Simulium ( Simulium ) tiomanense, Takaoka & Sofian-Azirun & Belabut, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5349718 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F687C3-171C-FFFA-C85D-0B24FB9411F2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Tatiana |
|
scientific name |
Simulium ( Simulium ) tiomanense |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Simulium ( Simulium) tiomanense View in CoL , new species
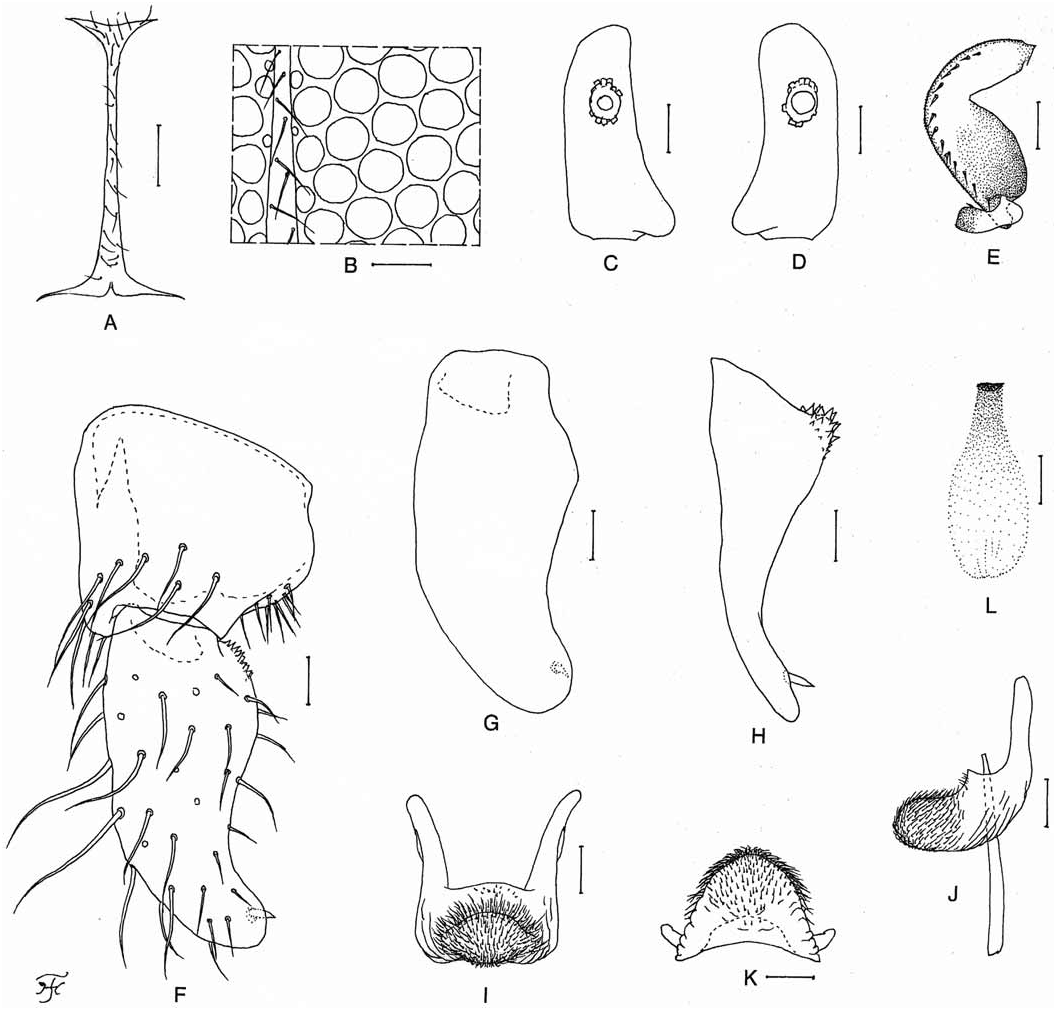
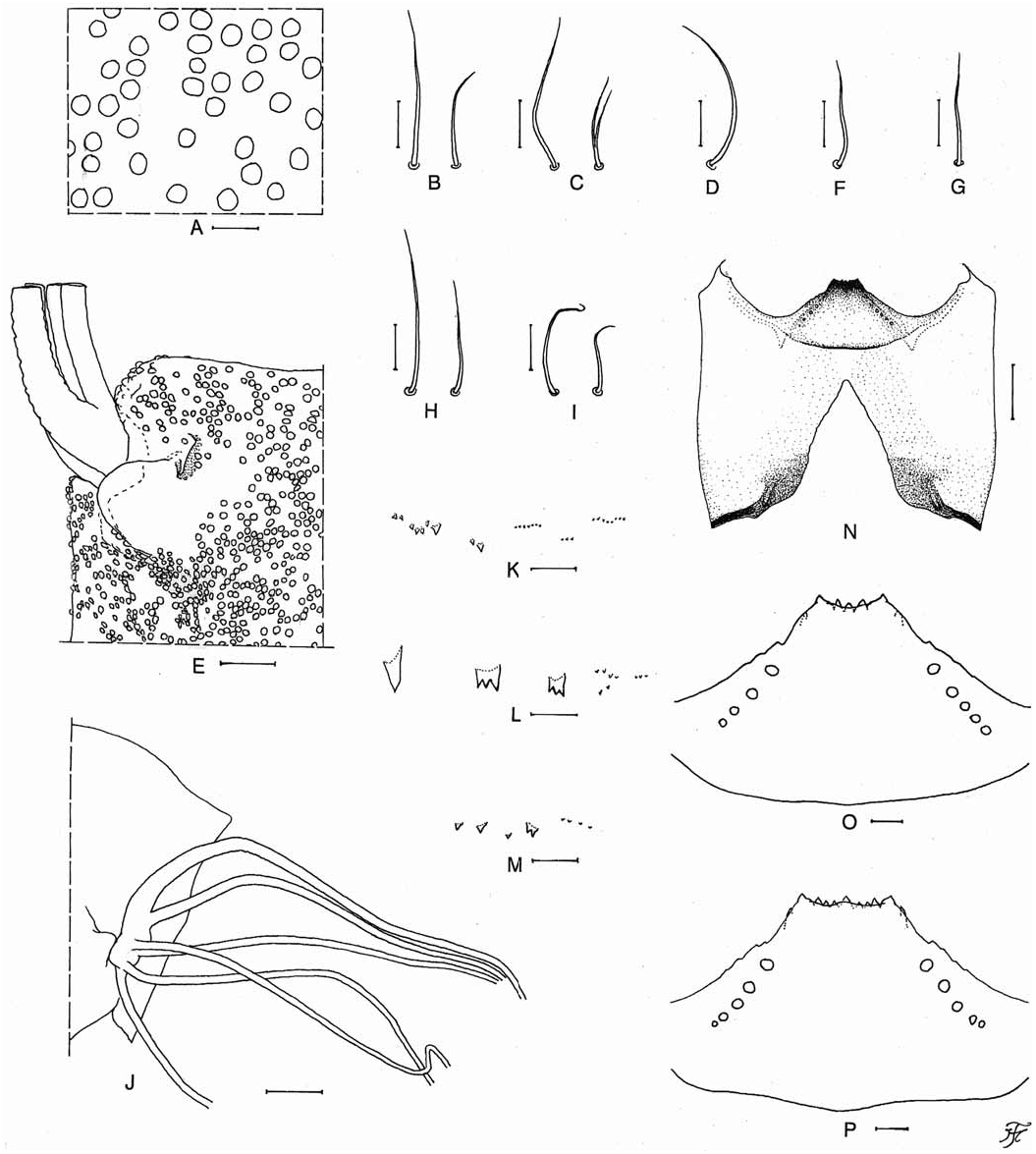
( Figs. 4A–L View Fig , 5A–P View Fig )
Material examined. — Holotype: pharate male (with associated pupal exuviae and cocoon) (preserved in 80% ethanol), collected from a small stream (Sungai Tedau, width 0.5–2.0 m, water temperature 25.0°C, shaded) moderately flowing in a forest, Tioman Island , Malaysia, coll. D.M. Belabut, 3–7 Apr.2011.
Paratypes: 1 mature larva and 1 immature larva (preserved in 80% ethanol), same data as those of holotype .
Description. — Pharate male (dissected out of pupa). Body length 2.4 mm. Nearly as in male of S. ( S.) jasmoni , new species, except following characteristics. Head. Dichoptic. Frons ( Fig. 4A View Fig ) present, though very narrow, and covered with dark short hairs. Upper eye consisting of 16 vertical columns and 16 or 17 horizontal rows of large facets, which are slightly separated from one another leaving distinct interspaces (usually closely spaced, leaving no interspaces) and nearly round (usually hexagonal) ( Fig. 4B View Fig ). Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and 9 flagellomeres, dark brown except scape and pedicel dark yellow; 1 st flagellomere elongate, 1.8 times as long as 2 nd one. Proportional lengths of 3 rd, 4 th, and 5 th segments of maxillary palp 1.00:1.10:2.43; 3 rd segment ( Fig. 4C, D View Fig ) with widened apical portion; sensory vesicle ( Fig. 4C, D View Fig ) ellipsoidal, 0.24 times as long as 3 rd segment and with medium-sized or large opening. Legs. Foreleg: coxa yellow; trochanter light brown; femur light brown except apical cap dark brown; tibia dark brown (though median portion of inner surface light brown) except median large portion of outer surface white and with white sheen when illuminated at certain angle of light; tarsus brownish-black to black with relatively thick hair crest; basitarsus greatly dilated, 4.27 times as long as its greatest width. Midleg: coxa brownish-black; trochanter light brown; femur light brown except apical cap dark brown; tibia medium to dark brown except posterior surface of basal 1/3 narrowly white and with white sheen when illuminated at certain angle of light; tarsus light brown except basal 3/4 of basitarsus and basal 1/2 of 2 nd tarsomere yellowish-white. Hind leg: coxa dark brown; trochanter light brown; femur light brown with apical cap dark brown and base yellow; tibia medium to dark brown except posterior surface of basal 1/4 white, and with white sheen when illuminated at certain angle of light; tarsus ( Fig. 4E View Fig ) medium to dark brown except little more than basal 1/2 of basitarsus yellowish-white and 2/3 of 2 nd tarsomere yellowish-white; basitarsus ( Fig. 4E View Fig ) enlarged, possibly wedge-shaped; calcipala ( Fig. 4E View Fig ) nearly as long as wide. Pedisulcus ( Fig. 4E View Fig ) well developed. Abdomen. Segments 2, 6, and 7 each with pair of white dorsolateral patches which are brilliantly shiny when illuminated at certain angle of light. Genitalia. Coxite in ventral view ( Fig. 4F View Fig ) nearly quadrate, nearly as long as wide. Style in ventral view ( Fig. 4F View Fig ) gently bent inward, widened from base toward basal 1/3, then gradually tapered to apex and with subapical spine; style in ventrolateral view ( Fig. 4G View Fig ) widened from base to basal 1/3, then gradually tapered to apex, with subapical spine, and 2.21 times as long as its greatest width at basal 1/3; style in medial view ( Fig. 4H View Fig ) 1.55 times as long as coxite, with short basal protuberance bearing about 16 stout cone-like spines, gradually tapered to little more than apical 1/3, then nearly parallel-sided to apex, and with subapical spine. Ventral plate in ventral view ( Fig. 4I View Fig ) with body quadrate, though very slightly widened posteriorly, 0.55 times as long as wide, with anterior margin very slightly produced and posterior margins nearly straight, and basal arms of moderate length, directed forward and moderately divergent; ventral plate in lateral view ( Fig. 4J View Fig ) with ventrally produced hairy process; ventral plate in end view ( Fig. 4K View Fig ) rounded ventrally, with lateral margins weakly toothed on basal 1/2, and moderately covered with microsetae on posterior surface except lateral areas of basal 1/2 widely bare. Median sclerite ( Fig. 4L View Fig ) gradually widened from base to middle, then nearly parallel-sided to near apex, plate-like, and well sclerotized basally; base of median sclerite located apart from anterior margin of ventral plate ( Fig. 4J View Fig ). Abdominal segment 10 with 5 or 6 fine short hairs on each posterolateral surface. Cercus small, rounded, with 7 or 8 fine short hairs.
Pupa. Body length 2.5 mm. Head. Integument yellowishbrown, moderately covered with round relatively large tubercles ( Fig. 5A View Fig ) on frons and on upper part of lateral surfaces; antennal sheath with low protuberances and sparsely or moderately covered with round smaller tubercles; frons with 2 pairs of trichomes with uncoiled apices (1 simple and medium-long, 1 simple or bifid and short) ( Fig. 5B, C View Fig ); face with pair of simple medium-long trichomes with uncoiled apices ( Fig. 5D View Fig ). Thorax. Integument yellow to yellowish-brown, moderately covered with round relatively large tubercles, with small pit-like organ near base of gill on each side ( Fig. 5E View Fig ), and with 1 simple short trichome with uncoiled apex anterodorsally ( Fig. 5F View Fig ), 1 simple short trichome with uncoiled apex ( Fig. 5G View Fig ) mediodorsally, 2 simple trichomes with uncoiled apices (1 medium-long and 1 short) anterolaterally ( Fig. 5H View Fig ), and 2 simple short trichomes with uncoiled apices ventrolaterally ( Fig. 5I View Fig ) on each side; mediolateral trichome and 1 of 3 ventrolateral trichomes lost on each side. Gill ( Fig. 5J View Fig ) composed of 6 slender threadlike filaments, arranged in 2+1+1+2 filaments from dorsal to ventral, with no common basal stalk; dorsal paired filaments with very short stalk, ventral pair with very short stalk or almost sessile, and 2 filaments in middle unpaired and each arising individually though lying side by side very closely at base; all filaments light brown except uppermost filament dark brown; uppermost filament thick basally, then gradually tapered toward apex, other filaments nearly same in thickness for most of their lengths though slightly tapered near apex; relative thickness of 6 filaments from dorsal to ventral when basal portions are compared 1.00:0.60:0.45 (outer middle filament):0.56 (inner middle filament):0.45 (outer ventral filament):0.50 (inner ventral filament); relative length of 6 filaments not available due to loss of apical portions of all filaments; all filaments with well-defined annular ridges and furrows though becoming less marked apically, densely covered with minute tubercles. Abdomen. Nearly as in S. ( S.) jasmoni , new species, except following characteristics: segments 7–9 each with spine-combs in transverse row (though those on segments 7 and 9 much smaller than those on segment 8) ( Fig. 5K–M View Fig ); segment 9 without terminal hooks. Ventrally, segment 5 with pair of simple or bifid hooks submedially and few very short simple slender setae on each side; segments 6 and 7 each with pair of simple or bifid inner and simple outer hooks somewhat spaced from each other and few very short simple slender setae on each side. Cocoon. Wall-pocket shaped, tightly woven, not extended ventrolaterally; anterior margin thickly woven; posterior 1/2 with floor roughly or moderately woven; individual threads invisible; 2.8 mm long by 2.1 mm wide.
Mature larva. Body length 5.1 mm. Body almost uniformly dark gray to greyish-brown when viewed dorsally. Cephalic apotome yellowish-white on anterior 1/2 and light to medium brown on posterior 1/2, with medial area along posterior margin dark brown; anterior spot of 2 mediolongitudinal spots medium brown, well defined on yellowish-white background, posterior spot of 2 mediolongitudinal spots medium brown, not well defined, merged into medium brown background, lateral spots dark brown on anterior 1/2 and medium brown on posterior 1/2, and thus anterior part appearing positive and posterior part negative on medium to dark brown background, posterolateral spots light brown, appearing negative on medium brown background. Lateral surface of head capsule medium brown except eye-spot region whitish on dorsal 1/2 and yellowish except areas along ventral and posterior margins medium brown; eyebrow distinctly defined; spots below and posterior to eye-spot region indistinct. Ventral surface of head capsule ( Fig. 5N View Fig ) yellow except wide area along each lateral margin of postgenal cleft and near posterior margin medium brown; transverse spot on each side of postgenal cleft indistinct or faintly negative; basal area on each side of postgenal cleft dark brown as usual. Cervical sclerite composed of pair of yellow small oblong pieces, not fused to occiput, moderately separated medially from each other. Antenna composed of 3 segments and apical sensillum, much longer than stem of labral fan; proportional lengths of 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd segments 1.00:1.05:0.64. Labral fan with 40 main rays. Mandible with mandibular serration composed of 2 teeth; major and longer tooth at obtuse angle to mandible on apical side; comb-teeth decreasing in length from 1 st tooth to 3 rd one though 2 nd tooth very slightly longer than 3 rd one; supernumerary serrations absent. Hypostoma ( Fig. 5O View Fig ) with 5 anterior teeth consisting of 1 median tooth, 2 submedian teeth and 2 corner teeth (the reduced number of anterior teeth in this unique mature larva might be abnormal, because an immature larva of the same species has a hypostoma with 9 anterior teeth –– Fig. 5P View Fig ); each corner tooth prominent and median tooth shortest; lateral margins weakly serrate apically; 4 or 5 hypostomal bristles divergent posteriorly from lateral border on each side. Postgenal cleft ( Fig. 5N View Fig ) narrow, triangular, deep (4.37 times as long as postgenal bridge), with pointed apex. Thoracic cuticle almost bare. Abdominal cuticle almost bare except each side of anal sclerite and each lateral bulge moderately covered with short colourless setae. Rectal scales present. Rectal organ not observable because it was withdrawn. Anal sclerite X-shaped, with broadened anterior arms 0.71 times as long as posterior ones, with wide thinly-sclerotized extension between anterior arms; basal juncture area with very narrow median incision opening posteriorly; 9 sensilla posterior to posterior arms. Last abdominal segment on each side with moderately developed bulge laterally and small one ventrolaterally, appearing to be small ventral papillae when viewed ventrolaterally. Posterior circlet with 84 rows of hooklets with up to 14 hooklets per row.
Female. Unknown.
Biological notes. — The pupa and larvae of this new species were collected from stalks of grasses trailing in the water. Associated species were S. ( S.) jasmoni , new species and S. ( G.) sp.
Etymology. — The species name tiomanense refers to the name of the island, Tioman, where this new species was collected.
Remarks. — Simulium ( S.) tiomanense , new species, is assigned to the tuberosum species-group of the subgenus Simulium on the basis of the male genitalia ( Fig. 4F–L View Fig ) and the pupal gill with 6 filaments ( Fig. 5J View Fig ).
The male of this new species is striking in having the dichoptic head (in place of the usual holoptic head), which is divided by a very narrow frons ( Fig. 4A View Fig ), as well as the round enlarged facets (in place of the usual hexagonal facets), these characteristics being very rarely recorded in the family Simuliidae . However, future studies are needed to confirm whether these rare head characteristics seen in the holotype male are also commonly found in other male specimens of S. ( S.) tiomanense , new species.
This new species is also remarkable in having the pit-like organ adjacent to the base of the pupal gill ( Fig. 5E View Fig ). The pit-like organ is a diagnostic characteristic of the clathrinum species-group, one of the six species-groups of the subgenus Simulium ( Morops) Enderlein in the Australasian Region ( Takaoka, 2003). This has been also reported in four species of the tuberosum species-group of the subgenus Simulium : S. ( S.) brevipar from Peninsular Malaysia (Takaoka & Davies, 1995), Sumatra ( Takaoka et al., 2000) and southern Thailand ( Takaoka et al., 2009), S. ( S.) sigiti Takaoka & Hadi, 1991 from Java (Takaoka & Hadi, 1991), S. ( S.) tianchi Chen, Zhang & Yang, 2003 from Hainan, China ( Chen et al., 2003), and S. ( S.) yuphae Takaoka & Choochote, 2005 from northern Thailand (Takaoka & Choochote, 2005). This new species is easily distinguished from all these four known species by the small pit-like organ ( Fig. 5E View Fig ) and the relatively large tubercles without secondary projections on the frons and thorax ( Fig. 5A View Fig ) (the pit-like organs are medium-sized and prominent, and the relatively large tubercles bear secondary minute projections in all the four known species) and also from S. ( S.) sigiti and S. ( S.) tianchi by the different relative thickness of the six gill filaments ( Fig. 5J View Fig ) (all six gill filaments are equal in thickness to one another in the latter two known species).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |