Hyperstoma Wittmer, 1979
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.207679 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6194991 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F487AC-BC71-C849-FF2F-37EDFAF5F400 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hyperstoma Wittmer, 1979 |
| status |
|
Hyperstoma Wittmer, 1979 View in CoL
Hyperstoma Wittmer, 1979: 84 View in CoL .
Type species. Hyperstoma marginata Wittmer, 1979 (by monotypy).
Diagnosis. Hyperstoma can be distinguished from other Ototretinae by combination of following characters: t erminal maxillary and labial palpomere extremely long, male antennae flabellate with stout branches attached to antennomere apex, male terminal and penultimate abdominal terga fused, jointly trilobed.
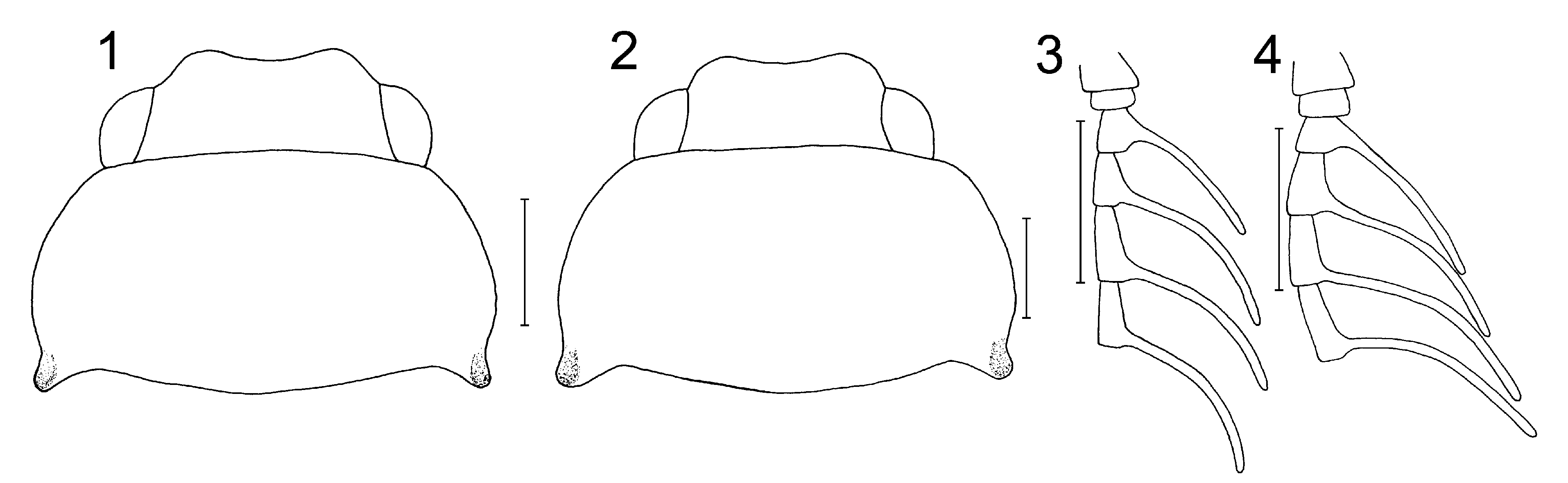
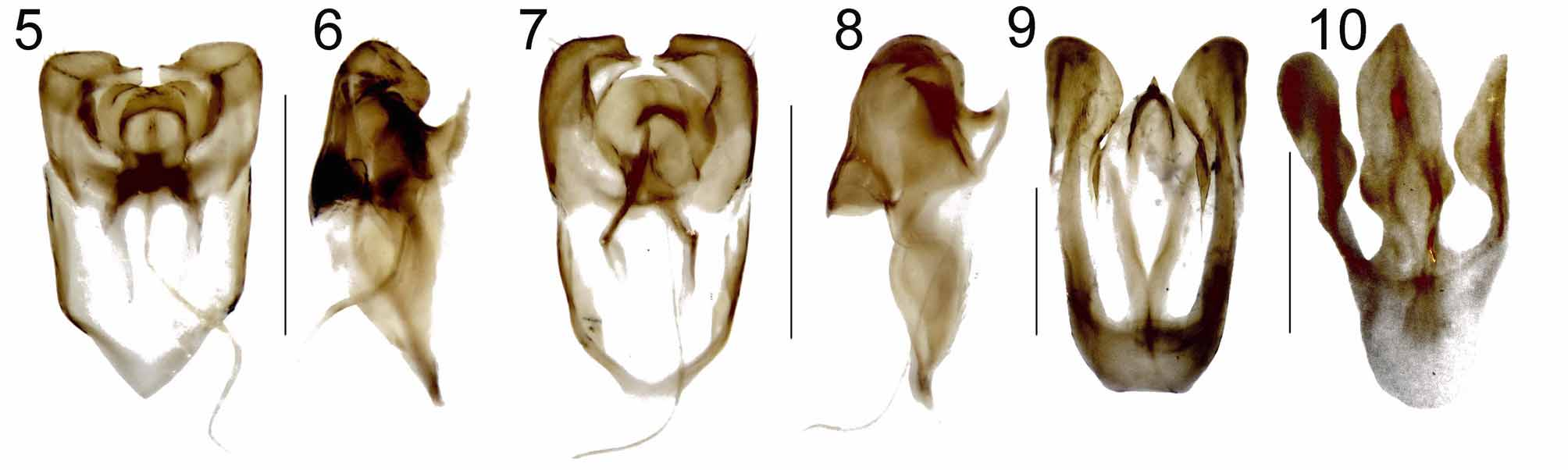
Description. Body length 5–5.5 mm, humeral width 2.05–2.35 mm, body oval, mainly yellow to light brown, distal portion of antennae and elytral margins dark brown. Head from above partly hidden by pronotum. Eyes small, distance between eyes 1.8–2× longer than eye diameter. Antennae 11-segmented, antennomeres 3–10 flabellate ( Figs 3, 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4. 1 – 2 ), lamellae strongly flattened, attached to antennomere terminal portion, branches of median antennomeres about 2.7–3× longer than antennomere body, branches of terminal antennomeres moderately shorter. Mandibles small, hooked, apically pointed. Maxillary palpi 4-segmented, labial palpi 3-segmented, terminal palpomeres of both palpi enlarged, flattened, oval, 2.2–3.3× longer than width. Pronotum ( Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1 – 4. 1 – 2 ) yellow to light brown, 1.8× as wide as long, anterior margin almost straight, anterior angles rounded, posterior angles triangular, projected obliquely backwards, provided with weak circular pit distally, median portion of pronotum with longitudinal groove. Scutellum triangular, yellow to light brown. Elytra elongate, each elytron about 2.7–3.4× longer than wide, widest medially, apex rounded. Elytra shiny, irregularly densely punctured, slightly pubescent, each elytron with 2 inconspicuous costae. Terminal abdominal sternum with oval basal portion and straight margins distally. Terminal and penultimate abdominal terga fused, jointly trilobed ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 5 – 10. 5 – 8 ) with straight or U-shaped basal portion. Penultimate tergum extending in 2 lateral protrusions, forming 2 longitudinal apertures along terminal tergum. Male genitalia with V-shaped phallobase ( Figs 5–8 View FIGURES 5 – 10. 5 – 8 ), paramerae robust, apex rounded or with oblique edge distally, paramerae about 1/5 longer than phallus. Phallus cochleariform, provided with short ventroapical projection and forked, angular projection basally ( Figs 6, 8 View FIGURES 5 – 10. 5 – 8 ). Female unknown.
Distribution. Sri Lanka.
Comment. Hyperstoma is closely related to the genera Lamellipalpus Maulik, 1921 and Lamellipalpodes Maulik, 1921 . All the genera share a unique synapomorphic character: fused terminal and penultimate terga.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Hyperstoma Wittmer, 1979
| Janisova, Kristyna & Bocakova, Milada 2011 |
Hyperstoma
| Wittmer 1979: 84 |