Nephelomilta medogensis Huang, Volynkin & Saldaitis, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5351.5.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9C6F1A9A-A773-49CA-AE66-CF5B23ED3F07 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8392119 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2FD7D9C3-B8EE-4517-84B1-083A799058B7 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:2FD7D9C3-B8EE-4517-84B1-083A799058B7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Nephelomilta medogensis Huang, Volynkin & Saldaitis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
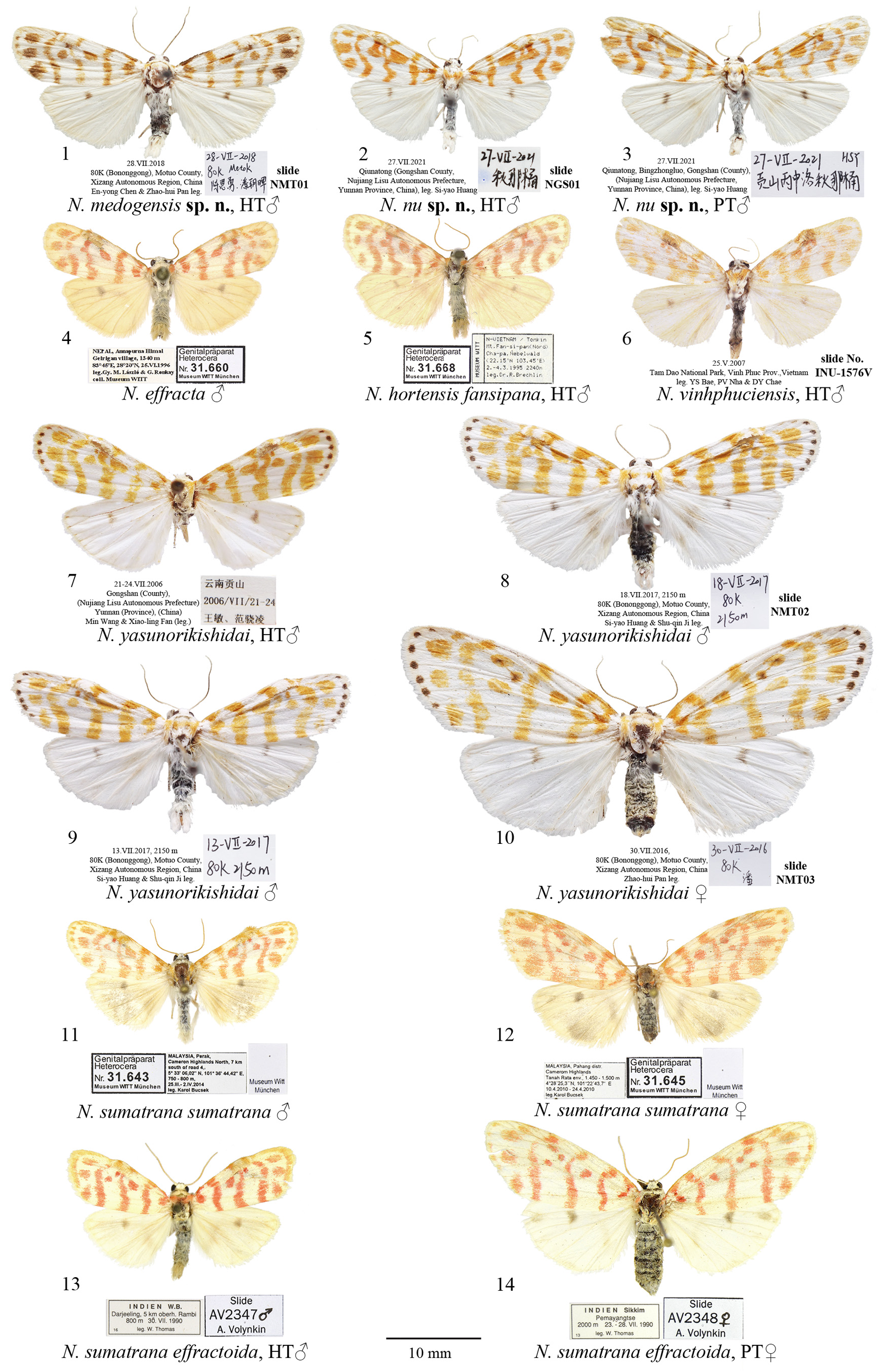
Nephelomilta medogensis Huang, Volynkin & Saldaitis , sp. n.
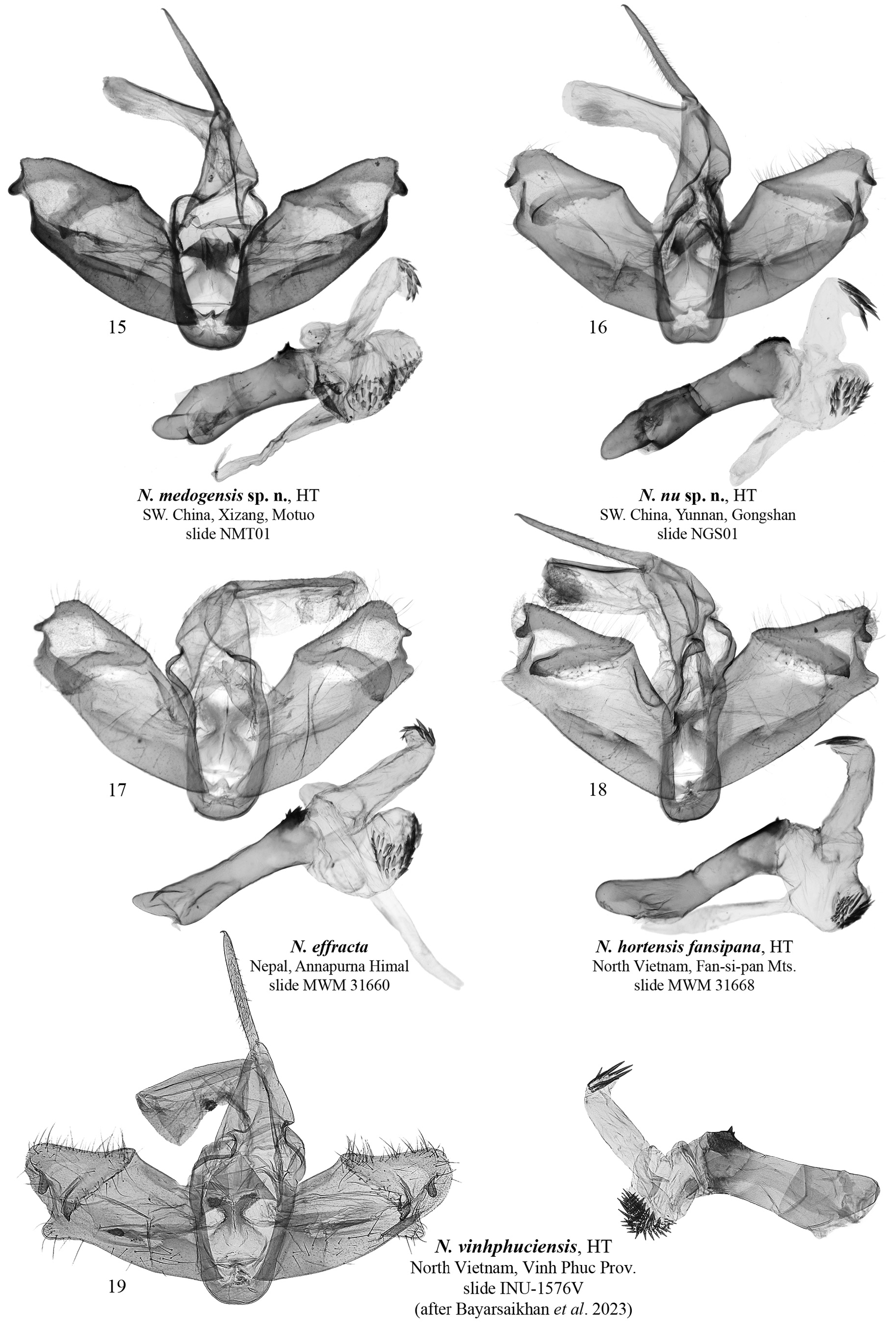
( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–14 , 15 View FIGURES 15–19 )
http://zoobank.org/ urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:2FD7D9C3-B8EE-4517-84B1-083A799058B7
Type material. Holotype ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–14 , 15 View FIGURES 15–19 ): male, 28. VII. 2018, 80K (Bononggong), Motuo County, Xizang Autonomous Region , China, En-yong Chen & Zhao-hui Pan leg., slide NMT01 (Coll. SCAU).
Diagnosis. The forewing length is 14 mm. Externally, N. medogensis sp. n. is unique amongst the genus Nephelomilta due to the ochreous brown forewing pattern, whereas that of the similar congeners is generally reddish or ocherous red. Judging from the male genitalia structure, the new species is hereby assigned with the effracta species group (erected and characterized by Volynkin & Černý 2018) due to the lack of the distal membranous lobe. Nephelomilta medogensis is externally reminiscent of N. effracta ( Walker, 1854) ( Figs. 4 View FIGURES 1–14 , 17 View FIGURES 15–19 ) but can readily be distinguished by the larger size and the ochreous brown forewing pattern. In the male genitalia capsule, N. medogensis differs from N. effracta in the noticeably narrower distal section of the valva, the markedly shorter and narrower ampulla, the larger apical costal lobe, and the larger ventral-apical costal process. The phallus of the new species is thicker than in the similar congener and has a carinal plate bearing smaller denticles. Compared to N. effracta , the vesica of N. medogensis has a narrower medial diverticulum bearing a larger apical cluster of cornuti, and a broader cornuti field in the distal diverticulum.
Distribution. The new species is currently known only from its type locality in Motuo County in southeastern Xizang Autonomous Region in southwestern China.
Etymology. The specific epithet medogensis is derived from the type locality of the new species, Motuo County, which is called Medog in Tibetan. The name is a noun in the nominative singular in apposition.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |