Xylocopa ( Neoxylocopa )
|
publication ID |
https://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3754.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B36E65F9-491C-4231-91AF-B41621F1F5E2 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D4D738-FFD3-FFDD-8BD2-FC97C78DFE56 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Xylocopa ( Neoxylocopa ) |
| status |
|
Key to species of the Xylocopa ( Neoxylocopa) present in Argentina
Females
1. Pubescence in part ferruginous on mesosoma or metasoma..................................................... 2 - Pubescence entirely black............................................................................... 4 2. Ferruginous pubescence restricted along sides and apex of metasoma ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 9 – 14 )............................... X. augusti - Ferruginous pubescence restricted to mesosoma............................................................. 3 3. T 2 -T 3 with median pubescence short, 0.3–0.6 times MOD; gena narrow and densely punctate; tegula dark brown..........
.......................................................................................... X. tacanensis - T 2 –T 3 with median pubescence long, 1.1–1.3 times MOD; gena wide and sparsely punctate; tegula ferruginous or light brown
............................................................................................. X. eximia 4. Integument of metasomal terga I–IV or I–V with reddish bands ( Figs. 11, 12 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ), if the integument is completely black, then
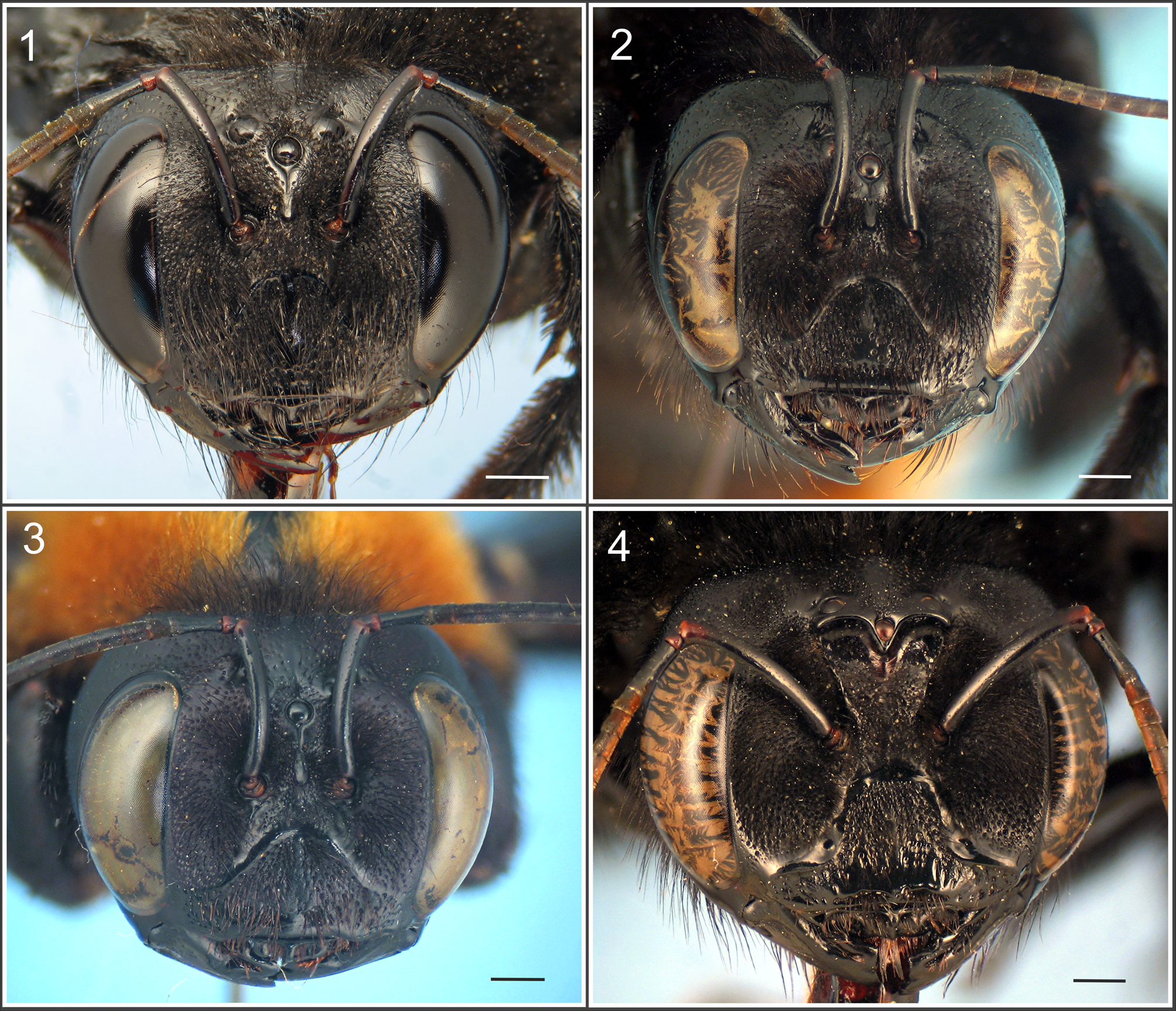
scutellum is angled as seen in profile...................................................................... 5 - Integument of metasomal terga without reddish bands, completely black, scutellum not angled in profile................ 6 5. Face with conspicuous carina below lateral ocelli ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ); scutellum gently rounded as seen in profile; T 2 –T 3 with short and
scattered hairs, generally specimens more than 30 mm long............................................. X. frontalis - Face without conspicuous carina below lateral ocelli; scutellum angle as seen in profile; T 2 –T 3 with short and abundant hairs,
generally specimens less than 30 mm long....................................................... X. nigrocincta 6. T 2 and basal third of T 3 with median pubescence very short, barely exiting the insertion puncture, 0.2–0.4 times MOD,
remaining of T 3 with hairs 3–4 times longer than those on T 2; supraorbital area wide ( 3.5–4.1 times DOM)….… X. mendozana - T 2 –T 3 with median pubescence short, hairs 0.3–0.5 times MOD, noticeably surparsing the insertion puncture; supraorbital
area narrow ( 2.4–2.8 times DOM)........................................................... X. atamisquensis
Males
Note: the male of X. tacanensis is unknown. Plumose hairs intermixed with simple hairs can be found on T 2–5 in all males studied.
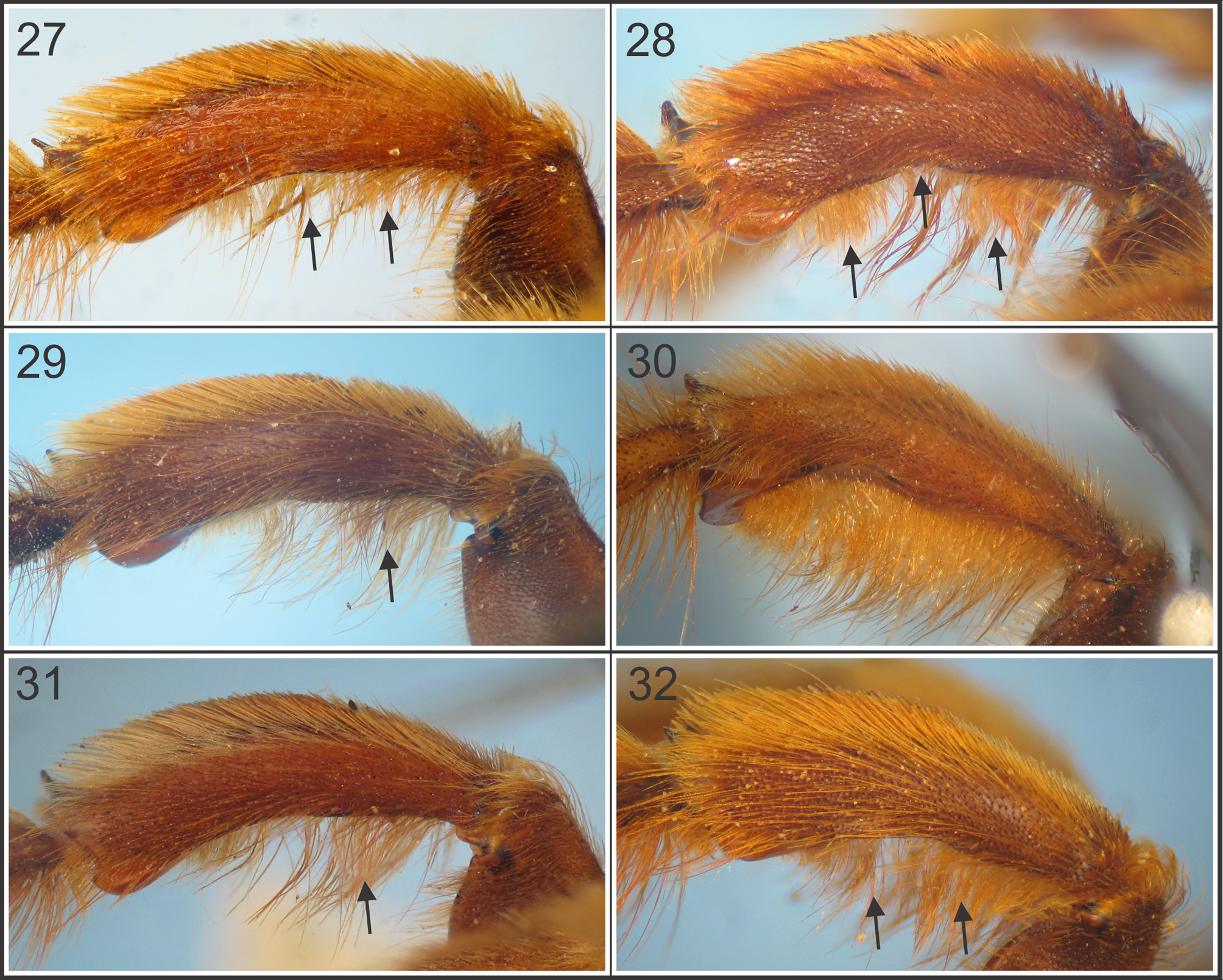
1. T 2 –T 3 with small contiguous punctures and median pubescence very short, barely surpassing the insertion puncture and apparently hairless ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 21 – 26 )........................................................................ X. mendozana
- T 2 –T 3 with punctures separated by one or more times puncture width, but never contiguous; median pubescence variable.. 2
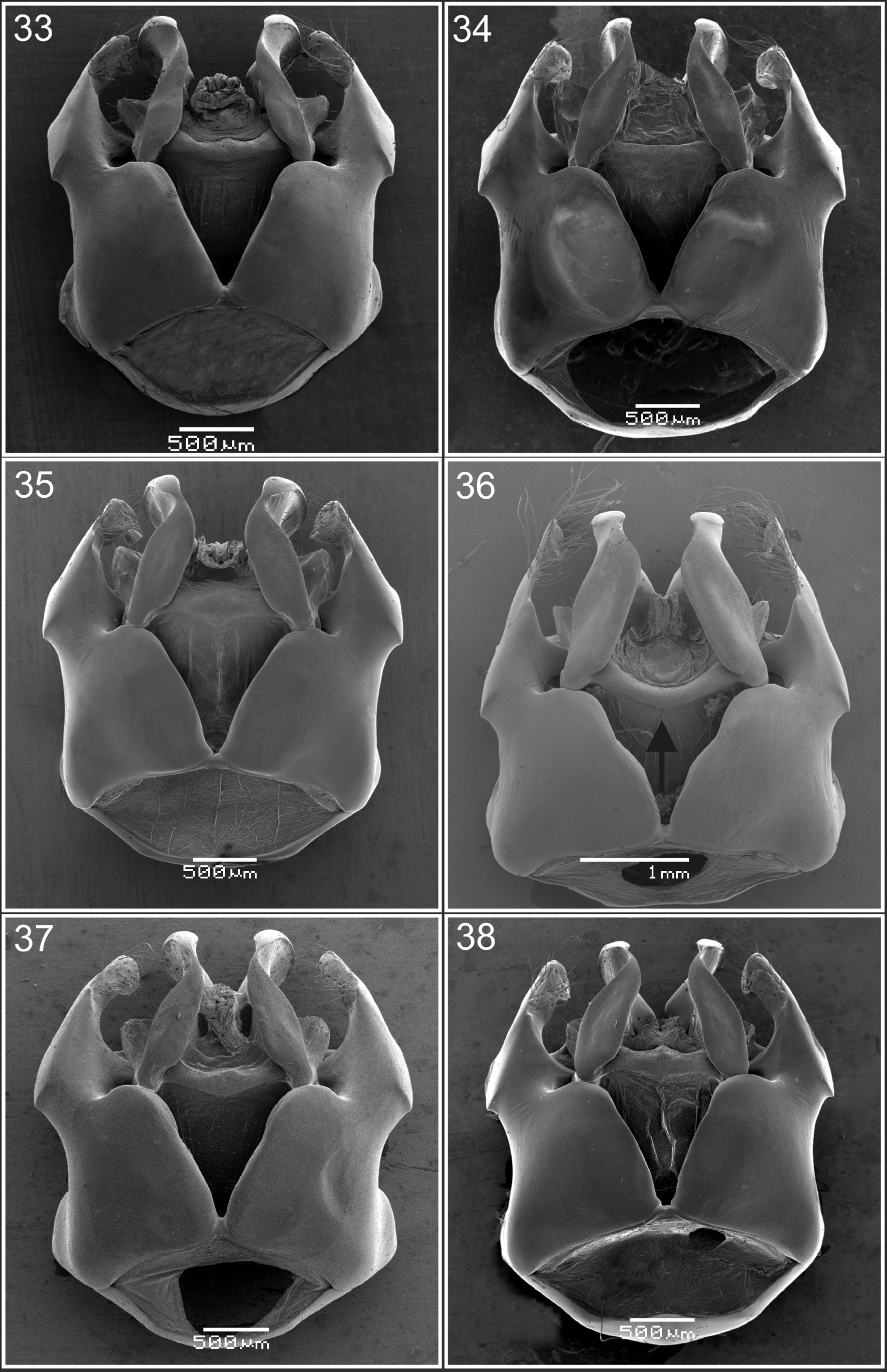
2. T 2 –T 3 with median pubescence short ( 0.1–0.3 times MOD); ventral surface of posterior tibia with pubescence distributed throughout the surface ( Fig. 30 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ). Specimens more than 30 mm long. Genitalia, in dorsal view, with sphata strongly curved ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 33 – 38 )........................................................................................ X. frontalis
- T 2 –T 3 with median pubescence long, abundant and dense; ventral surface of posterior tibia with pubescence distributed either basally, medially or subaplically. Specimens less than 30 mm long Genitalia, in dorsal view, with sphata not strongly curved..................................................................................................... 3
3. T 2 –T 3 with median pubescence short, ( 0.4–0.7 times MOD); ventral surface of the posterior tibia with pubescence restricted to the basal and median parts ( Fig. 32 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ). Genitalia, in dorsal view apex of pennis valve abruptly narrowed ( Fig. 56 View FIGURES 45 – 56 )..................................................................................................... X. nigrocincta
- T 2 –T 3 with median pubescence long more than 0.7 times MOD; ventral surface of the posterior tibia with pubescence variable.................................................................................................... 4
4. Ventral surface of the posterior tibia with pubescence forming two separate tufts (basal and subapical) and median small notch on the posterior edge ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ).................................................................... X. augusti
- Ventral surface of the posterior tibia with pubescence forming one tuft ( Fig. 27, 29 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ); posterior tibia without a median small notch on the posterior edge.............................................................................. 5
5. T 6–7 with dark brown to black pubescence ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 21 – 26 ); ventral surface of the posterior tibia with pubescence restricted to the base ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ). Genitalia, in ventral view, with apex of gonostyle as in figure 47............................. X. eximia
- T 6–7 with ferruginous pubescence ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 21 – 26 ); ventral surface of the posterior tibia with pubescence forming one tuft (basalmiddle) ( Fig. 27 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ). Genitalia, in ventral view, with apex of gonostyle as in figure 45..................... X. atamisquensis
| MOD |
University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Department of Biology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |