Rhinolophus lanosus, Volleth & Son & Wu & Li & Yu & Lin & Arai & Trifonov & Liehr & Harada, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3161/15081109ACC2017.19.1.003 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4328138 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D5879E-FFE5-C325-3AED-7A891E54FDF7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Rhinolophus lanosus |
| status |
stat. nov. |
Rhinolophus lanosus View in CoL stat. rev.
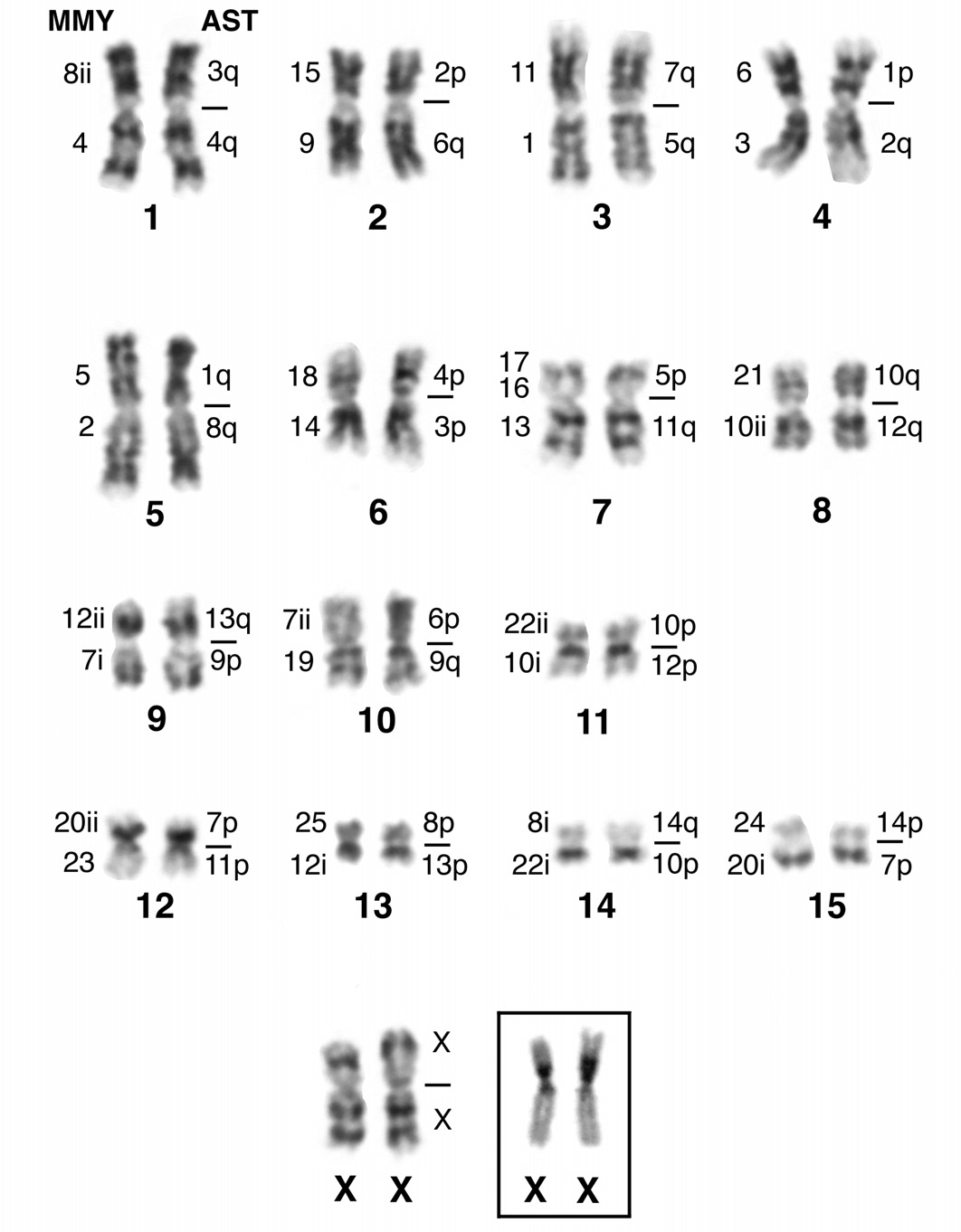
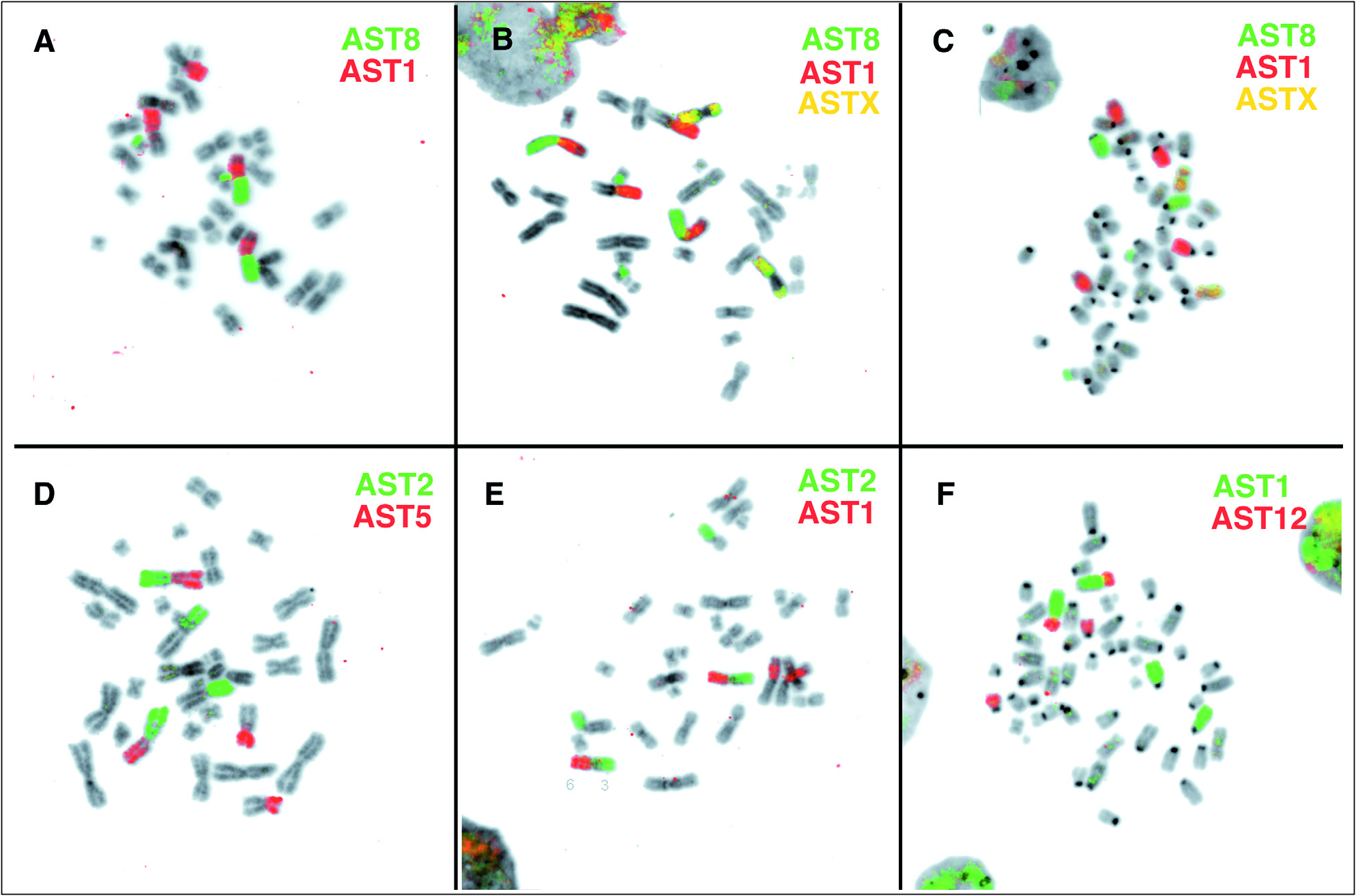
The female from Sichuan province, China, showed a diploid chromosome number of 2 n = 32 and a FNa = 60. The karyotype was composed of 15 meta- to submetacentric autosomal pairs and two metacentric X chromosomes ( Fig. 4 View FIG ). Heterochromatin was detected by C-banding at all centromeres and in the proximal part of the short arm of the X chromosome. The size of this heterochromatic segment differed between both homologs of the female studied (inset of Fig. 4 View FIG ). The NORs are located at the secondary constriction in the short arm of pair 8. This chromosomal arm is homologous to MMY21. The frequency of active NORs as detected by silver-staining was 1.8 NORs per cell (10 metaphase spreads analyzed). The composition of autosomal arms was studied by combination of whole chromosome painting probes from A. stoliczkanus , complemented by some M. myotis probes (MMY8, 14, 18). The hybridization results are summarized on the karyotype ( Fig. 4 View FIG ), and as examples
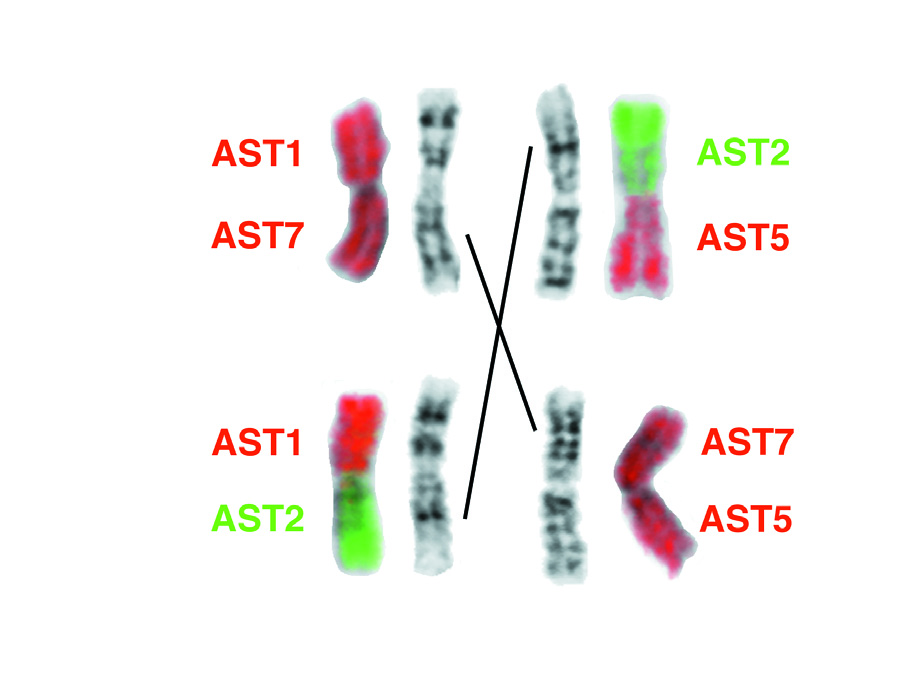
metaphase spreads hybridized with probes from AST 1, 2 and 8 are shown ( Fig. 3B and 3E View FIG ). G-banding and FISH results revealed that the karyotype of R. lanosus differs from that of R. luctoides and R. cf. luctoides from Vietnam by a whole arm reciprocal translocation (WART) between pairs 3 and 4. In the karyotype of R. cf. luctoides , pair 3 is composed of arms homologous to AST2 ad AST5, whereas in R. lanosus it consists of arms homologous to AST7 and AST5. Homology to AST1 and AST7 is found in pair 4 of R. cf. luctoides , but to AST1 and AST 2 in R. lanosus ( Fig. 5 View FIG ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |