Bullacta exarata ( Philippi, 1849 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2010.487574 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2D533758-A35D-FF89-E6D8-FB21FB8CFA21 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Bullacta exarata ( Philippi, 1849 ) |
| status |
|
Bullacta exarata ( Philippi, 1849) View in CoL
Bullaea exarata Philippi, 1849, p 141 ( China Borealis ; types untraceable, probably lost; neotype here designated: MNHN 4494 About MNHN , Paris, H = 14 mm).
Bullacta exarata Thiele 1926, p 106 View in CoL ; 1931, p 386; Tchang 1934, p 3, pls 1–7; Habe 1952, p 143; Guangyu 1997, p 109, text figures 8, 18–20, pl 10, Figure 6 View Figure 6 ; Burn and Thompson 1998, p 955, Figure 16.34; Higo et al. 1999; Guangyu 2004, p 146, pl 83, Figure P.
Haminea exarata Kobelt 1896, p 107 , pl 15, Figure 18; Menke 1854, p 46; Pilsbry 1895, p 362, pl 40, Figure 97.
Atyscaphander exarata Annandale 1924, p 34 , Figures 4 View Figure 4 , 5 View Figure 5 .
Bullaea caurina Benson, 1856, p 128 .
Philine caurina Pilsbry 1895, p 9 . Bullacta caurina Bergh 1901, p 293 View in CoL , pl 22, Figures 31–39, pl 23, Figures 1–8 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 View Figure 6 ; Pruvot-Fol 1953, p 8, 25, 97.
Haminea sinensis A. Adams, 1850, p 582 View in CoL , pl 104, Figure 98; Sowerby 1868, sp. 21, pl 4.
Sinohaminea tsangkouensis Tchang, 1933, p 371 View in CoL .
Diagnosis. Shell external: H in adults between 14 and 19 mm; shape ovo-philinoid, with spiral striae throughout, fragile, whitish, translucent. Aperture slightly longer than H. Cephalic shield with quadrangular shape; parapodial lobes short, not covering the shell laterally. Male copulatory system opening laterally on right side of mouth; bipartite; both parts connected at the atrium: one containing accessory glands and other the penis and prostate; penis invaginable, muscular, armed with apical sharp long hook; prostate large, tightly coiled in a complex coiled structure. Jaws narrow, embedded on margin of labial cuticle. Rachidian teeth absent; wide central toothless area; lateral teeth large, thin, pointed with broader base. Three gizzard plates, corneous, with eight V-shape transverse ridges; ridges bordered by short cylindrical sharp elements; gizzard spines absent. Cerebral and pleural ganglia fused; pedal ganglia separated; cerebral–pleural and pedal ganglia of similar size and larger than other ganglia.
Barcode. GenBank accession number GQ332576 View Materials
Material examined. Mouth of Kinko River , Chongko City, Chungchong-Namdo, South Korea, one specimen dissected, BMNH 20070443 , H = 17 mm, 10 June 2006, mud tidal flat. Tahé-Kiang, China, four specimens dissected, coll. MNHN Paris [ David coll. No 15, 1872], H = 14, 17, 18 mm. Swatow, China, four shells, BMNH 1906.5.8.91-94; two shells, RMNH. MOL.122353, H = 10 mm. China, two shells, BMNH ( Mrs De Burgh colln) . China, three shells, BMNH ( V.W. Macandrew colln). China, three shells, BMNH 1852.4.64-66.
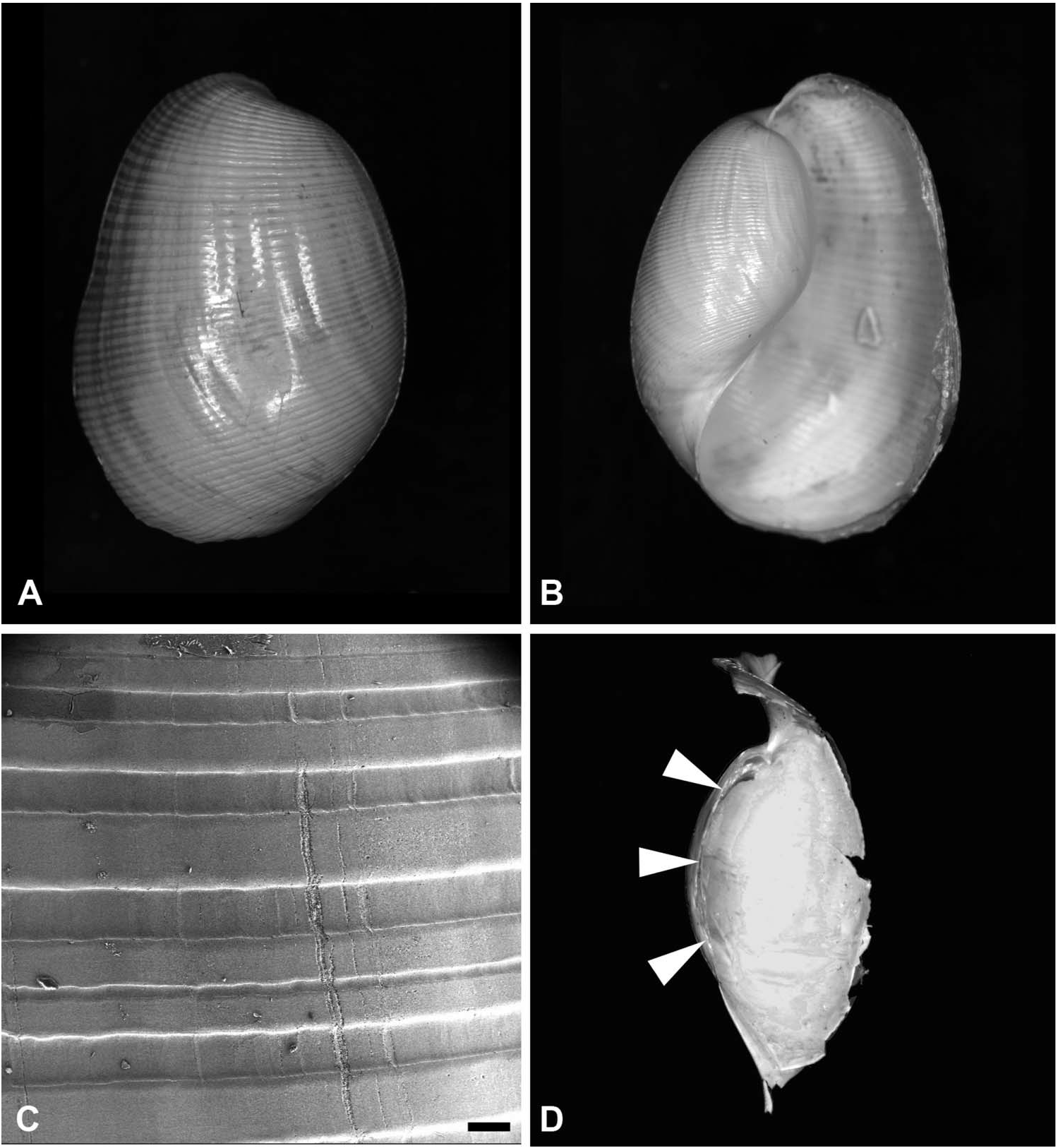
Description. Shell ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 ): external, formed by last whorl, fragile, ovo-philinoid, with conspicuous spiral striae all over, whitish, translucent. Columellar lip smooth, narrow, and white; columella reduced to internal folded cord of periostracum. Parietal callus absent. Spire absent. Aperture wide, longer than H. Periostracum fine, yellowish.
External body: cephalic shield with quadrangular shape, well-developed posteriorly, covering anterior part of shell, posterior notch absent. Eyes not visible through skin in preserved specimens. Pair of Hancock organs located laterally on anterior sides of head; smooth, quadrangular, slightly elevated from rest of epidermis. Parapodial lobes short, not covering laterally the shell. Foot shorter than shell, complemented by posterior pallial lobe. Operculum absent in adults.
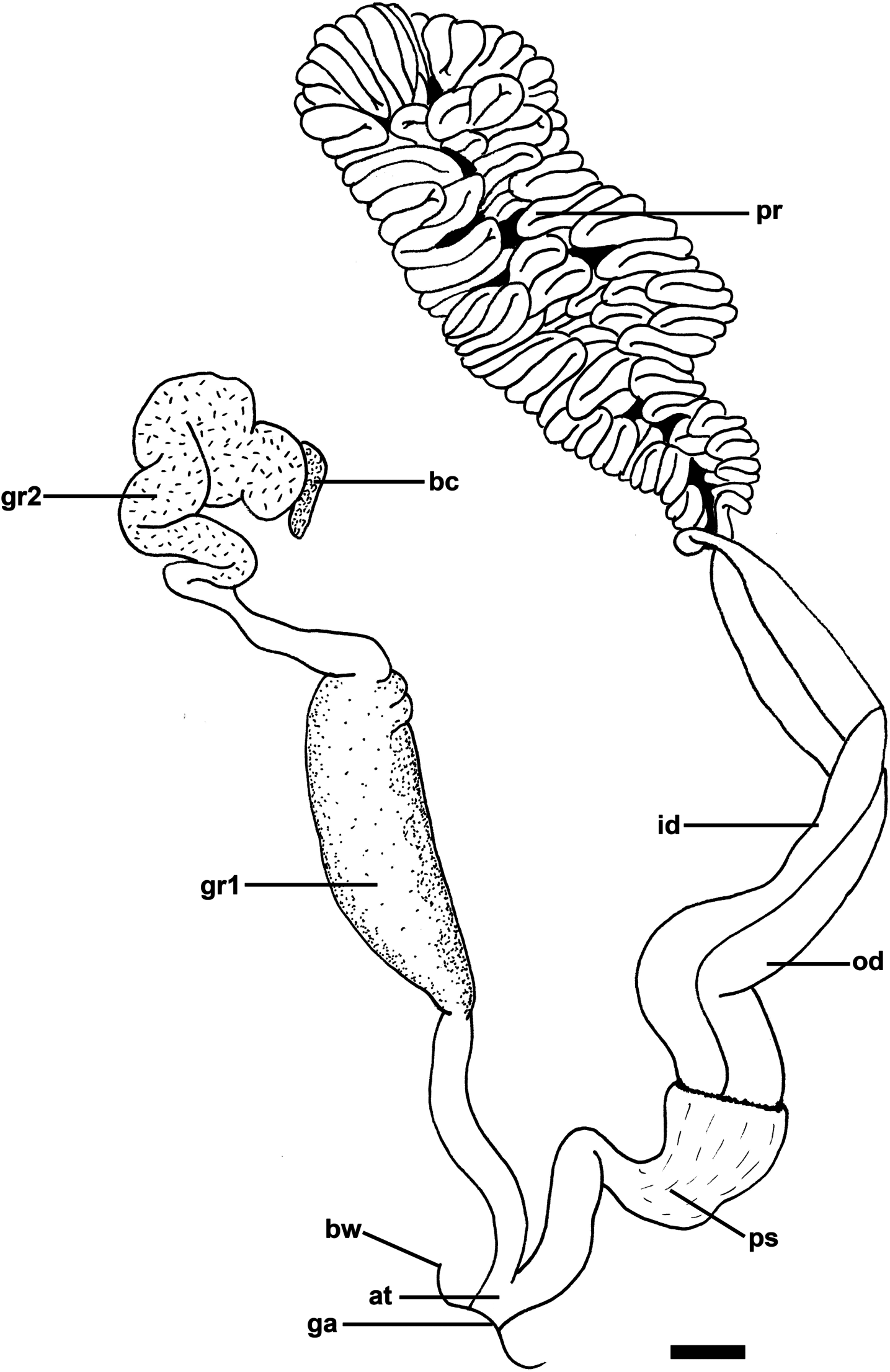
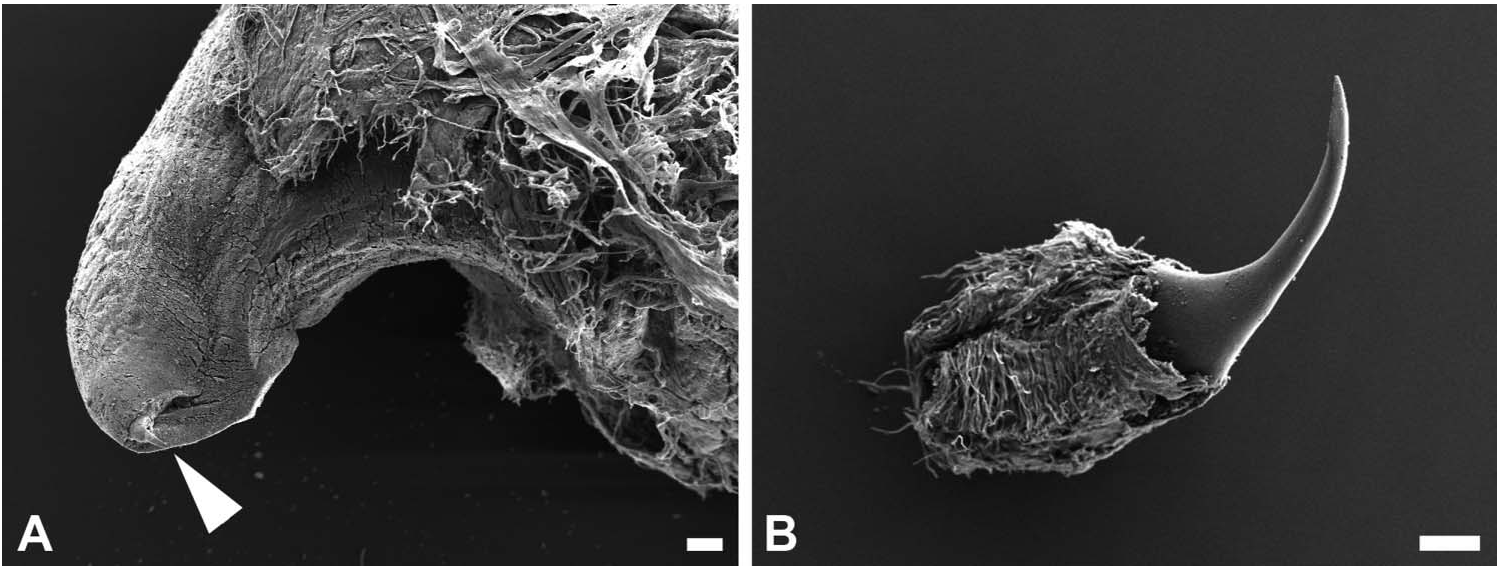
Reproductive system ( Figures 2 View Figure 2 , 3 View Figure 3 ): separated into two parts: male copulatory system in cephalic region opening laterally at the right side of mouth and hermaphroditic gonoduct in posterior part of body (not studied; glands were burst); both parts interconnected through external seminal groove that lies laterally along right side of body. Male copulatory system: genital opening followed by short atrium bifurcated into two distinct parts (hereafter designated as penial and glandular); penial part with invaginable penis enclosed in thick sheath; penis muscular, armed with apical sharp long hook; penis connected to long wide pair of ducts fused axially to each other, continuous with large prostate; prostate tightly coiled in a complex convoluted duct structure. Glandular part with tubular shape; two wider glandular regions, distal one convoluted, ending as a narrow terminal blind caecum.
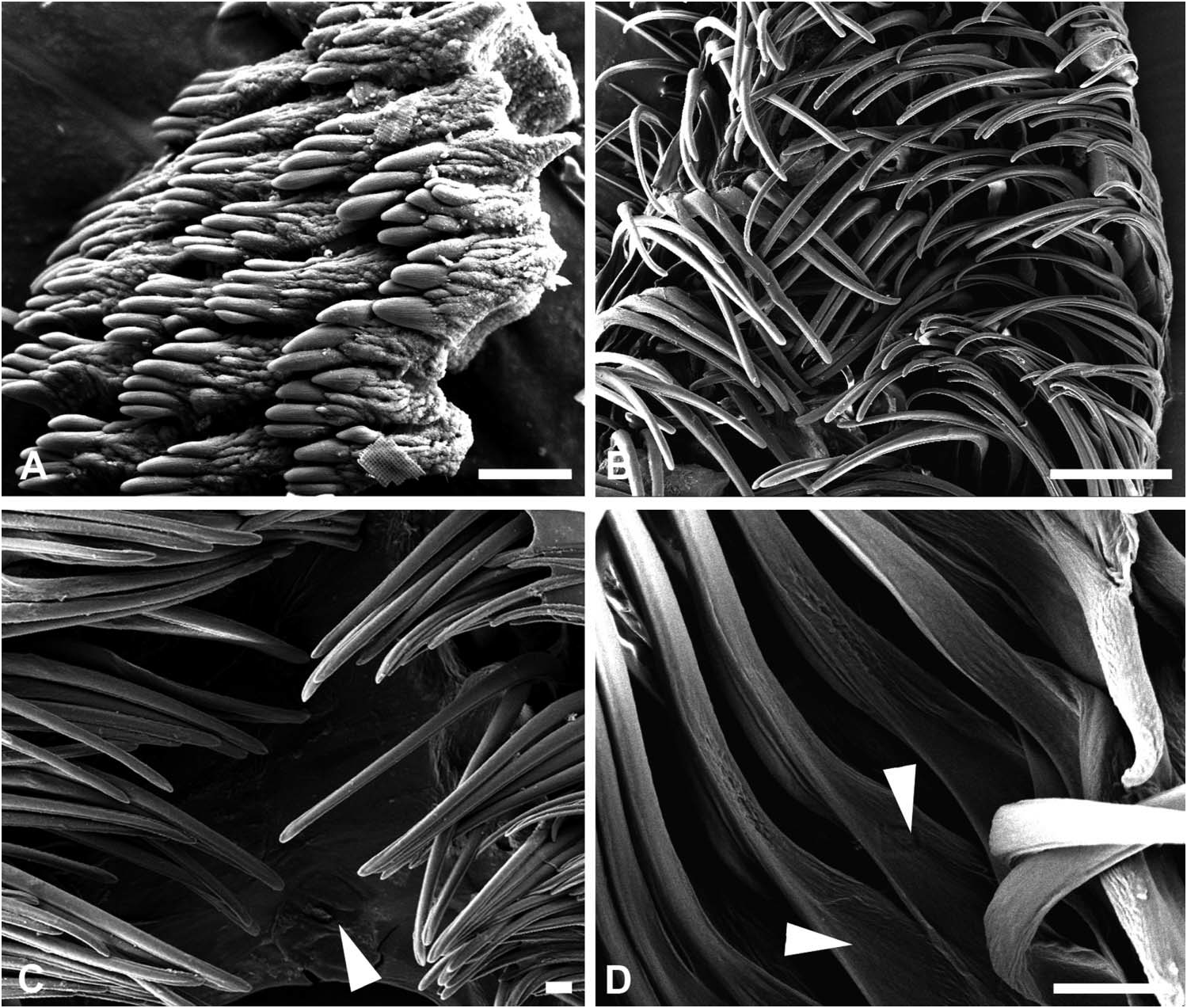
Jaws ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 ): paired, located on each side of mouth; narrow plate, embedded on margin of labial cuticle; composed of developed denticulate, multifid elements.
Radula ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 ): radular formula 25-13.0.13-25. Rachidian tooth absent; wide central toothless area. Lateral tooth large and thin, with smooth edges and broader base.
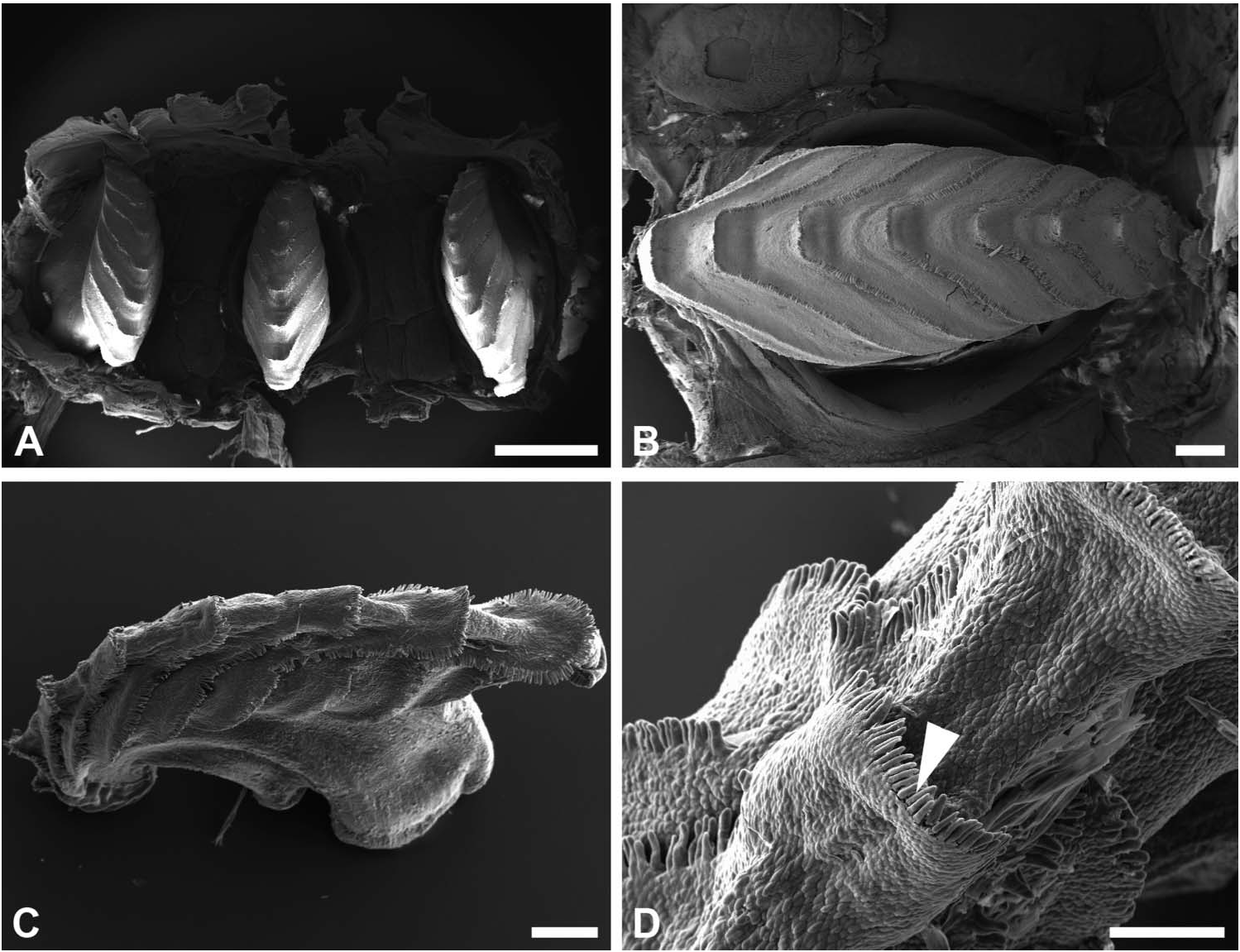
Gizzard ( Figure 5 View Figure 5 ): located between oesophagus and stomach; three corneous plates, with identical shape and size; plates with eight transverse V-shape ridges, with margin slightly hanging over the following ridge; rim of ridges bordered by row of short cylindrical sharp elements. Gizzard spines absent.
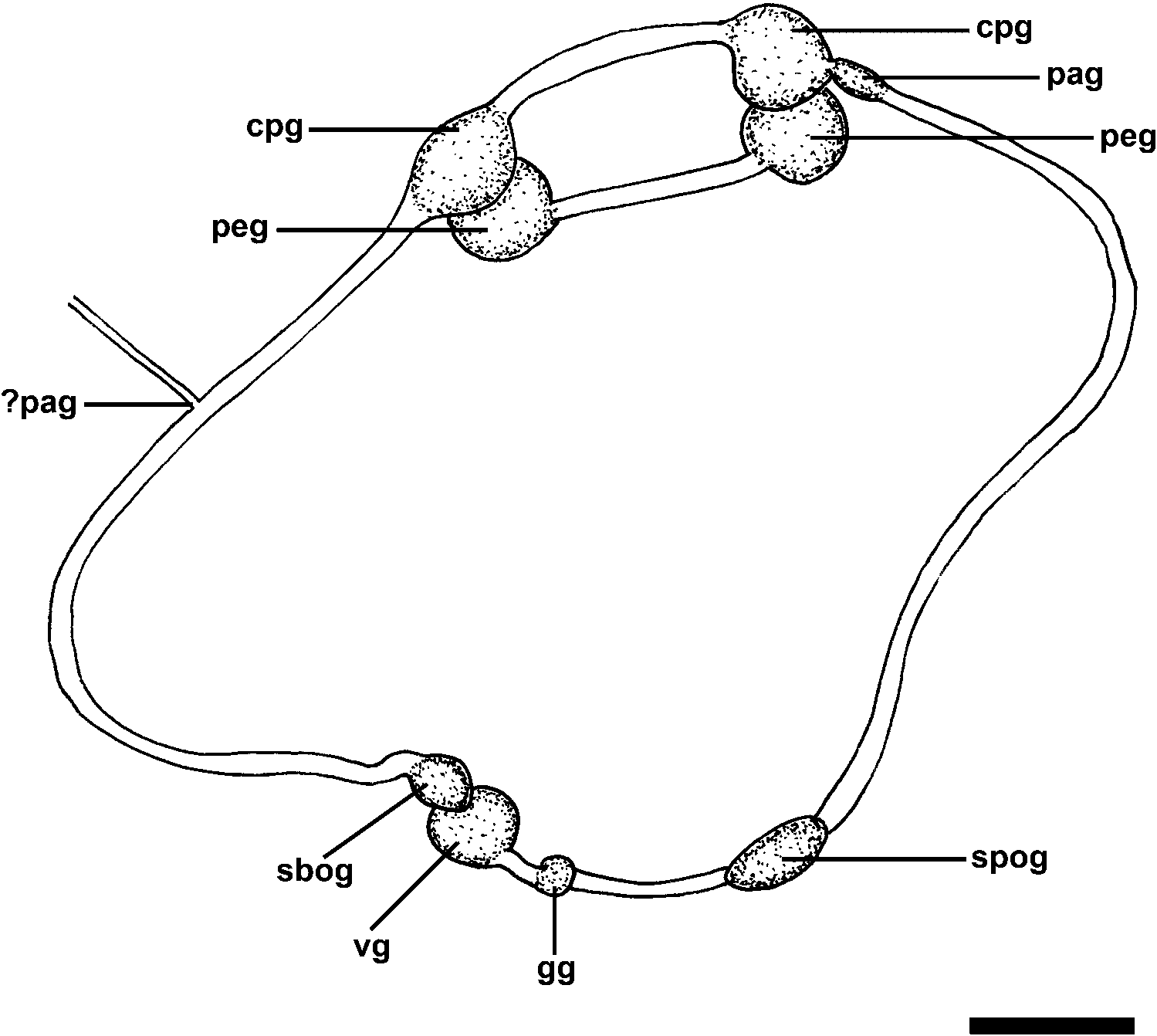
Central nervous system ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 ): euthyneuran. Circumoesophageal nerve ring post-pharyngeal. Cerebral and pleural ganglia fused; pedal ganglia separated. Cerebral– pleural and pedal ganglia of similar size and larger than others; left and right cerebral– pleural and pedal ganglia connected to each other by commissures. Right parietal ganglion smaller, connected to cerebral–pleural ganglion. Left parietal ganglia imperceptible (maybe absent). Larger supraoesophageal ganglion arising from nerve cord on posterior right side. Smaller suboesophageal ganglion in left nerve cord, contiguous with larger visceral ganglion. Genital ganglion on posterior left side, located behind visceral ganglion where both nerve cords merge.
Phylogenetic analysis. The phylogenetic analysis yielded a clade containing all genera of Haminoeidae including Bullacta with a PP of 0.9 ( Figure 7).
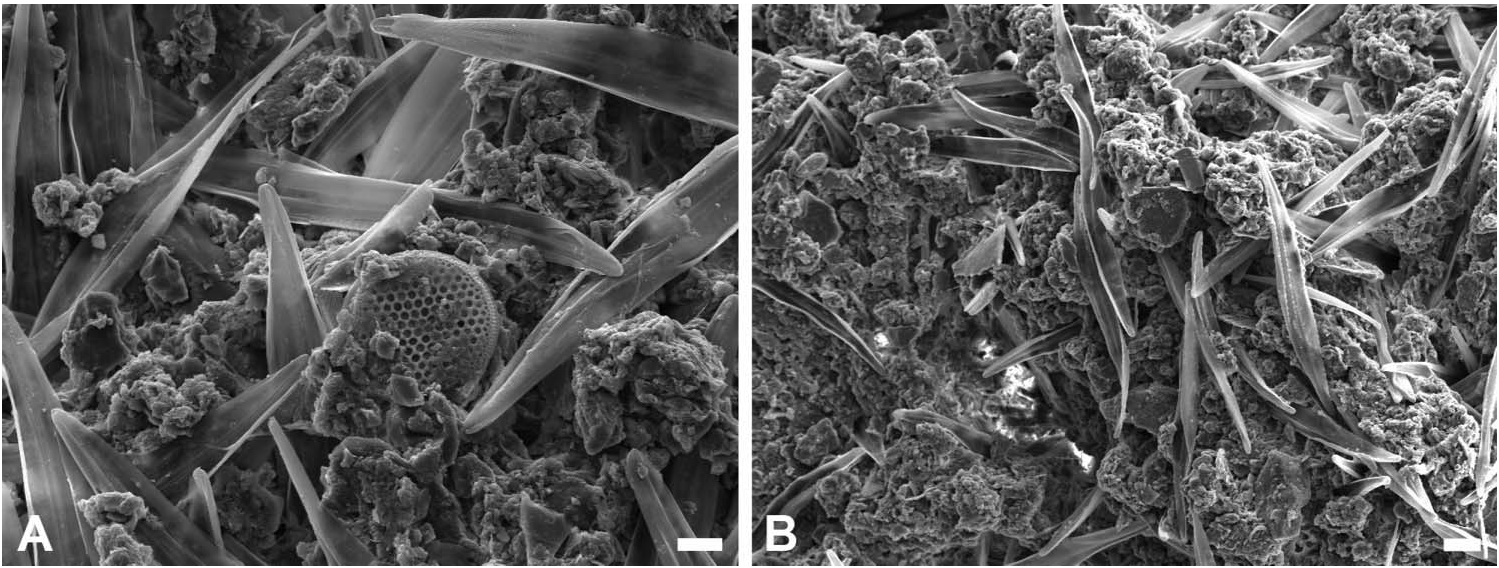
Trophic ecology. Observation of the food items contained in the gut of two specimens of Bullacta exarata revealed exclusively the presence of diatoms embedded in a matrix of mucous with few sand grains; there was a clear dominance of an unidentified species of the order Pennales with sporadic occurrence of Centrales diatoms ( Figure 8 View Figure 8 ).
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Bullacta exarata ( Philippi, 1849 )
| details, Publication, authors, including instructions for, information, subscription, http, www. tandfonline. com, loi & tnah 20 2010 |
Sinohaminea tsangkouensis
| Tchang S 1933: 371 |
Bullacta exarata
| Guangyu L 2004: 146 |
| Burn R & Thompson TE 1998: 955 |
| Guangyu L 1997: 109 |
| Habe T 1952: 143 |
| Tchang S 1934: 3 |
| Thiele J 1926: 106 |
Atyscaphander exarata
| Annandale TN 1924: 34 |
Haminea exarata
| Kobelt W 1896: 107 |
| Pilsbry HA 1895: 362 |
| Menke KT 1854: 46 |
Philine caurina
| Pruvot-Fol A 1953: 8 |
| Bergh R 1901: 293 |
| Pilsbry HA 1895: 9 |
Bullaea caurina
| Benson WH 1856: 128 |
Haminea sinensis A. Adams, 1850 , p 582
| Adams A 1850: 582 |
Bullaea exarata
| Philippi RA 1849: 141 |