Haplogonaria sophiae, Hooge, Matthew D. & Rocha, Carlos E. F., 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.174287 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6263425 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DE87D4-E623-FFB3-FE84-16AFFEC3FCDB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Haplogonaria sophiae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Haplogonaria sophiae sp. nov.
( Figs. 8–9 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 )
Type material. Holotype. MZUSP PL. 183, one set of 2-µm-thick serial sagittal sections of epoxy-embedded specimen stained with toluidine blue. Paratype. MZUSP PL. 184, one set of 2-µm-thick serial sagittal sections of epoxy-embedded specimens stained with toluidine blue.
Type locality. Itaçucê Island, São Sebastião Channel, São Paulo, Brazil, from coarse shelly sand with silt taken from 5 m water depth ( 23°49’S, 45°20’W).
Other material examined. Living specimens in squeeze preparations; whole mount for fluorescence imaging of musculature.
Etymology. Species name in honor of Ms. Sophie Suhr of Portland, Oregon, USA.
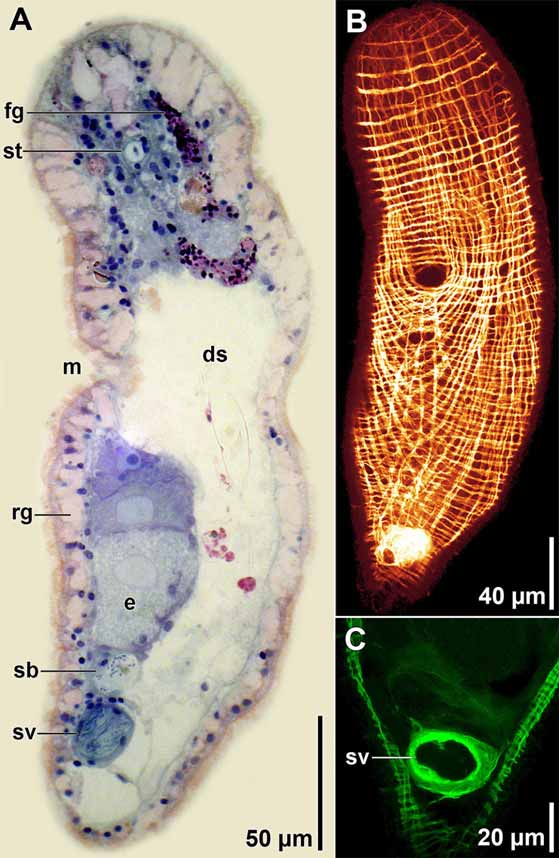
Description. Living specimens 450–650 µm long and 150 µm wide ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 A). Anterior and posterior ends rounded; posterior end more narrow. Body colorless by transmitted light. Digestive syncytium often with red and green contents, including conspicuous pennate diatoms ( Figs. 8 View FIGURE 8 B, 9A). Epidermis completely ciliated. Many large, scattered rhabdoid glands present ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 C, 9A). Frontal organ well developed; cell bodies of frontal glands positioned ~100 µm behind frontal pore ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 A). Mouth opening on ventral surface, middle of body. Digestive central syncytium extends from posterior end of frontal glands to level of seminal vesicle.
Musculature with circular muscles that encircle the body along entire length of animal; straight longitudinal muscles present between frontal organ and anterior edge of mouth; longitudinal-cross-over muscles (fibers with a longitudinal orientation anteriorly, but bend medially to cross diagonally) present in both dorsal and ventral body wall; longitudinal muscles in anterior half of body that wrap around posterior rim of mouth (U-shaped muscles) present in ventral body wall; ventral diagonal muscles in anterior half of body absent ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 B).
Ovaries paired, ventral; extend from level of mouth posteriorly to seminal bursa ( Figs. 8 View FIGURE 8 A, B, 9A). Testes paired, lateral to ovaries; extend from frontal glands posteriorly to male copulatory organ.
Female gonopore absent. Thin-walled seminal bursa positioned ventrally, immediately anterior to seminal vesicle and posterior to developing oocytes ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 A).
Male gonopore ventral at posterior end of body; opens to ciliated male antrum. Antrum opens to muscular seminal vesicle filled with sperm. Penis absent. ( Figs. 8 View FIGURE 8 B, 9A, C).
Remarks. In most of the 15 described species of Haplogonaria , the seminal bursa and seminal vesicle connect to a common gonopore. Although we could not discern a connection between the gonopore and seminal bursa in our species, the close proximity of these structures raises the possibility that a facultative connection exists. H. sophiae is similar to H. idia in having paired ovaries; all other known species in the genus have an unpaired ovary. Hooge and Eppinger (2005) pointed out that the genus Haplogonaria contains some species, such as H. sophiae , with a muscular seminal vesicle, and others with a non-muscular or weakly muscular seminal vesicle. It is probable that this character is of systematic importance and is indicative of separate phylogenetic lineages within the genus.
| MZUSP |
Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
SubPhylum |
Acoelomorpha |
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |