Dipolydora anatentaculata, Vı & Delgado-Blas, 2008
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222930701831240 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E87546-2560-FF9C-B2C7-FF20FDBAF974 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Dipolydora anatentaculata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Dipolydora anatentaculata View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figure 2 View Figure 2 )
Type material
Gulf of Mexico: Rookery Bay , Florida (26 ° 209N, 81 ° 789W), holotype (USNM- 1073344) .
Description
Holotype
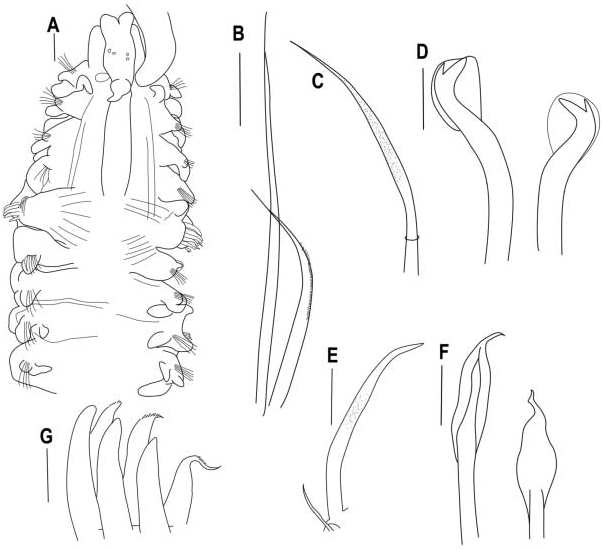
Incomplete specimen with 59 anterior segments, 8.5 mm long, 0.5 mm wide at chaetiger 6. Prostomium bifid, deeply notched along anterior margin, with two rounded antero-lateral processes. Four black eyes present in trapezoid arrangement.Caruncle extending posteriorly to segment 4. Occipital antenna present ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 ) at posterior end of prostomium, thick basally, tapering to pointed apex ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 ). Palps extending posteriorly for 23 segments. Colour in alcohol pale yellow. Body and palp pigmentation absent.
Chaetiger 1 with well-developed neuro- and notopodial lamellae ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 ), two to three capillaries in notopodia, and numerous longer capillaries in neuropodia. Winged capillary notochaetae of segments 2–4, 6 arranged in two rows; posterior notochaetae consisting of two types: anterior row of bristled chaetae, and posterior row of long slender capillaries ( Figure 2B View Figure 2 ). Neurochaetae of chaetigers 2–4, and 6 with two rows of unilimbate capillaries having fine granulations on shaft ( Figure 2C View Figure 2 ). Five bidentate hooded hooks ( Figure 2D View Figure 2 ) in neuropodia from chaetiger 7, with up to six hooks in a series at chaetiger 13, accompanied by two capillary chaetae on chaetigers 7–10, and up to five capillaries at chaetiger 11; hooks curved with wide angle between main fang and shaft, narrow angle between main fang and apical tooth, no constriction on shaft ( Figure 2D View Figure 2 ).
Chaetiger 5 greatly modified, larger than adjacent segments, lacking postchaetal lamellae, with five dorsal superior alimbate capillaries and one small capillary ( Figure 2E View Figure 2 ), and three to four ventral geniculate capillaries; slightly curved row of five major spines alternating with pennoned companion chaetae bearing bristles ( Figure 2F, G View Figure 2 ). Major spines simple falcate, without subterminal protuberance ( Figure 2G View Figure 2 ).
Branchiae starting from chaetiger 8, continued to posterior end of fragment. All branchiae basally free of notopodial lamellae.
Gizzard-like structure present in intestinal tract on segments 17–21.
Pygidium unknown.
Ecology
Dipolydora anatentaculata is found burrowing in gastropod shells, Cerithium eburneum (Bruguière) .
Remarks
Dipolydora anatentaculata sp. nov. belongs to the Dipolydora concharum / coeca / flava / socialis Group as defined by Blake (1996). It differs from all of them in possessing an occipital antenna. This species most closely resembles D. tentaculata Blake and Kudenov, 1978 in bearing an occipital antenna and in the simple nature of the major spines on chaetiger 5. It differs from D. tentaculata in having four eyes instead of none to two, simple falcate spines instead of spines with a subterminal swelling ( Blake and Kudenov 1978, Figure 39f), angle between teeth of hooded hooks consistent within a fascicle instead of angle between teeth decreasing from dorsal to ventral side of neurosetal fascicle, and in lacking pigment bars instead of having pigment bars on some anterior chaetigers.
Etymology
Gr. ana -, meaning similar to D. tentaculata .
Distribution
Gulf of Mexico: Rookery Bay , Florida .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |