Trassedia luapi Cancemi 1996
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1093/isd/ixy015 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:68249DCE-5520-4415-85D1-80CCA002A48D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7169204 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DD3922-C559-C72F-FCA1-0453FC43FDCD |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Trassedia luapi Cancemi 1996 |
| status |
|
Trassedia luapi Cancemi 1996 View in CoL
Diagnosis
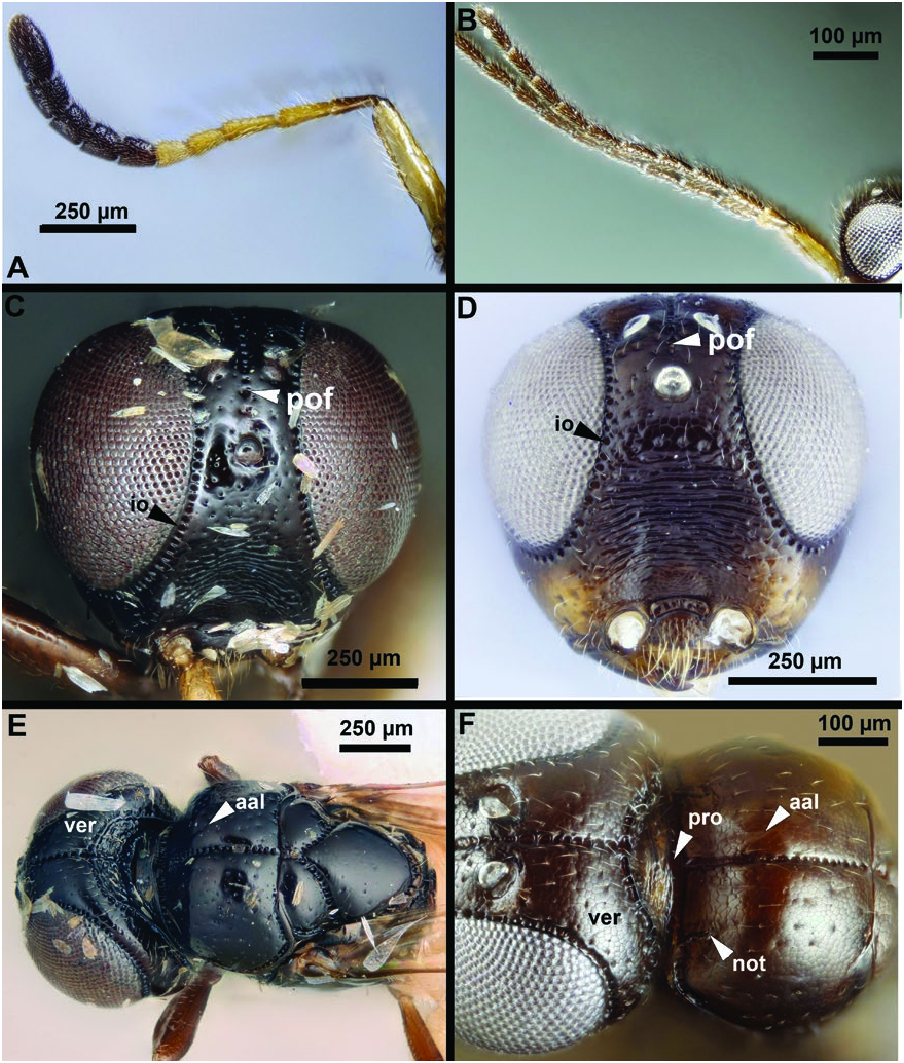
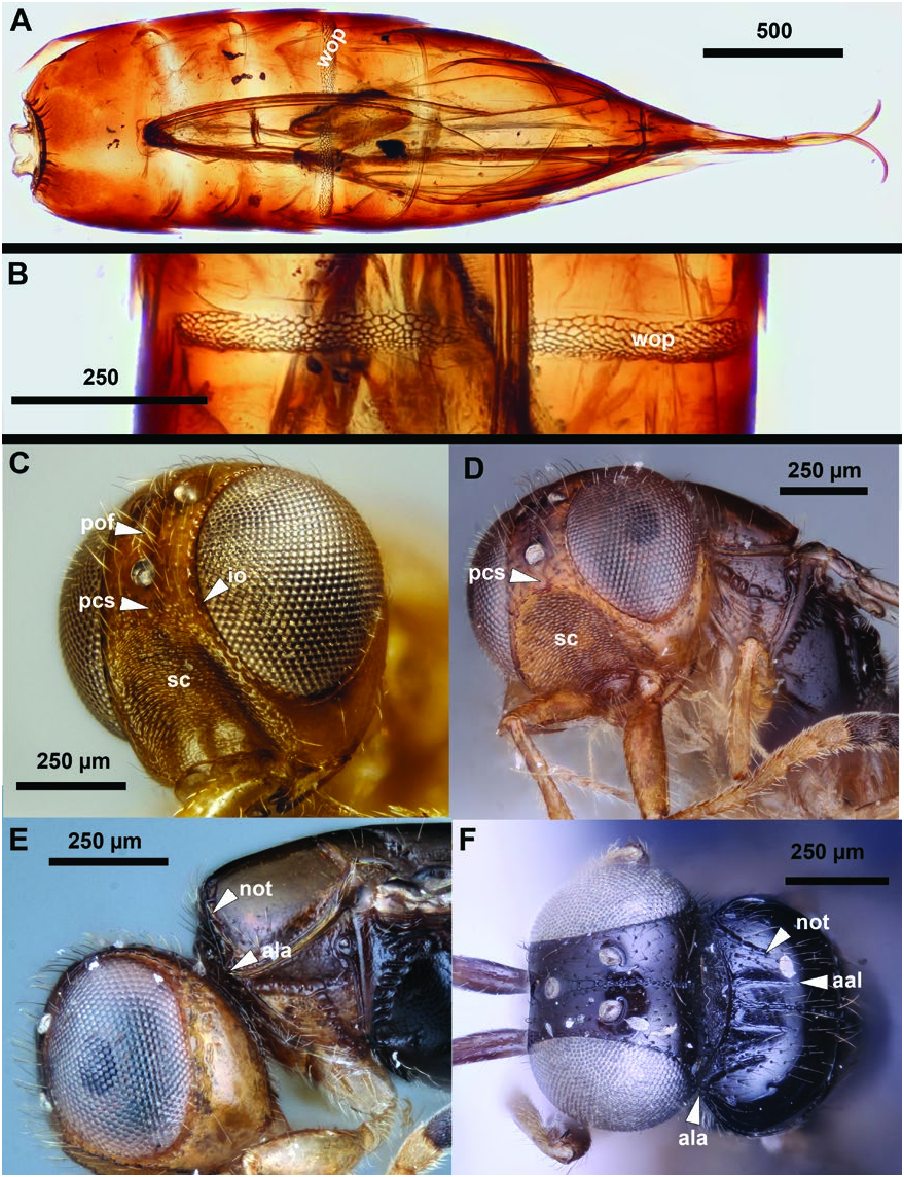
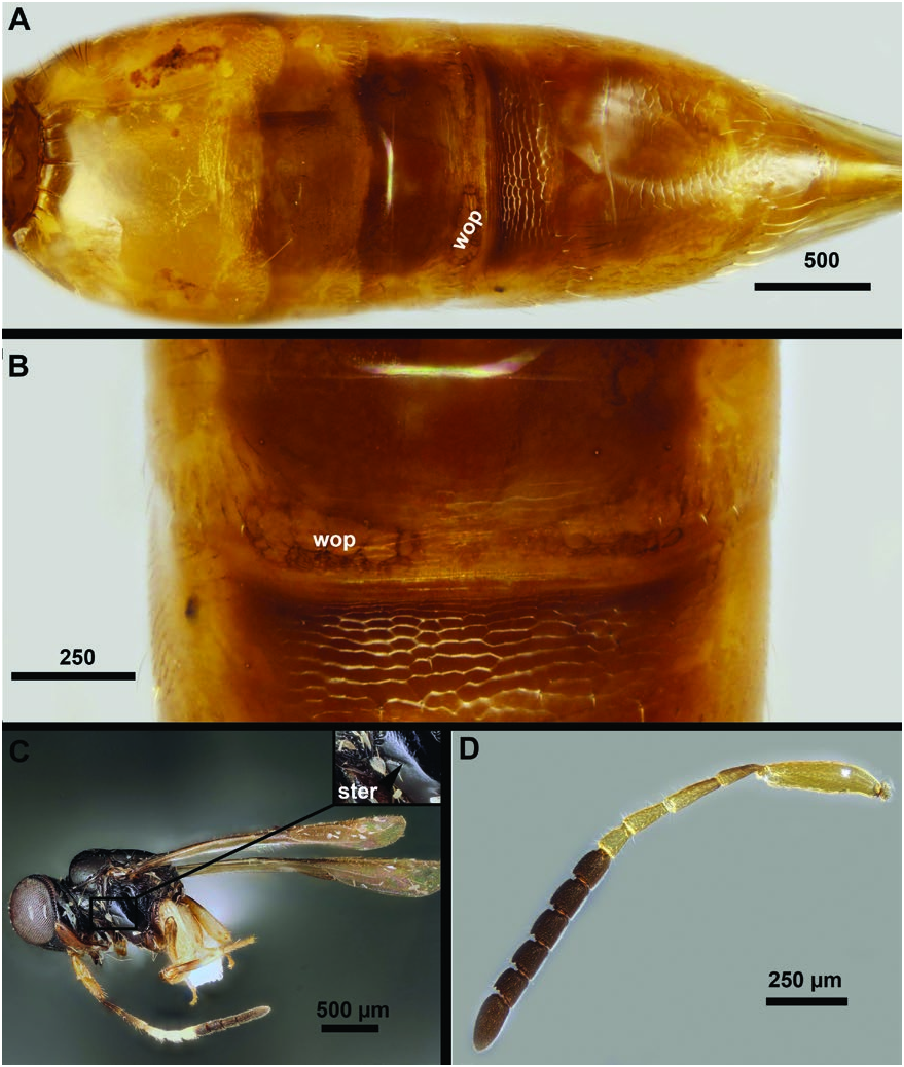
Trassedia luapi shares the following characters with T. yanegai and T. australiensis : short setae on the dorsal region of the cranium (shorter than the diameter of the median ocellus; Fig. 3C and D View Fig ); reduced anterior ocellar fovea that do not extend to the antennal scrobe ( Fig. 3C and D View Fig ); a punctate ocular impression along the inner orbit (io: Fig. 3C and D View Fig ); and a wide Waterston’s evaporatorium that reaches the lateral 1/3 of the tergite (wop: Fig. 4A and B View Fig ). Trassedia luapi differs from T. yanegai by the preoccipital sulcus not widening gradually anteriorly (pof: Fig. 3C View Fig ) and by the presence of the notaulus, scutes on the vertex, a foveolate sternaulus (ster: Fig. 5C View Fig ) and large eyes (HW/IOS = 3.7, Fig. 3C View Fig ). The female pedicel and F1 are brown and F2–F4 are whitish in T. yanegai , while the female pedicel and F1–F3 are yellow and F4–F9 are dark brown in T. luapi . Trassedia luapi differs from T. australiensis in cranium shape (cranium as long as wide in dorsal view in T. australiensis and 1.4× as wide as long in T. luapi ), POL:OOL ratio (POL 2× as long as OOL in T. australiensis and equal to OOL in T. luapi ), the length of the harpe (harpe 2× as long as the gonossiculus in T. australiensis and 1.5× as long as the gonossiculus in T. luapi ) and the position of the distal sensilla of the gonossiculus (sensilla closer to the distal margin than to the proximal margin of the gonossiculus in T. luapi and equidistant from both margins in T. australiensis ).
Description
Body length: 1.80–2.90 mm. Color hue pattern female: brown, F1–F3, legs yellow. Color intensity pattern female: F4–F9 darker than cranium, scape, pedicel, mesosoma and metasoma. Color hue pattern male: ochre, legs, scape, pedicel, F1 yellow. Structure of scutes on head and mesosoma: Scute surface on head and mesosoma flat, scutes indistinct. HW:HH = 0.9–1.3. Head: HW/IOS Female: 2.5–2.7. HW/IOS Male: 2.2. Maximum eye diameter versus minimum eye diameter: 1.1–1.3. Interommatidial seta length: Interommatidial seta length less than facet diameter. Occipital carina medially: continuous medially. Seta length on dorsal region of cranium versus diameter of median ocellus: shorter. Setal pit on vertex size: smaller than diameter of scutes. Scutes on vertex count: present. Preoccipital furrow anterior extension: adjacent anteriorly to the posterior margin of the median ocellus. Preoccipital furrow anterior region versus posterior region sculpture: crenulate in its entire length. Preoccipital furrow anterior region width versus posterior region width: as wide anteriorly as posteriorly. Female OOL: POL: LOL: 0.2–0.6:0.5–0.7:1.0. Male OOL: POL: LOL: 0.6:0.7:1.0. Preocellar pit count: absent. Carina delimiting antennal scrobe count: absent. Transverse striation on upper face count: present. Anterior ocellar fovea shape: fovea not extended ventrally into facial sulcus. Supraclypeal depression count: present. Ocular impression sculpture: punctate (fovea of ocellar impression are well separated from each other). Antenna: Length of setae on male flagellomere versus male flagellomere width: setae shorter than width of flagellomeres. Male scape length versus pedicel length: 2.6. Male F1 length versus pedicel length: 1.8. Male scape length versus combined length of F1+F2: shorter. Male F6 length versus combined length of F7+F8: Shorter than length of flagellomere 7 + 8. Number of flagellomeres with male-specific ventral sensilla: F4–F9. Female scape length versus pedicel length: 2.4–2.8. Female F1 length versus pedicel length: 1.2–1.4. Female ninth flagellomere length: F9 less than F7+F8. Mesosoma: Mesosoma shape: not compressed laterally, as wide as high or wider than high. Pronope count: present. Anterior slope of mesonotum shape: Anterior slope of mesonotum at obtuse angle to dorsal surface of mesonotum in lateral view. Antero-admedian line count: present. Notaulus count: present. Notaulus anterior origin versus anterolateral angle of mesoscutum (ball-and-socket articulation between pronotum and mesoscutum): notaulus arises medially of anterolateral angle of the mesoscutum. Posterior end of notaulus versus posterior end of antero-admedian line location: antero-admedian line extends more posteriorly than notaulus. Scutes on posterior region of mesoscutum and dorsal region of mesoscutellum count: present. Epicnemial carina count: complete. Sternaulus count: present. Sternaulus sculpture: smooth. Anterior metapleural carina count: present. Carina limiting posteriorly antecosta count: present. Propodeal spiracle dilator muscle apodeme pit location: On metapleural carina. Longitudinal carina between plica and median propodeal carina count: absent. Lateral propodeal carina count: present. Wings: Stigmal vein length versus pterostigma marginal length: stigmal vein longer than the pterostigma marginal length. Metasoma: Waterston’s evaporatorium shape medially male: paired, left and right evaporatoria are not continuous medially; not paired, single median evaporatorium present. Male genitalia: Anterior margin shape of male S9: concave. Male S9 distal setal line/setal patch count: distal setae composing setiferous patch(es). Distomedian, hairless area (interrupting transverse row of setae or patch) on male S9 count: absent (distal setiferous patch/line continuous medially). Distal margin of male S9 shape: straight. Proximolateral corner of male S9 shape: acute. Gonostyle/volsella complex length: wider than long. Gonostyle/ volsella complex proximodorsal margin shape: with deep concavity medially. Distal sensilla on gonossiculus versus proximal margin of gonossiculus location: closer to distal margin than to proximal margin of gonossiculus. Distal margin of harpe in lateral view: shape: straight. Lateral setae of harpe count: absent. Harpe length versus gonossiculus length: harpe 2× as long as gonossiculus. Lateral margin of harpe shape: widest point of harpe is in its proximal one-third. Dorsomedial cupulo-gonostipal muscles orientation: diverging proximally. Ventral gonostipo-penisvalval muscles site of origin-proximal extension: not extends distally on parossiculus.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.