Chelonus (Stylochelonus), Hellen, 1958
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5412.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DB6DD20F-6EB7-4152-AC80-2F67EE06684B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10729347 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2B5587AD-F07E-7308-FF39-6CE5FA4EB840 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chelonus (Stylochelonus) |
| status |
|
Subgenus Stylochelonus Hellén, 1958
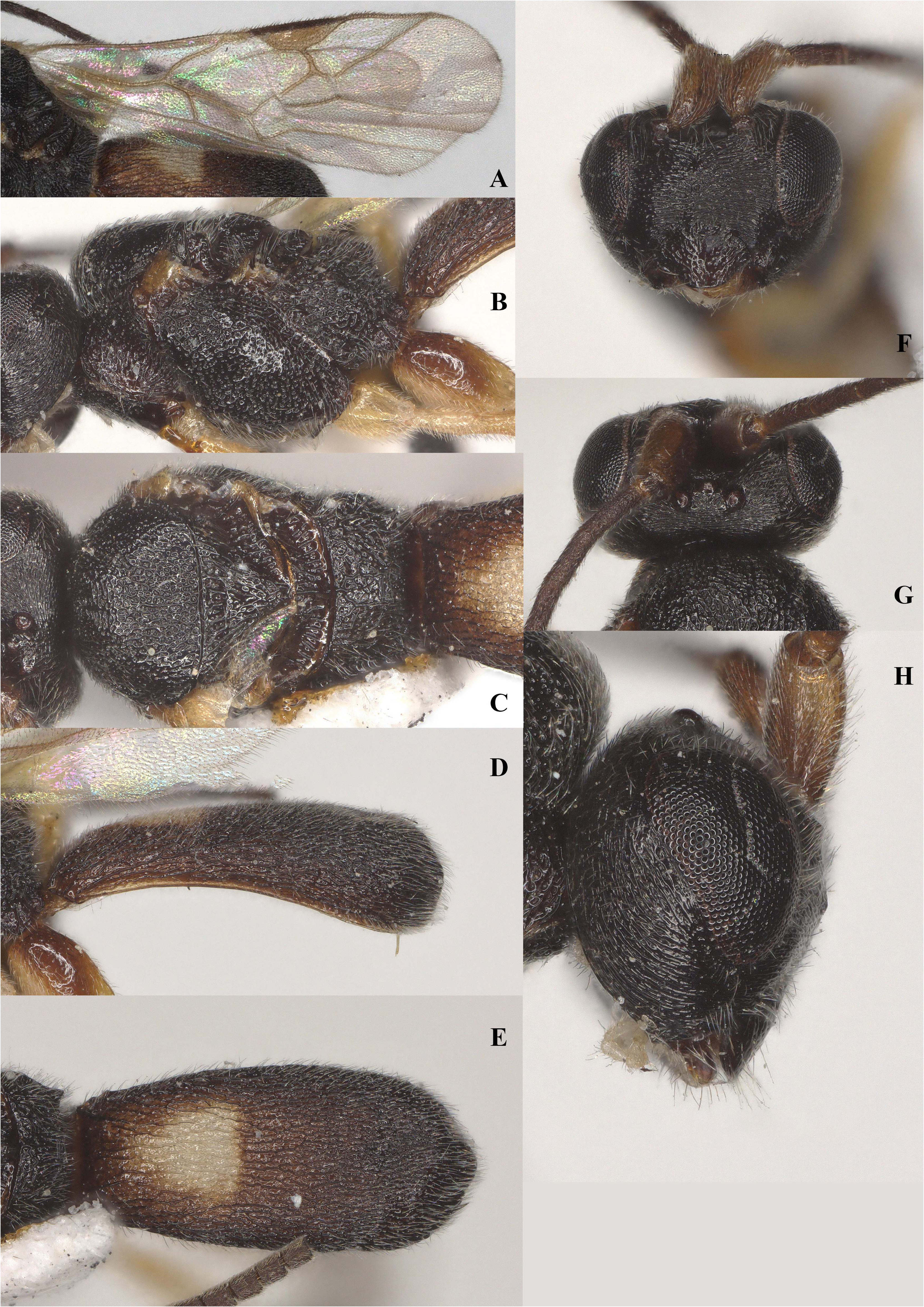
Diagnosis. Head transverse; antennomeres of both sexes more than 16, often distinctly widened medially in females; eye densely setose; frons and vertex very coarsely rugose; face flat, either striate-rugose or reticulate-rugose; clypeus often finely punctate, with distinct setosity and shiny; mesoscutum and scutellum evenly convex, densely alveolate-rugose; propodeum coarsely rugose; vein 1-SR+M of fore wing absent; hind coxa, femur and apex of tibia distinctly robust; metasomal carapace of male with small apical opening, which may be filled by point-like sclerite; carapace of female usually with an apical tooth; carapace apically usually rounded in dorsal view, rarely narrowed posteriorly.
Biology. Parasitoids of Elachistidae and Tortricidae ( Yu et al. 2016) .
Distribution. Worldwide ( Yu et al. 2016).
Key to species of subgenus Stylochelonus Hellén, 1958
1 Females............................................................................................. 2
- Males............................................................................................. 14
2 Carapace of female without an apical tooth in dorsal view ( Fig. 102E View FIGURE 102 )........................................... 3
- Carapace of female with an apical tooth in dorsal view ( Fig. 106E View FIGURE 106 ).............................................. 4
3 Temples strongly narrowed behind eyes in dorsal view; head 2.5 × wider than long in dorsal view ( Fig. 102G View FIGURE 102 ); legs dark ( Fig. 101 View FIGURE 101 )............................................................................. C. ( S.) acaretrus sp. nov.
- Temple almost parallel-sided behind eyes in dorsal view; head 1.6 × wider than long in dorsal view; legs pale...................................................................................... C. ( S.) interpositus ( Tobias, 1995)
4 Legs pale or yellowish brown ( Fig. 105 View FIGURE 105 )................................................................... 5
- Legs dark brown or black............................................................................... 9
5 Temples distinctly widened behind eyes in dorsal view; [vein 1-R1 of fore wing shorter than pterostigma]............... 6
- Temples parallel-sided or slightly narrowed behind eyes in dorsal view ( Fig. 106G View FIGURE 106 )................................. 7
6 Length of 3 rd antennomere 4.0 × its width; mesosoma 1.3 × longer than high in lateral view................................................................................................. C. ( S.) mucronatus ( Thomson, 1874) View in CoL
- Length of 3 rd antennomere 3.0 × its width; mesosoma 1.7 × longer than high in lateral view. C. ( S.) pedator ( Dahlbom, 1833) View in CoL
7 Vein 1-R1 of fore wing shorter than pterostigma; vein r of fore wing straight ( Fig. 106A View FIGURE 106 )...... C. ( S.) punctulosus sp. nov.
- Vein 1-R1 of fore wing as long as or longer than pterostigma; vein r of fore wing curved............................. 8
8 Mesosoma 1.5 × longer than high in lateral view; face 2.0 × wider than high............ C. ( S.) pusillus ( Szépligeti, 1908)
- Mesosoma 1.7 × longer than high in lateral view; face 1.5 × wider than high............. C. ( S.) elachistae ( Tobias, 1995)
9 Temples distinctly widened behind eyes in dorsal view....................................................... 10
- Temples parallel-sided or slightly narrowed behind eyes in dorsal view.......................................... 12
10 Vein 1-R1 of fore wing longer than pterostigma; penultimate antennomere shorter than wide.. C. ( S.) koponeni ( Tobias, 1995)
- Vein 1-R1 of fore wing as long as or shorter than pterostigma; penultimate antennomere as long as wide or longer....... 11
11 Penultimate antennomere as long as wide; antennomeres of female 21–22................ C. ( S.) karadagi ( Tobias, 1995)
- Penultimate antennomere longer than wide; antennomeres of female 23................ C. ( S.) subpedator ( Tobias, 1995)
12 Posterior excavation of head deep; antennomeres of female 17; sculpture at base of carapace reticulate-rugose................................................................................ C. ( S.) septemdecimplex ( Tobias, 1986)
- Posterior excavation of head shallow; antennomeres of female 20; sculpture at base of carapace longitudinally rugose................................................................................ C. ( S.) magadani ( Tobias, 1994)
14 Carapace of male with an apical tooth in dorsal view ( Fig. 108E View FIGURE 108 )......................... C. ( S.) punctulosus sp. nov.
- Carapace of male without an apical tooth in dorsal view ( Fig. 104E View FIGURE 104 )............................................ 15
15 Fifth-ninth antennomeres of male yellow and more distal antennomeres brown; antenna clearly widened beyond middle ( Fig. 104I View FIGURE 104 ); [vein r of fore wing slightly curved ( Fig. 104A View FIGURE 104 ); temples narrowed behind eyes in dorsal view ( Fig. 104H View FIGURE 104 )]......................................................................................... C. ( S.) acaretrus sp. nov.
- Fifth-ninth antennomeres of male brown or dark brown as more or less distal antennomeres......................... 16
16 Legs pale or yellowish brown........................................................................... 17
- Legs dark brown or black.............................................................................. 19
17 Temples distinctly widened behind eyes in dorsal view; vein 1-R1 of fore wing shorter than pterostigma........................................................................................... C. ( S.) pedator ( Dahlbom, 1833) View in CoL
- Temples parallel-sided or slightly narrowed behind eyes in dorsal view; vein 1-R1 of fore wing as long as pterostigma or longer............................................................................................. 18
18 Mesosoma 1.5 × longer than high in lateral view; metasomal carapace 2.0 × longer than wide in dorsal view....................................................................................... C. ( S.) interpositus ( Tobias, 1995)
- Mesosoma 1.7 × longer than high in lateral view; metasomal carapace 1.8–1.9 × longer than wide in dorsal view.................................................................................... C. ( S.) elachistae ( Tobias, 1995)
19 Apical aperture of carapace in posterior view large, occupying about 0.3 of carapace width.......................... 20
- Apical aperture of carapace in posterior view occupying 0.1–0.2 of carapace width................................ 21
20 Face narrow, about 1.6 × wider than high; mesosoma 1.5 × longer than high in lateral view.. C. ( S.) lissofossa ( Tobias, 2000)
- Face about 2.0 × wider than high; mesosoma 1.3 × longer than high in lateral view...... C. ( S.) cariniventris ( Tobias, 1996)
21 Apical aperture located in upper half of posterior part of metasomal carapace and oblique to horizontal plane; [vein 1-R1 of fore wing shorter than pterostigma; mesosoma 2.0 × longer than high in lateral view]............ C. ( S.) elongatus ( Papp, 1971)
- Apical aperture located in middle of posterior face of metasomal carapace and in vertical plane...................... 22
22 Vein 1-R1 of fore wing longer than pterostigma; [mesosoma 2.0 × longer than high in lateral view; apical aperture in posterior view occupying about 0.2 of metasomal carapace width].............................. C. ( S.) koponeni ( Tobias, 1995)
- Vein 1-R1 of fore wing as long as pterostigma or shorter..................................................... 23
23 Vein r of fore wing shorter than vein 3-SR; [antennomeres of male 23; apical aperture in posterior view occupying 0.18–0.23 of metasomal carapace width]................................................... C. ( S.) karadagi ( Tobias, 1995)
- Vein r of fore wing longer than vein 3-SR................................................................. 24
24 Face about 3.0 × wider than high; [antennomeres of male 25; mesosoma 1.5 × longer than high in lateral view]........................................................................................ C. ( S.) clausus ( Tobias, 1996)
- Face less than 2.0 × wider than high..................................................................... 25
25 Length of 3 rd antennomere 4.0 × its width; mesosoma 1.3 × longer than high in lateral view................................................................................................. C. ( S.) mucronatus ( Thomson, 1874) View in CoL
- Length of 3 rd antennomere less than 3.5 × its width; mesosoma more than 1.5 × longer than high in lateral view......... 26
26 Face 2.0 × wider than high; metasomal carapace 1.8–1.9 × longer than wide in dorsal view..................................................................................................... C. ( S.) pusillus ( Szépligeti, 1908)
- Face 1.5 × wider than high; metasomal carapace 2.0–2.2 × longer than wide in dorsal view.................................................................................................... C. ( S.) subpedator ( Tobias, 1995)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |