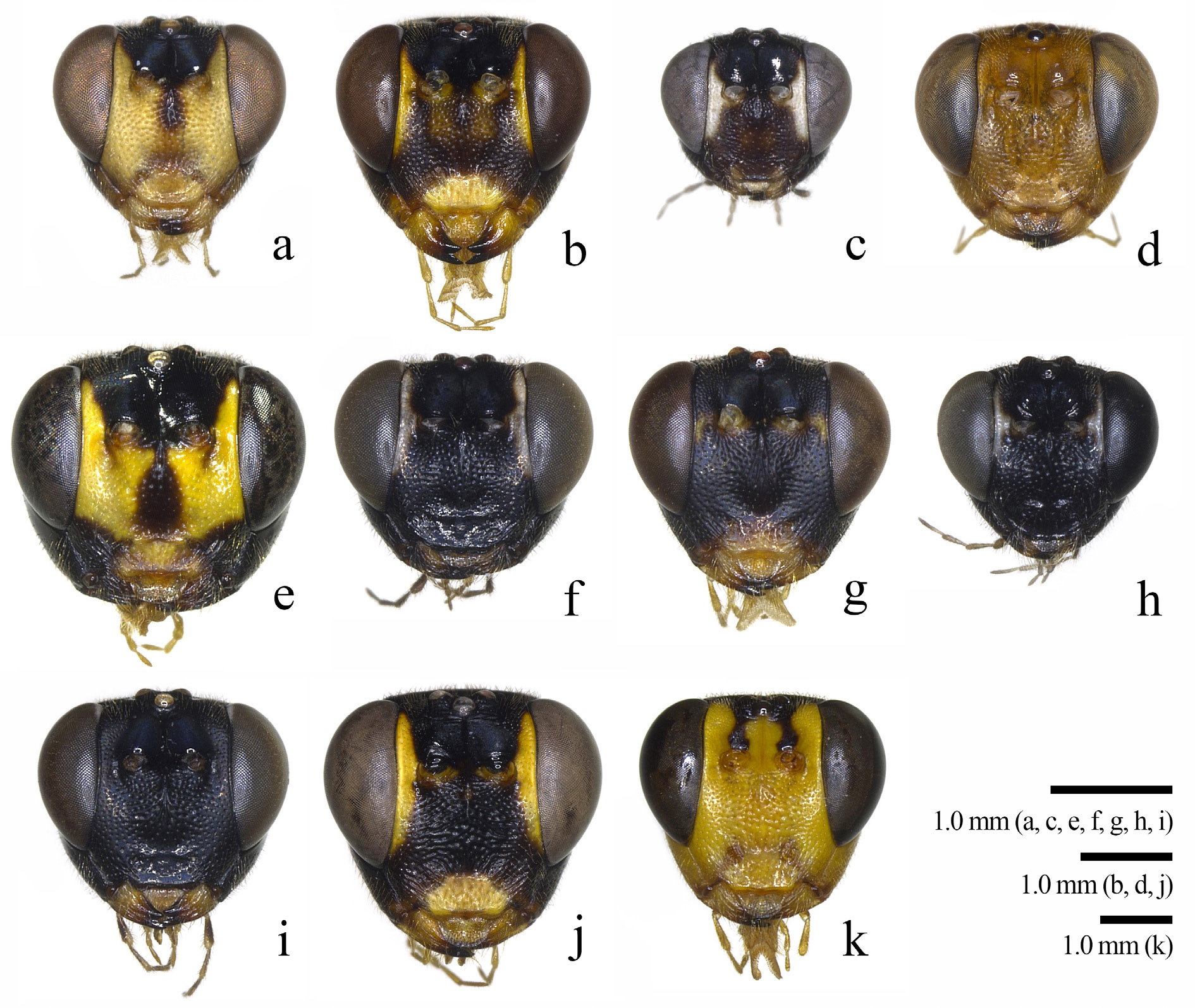
Figs 2e View Fig , 3e View Fig , 4e View Fig , 5e View Fig , 6e View Fig , 7 View Fig i–j, 8e
Spilopteron mucronatus Lee, 2008 in Lee et al. 2008: 276 . Type locality: Korea, Gyeonggi-do Province, Yangpyeong-gun Yongnum-myeon Mt Yongmun.
Spilopteron mucronatus – Yu et al. 2012. — Ito et al. 2012: 445.
Material examined
JAPAN: 1 ♂, Soun-kyo, Kamikawa-cho, Hokkaido Pref., 13 Jul. 2012, M. Ito ( LC041302 View Materials , NIAES); 1 ♀, Mt Teinekanayama, Sapporo city, Hokkaido Pref., 19 Jul. 2012, Y. Nakatani ( NSMT); 1 ♀, Rishiri Is., Hokkaido, 15 Jul. 1975, E. Nishida ( OMNH); 1 ♀, Mt Hayachinesan, Iwate Pref., 25 Jul.–2 Aug. 1989, M. Sharkey and H. Makihara ( NIAES); 1 ♀, Hanase-toge, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto Pref., 23 Jun. 2012, M. Ito ( LC041301 View Materials NIAES); 1 ♀, Ideno, Mitsuse-mura, Saga Pref., 17 May 1998, R. Matsumoto ( OMNH); 3 ♀♀, Mt Hiko-san, Soed-cho, Fukuoka Pref., 15 Jun. 1996, R. Matsumoto ( OMNH); 1 ♀, Mt Taterasan, Tsushima Is., Nagasaki Pref., 28 May 1997, N. Takahashi ( OMNH); 1 ♂, Kamisaka, Tsushima Is., Nagasaki Pref., 3 Jun. 1996, R. Matsumoto ( OMNH).
Differential diagnosis
This species can easily be distinguished from other species of Spilopteron by the ventral convexity of the hind femur, and the distinct sharp projection on S1 (see Ito et al. 2012).
Description
Female (n = 8)
BODY LENGTH. 11.5–15.0 mm.
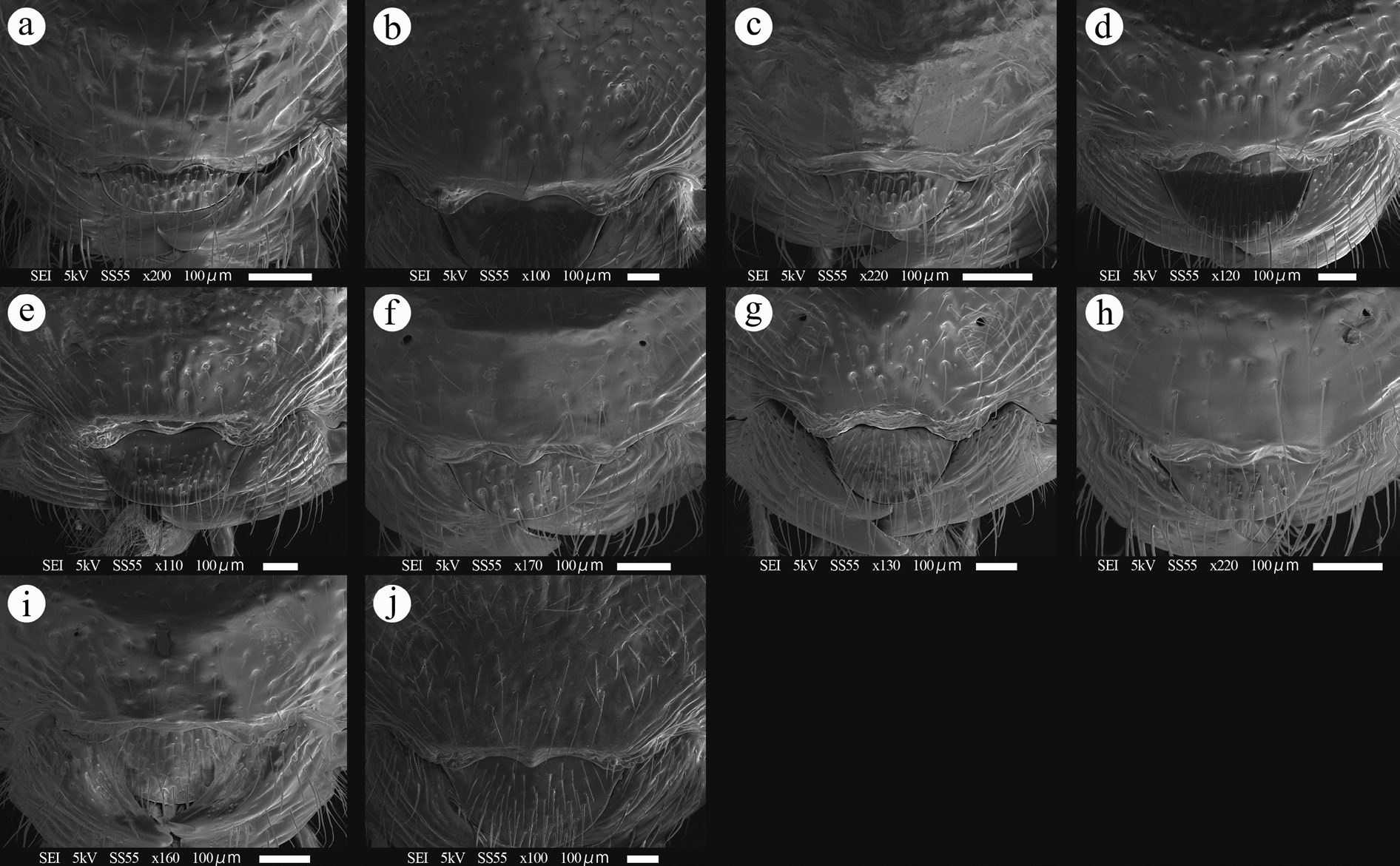
HEAD. Vertex 0.7–0.9 times as long as maximum length of eye in dorsal view. Frons without a depression between eye and antennal socket in frontal view ( Fig. 2e View Fig ). Clypeus 0.5–0.6 times as long as wide, with two strong lateral projections and a weak median projection ( Figs 2e View Fig , 3e View Fig ). Face 0.6 times as long as wide. Length of malar space 0.9–1.0 times as long as basal mandibular width. Ocello-ocular line/lateral ocellar diameter = 2.0–2.1. Postocellar line/lateral ocellar diameter = 1.4–1.6. Antenna with 33–35 flagellomeres; first flagellomere 1.2–1.4 times as long as second flagellomere.
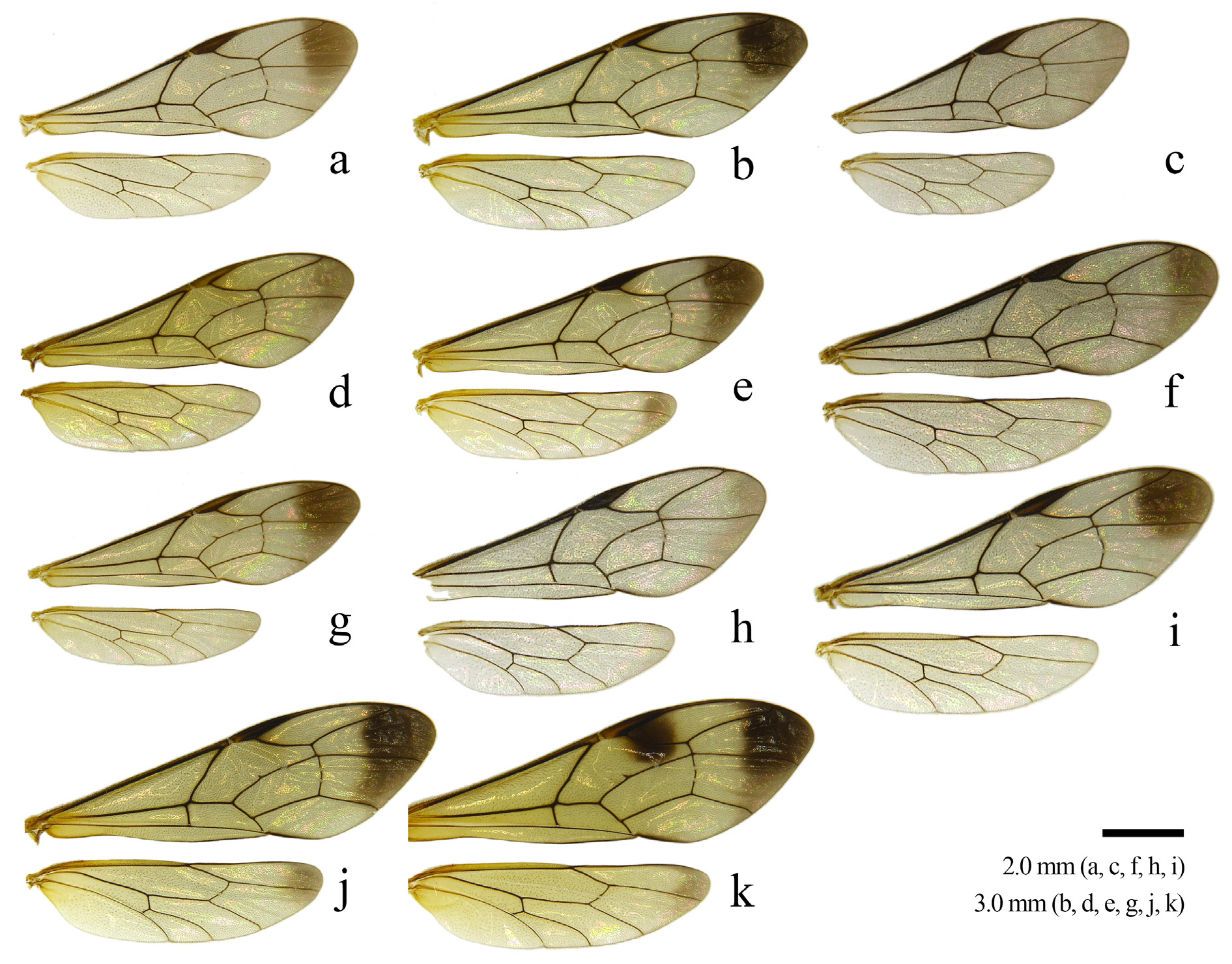
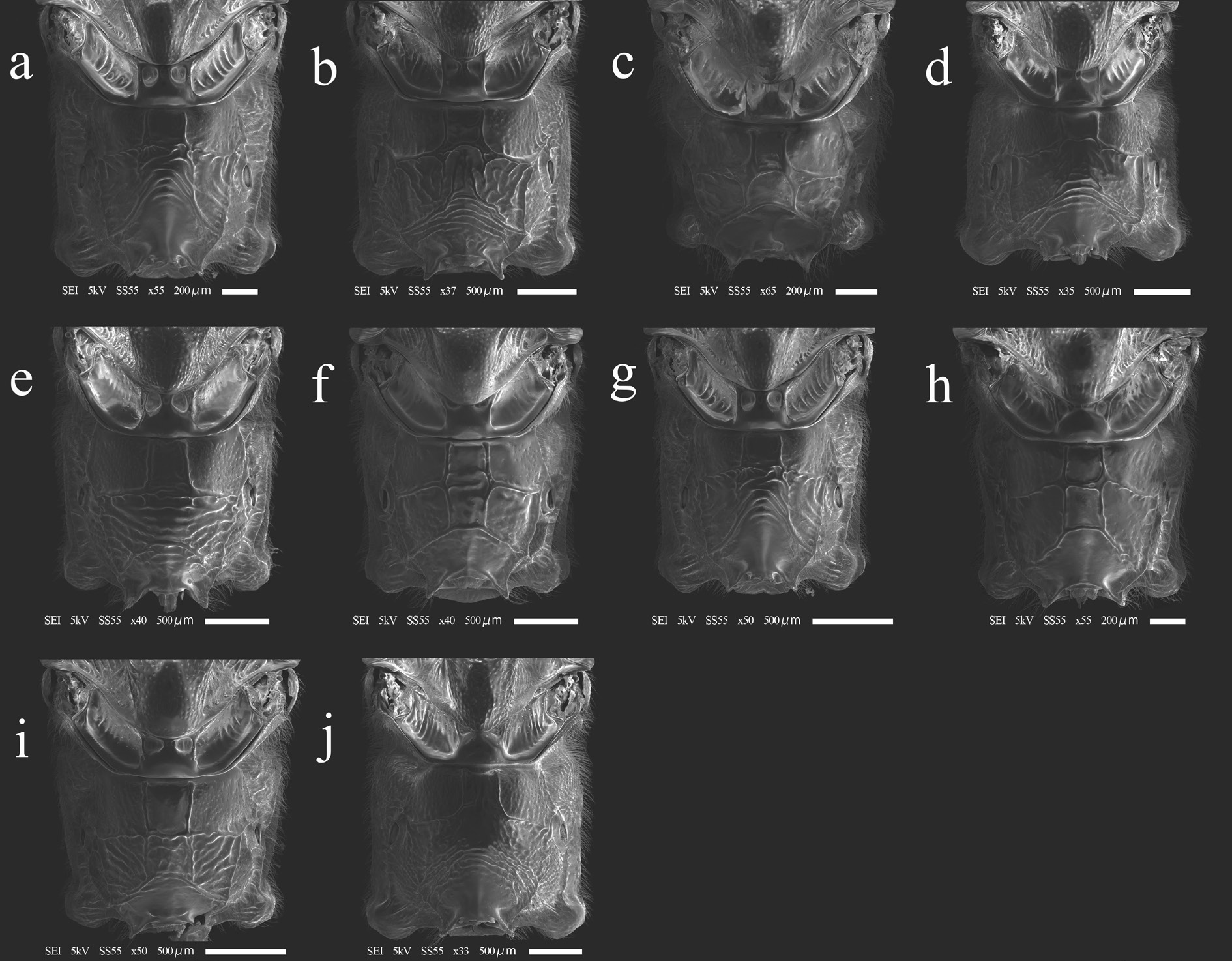
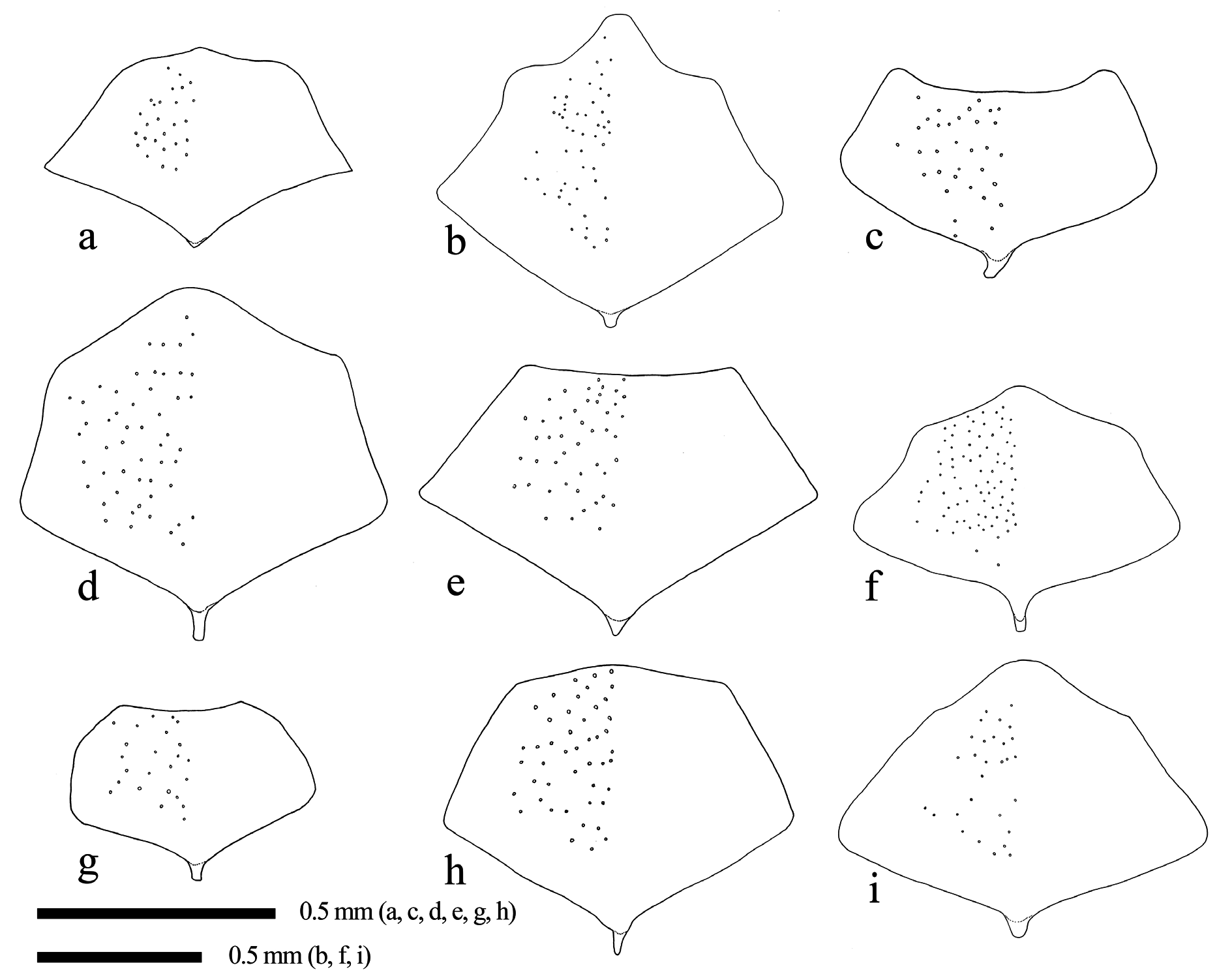
MESOSOMA. Propleuron densely punctate ( Fig. 5e View Fig ). Lateral area of pronotum densely punctate and transversely striate medially ( Fig. 5e View Fig ). Collar densely punctate. Mesoscutum densely punctate. Subalar prominence densely punctate ( Fig. 5e View Fig ). Scutellum strongly and sparsely punctate in dorsal view. Postscutellum flattened in lateral view ( Fig. 5e View Fig ). Metapleuron strongly punctate ( Fig. 5e View Fig ). Propodeum weakly carinate ( Fig. 6e View Fig ). Area externa densely punctate ( Fig. 6e View Fig ). Area basalis polished ( Fig. 6e View Fig ). Area dentipara confluent with area superomedia and transversely carinate ( Fig. 6e View Fig ). Area posteroexterna confluent with area petiolaris and transversely carinate ( Fig. 6e View Fig ). Fore wing length 9.0–12.0 mm. Vein cu-a basad of vein Rs&M ( Fig. 4e View Fig ). Vein rs-m opposite or basad of vein 2m-cu ( Fig. 4e View Fig ). Hind femur 3.1–3.5 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view, with a distinct convexity ventrally. Hind tibia 10.6–12.0 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view. First hind tarsomere 2.5–3.2 times as long as second and 3.0–3.6 times as long as longer hind tibial spur.
METASOMA. T1 2.7–2.9 times as long as maximum width, 2.3–2.4 times as long as T2. T2 0.7–0.8 times as long as maximum width. T1 and T2 weakly and sparsely punctate. T2–T8 weakly and densely punctate. S1 with a distinct sharp projection basally. Ovipositor sheath 2.7–3.0 times as long as hind tibia.
COLOR. Body black ( Fig. 5e View Fig ). Antennal flagellum without a white band, brown apically. Face and postscutellum yellow with black marking medially, but sometimes entirely black except for inner margin of eye. Clypeus, subalar prominence, propodeum, fore and mid legs, hind trochanter, hind trochantellus, apex of hind femur, and apex of T1 yellow. Fore wing with an apical dark mark extending downwards ( Fig. 4e View Fig ).
Male (n = 2; genitalia, n = 2)
Similar to female. Body length 10.0–13.0 mm. Face 0.6–0.7 times as long as wide. Length of malar space 0.8–0.9 times as long as basal mandibular width. Postocellar line/lateral ocellar diameter = 1.4– 1.7. Antenna with 37–42 flagellomeres. Hind femur 3.0–3.1 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view. First hind tarsomere 3.0–3.3 times as long as second. T1 3.1–3.2 times as long as maximum width, 2.0–2.2 times as long as T2. T2 0.8–1.0 times as long as maximum width. Antennal flagellum brown in apical half. Face entirely yellow. Basal area of hind tibia and apex of hind tarsus yellow.
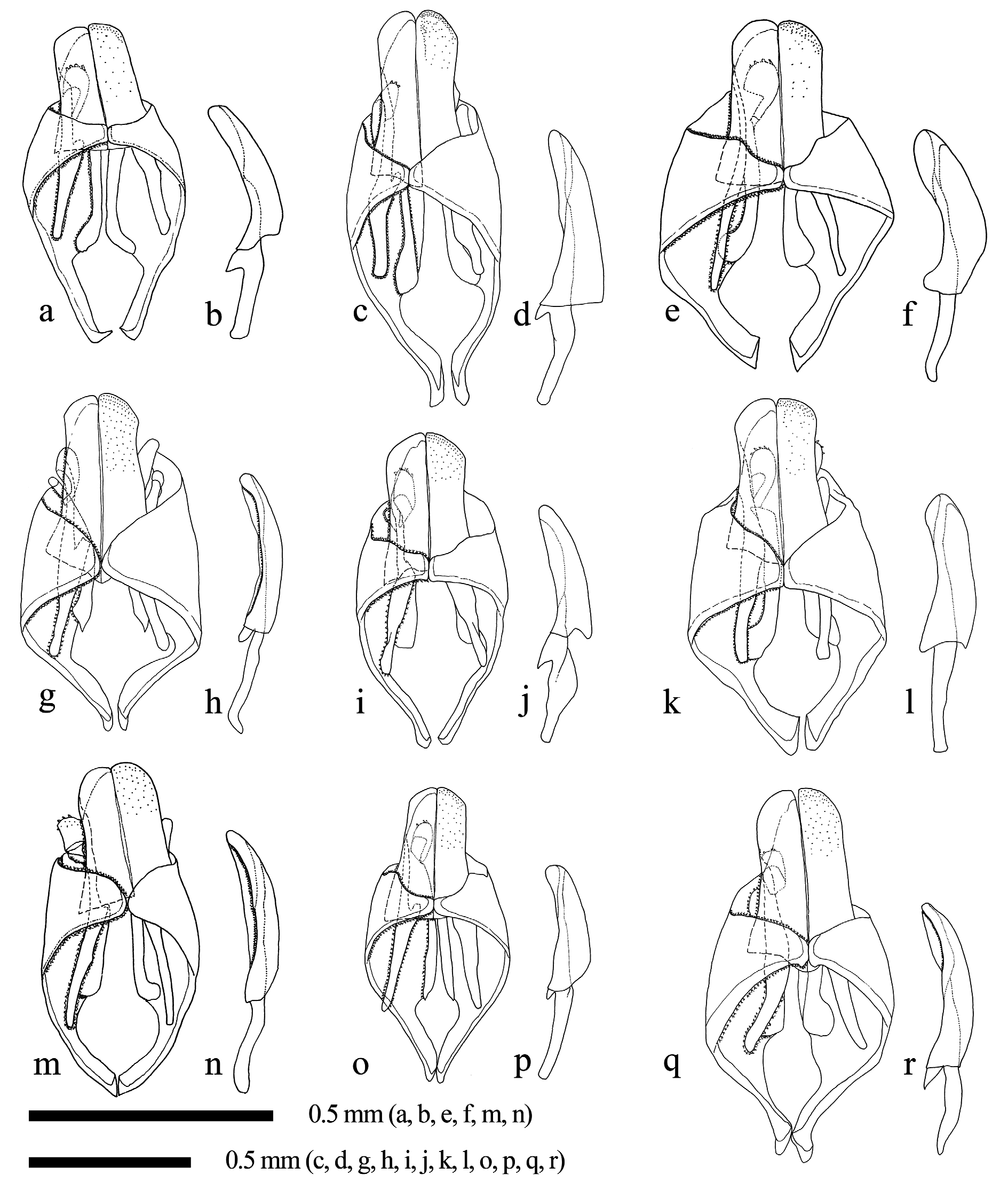
Subgenital plate pentagonal with basal angle obtuse ( Fig. 8e View Fig ). Paramere short, basal part strongly projecting towards base of subgenital plate ( Fig. 7i View Fig ). Aedeagus gently curved, its penis valve ca 2.0 times as long as basal apodeme ( Fig. 7j View Fig ).
Distribution
Japan (Hokkaido, Rishiri Is.*, Honshu, Kyushu, and Tsushima Is.) and Korea. * New record.
Bionomics
Host unknown. Adults mainly fly from May to July.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Acaenitinae |
|
Genus |
Spilopteron mucronatus Lee, 2008
| Ito, Masato & Maeto, Kaoru 2017 |
Spilopteron mucronatus Lee, 2008 in Lee et al. 2008: 276
| Lee J. W. & Jeong J. C. & Lee S. M. 2008: 276 |
Spilopteron mucronatus
| Ito M. & Watanabe K. & Maeto K. 2012: 445 |
| Yu et al. 2012 |