Callococcus Ferris 1918
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4765.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C442D94C-0EB4-4509-B762-913707214819 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3796797 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B2EA64-0A66-461B-2CFC-FE09FD7DD172 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Callococcus Ferris 1918 |
| status |
|
Callococcus Ferris 1918: 328 . Type species: Sphaerococcus pulchellus Maskell by monotypy and original designation.
Introduction. The generic name Callococcus was introduced by Ferris in 1918 to take Sphaerococcus pulchellus Maskell , at that time the only species placed in the genus, which was then considered to belong to the Asterolecaniidae . Later, Morrison and Morrison (1927) revised the genus, transferred 2 more of Maskell’s Sphaerococcus View in CoL species to Callococcus , namely S. acaciae Maskell 1893 and S. leptospermi Maskell 1894 , but retained Callococcus within the Asterolecaniidae . However, the type species of the genus Sphaerococcus View in CoL ( S. casuarinae Maskell 1892 ) belongs to the Pseudococcidae View in CoL and so the species previously placed in Sphaerococcus Maskell View in CoL were reviewed by Miller et al. (1998) and most were transferred to other families and genera. Miller et al.’s revision confirmed the placement of S. acaciae and S. leptospermi in Callococcus and transferred S. newmanni Froggatt 1921 to it. Miller et al. also placed Callococcus Ferris within the Eriococcidae View in CoL . The genus therefore now contains 4 species, all from mainland Australia. The adult male of C. leptospermi (Maskell) is redescribed below and it is clear that the males of this species are very similar to those of other Gondwanan eriococcids and therefore that the placement within the Eriococcidae View in CoL is correct.
The adult male of C. leptospermi Maskell was first described by Coles et al. (1988). They found that the secondinstar female nymphs of C. leptospermi induced woody galls on the stems of Leptospermum laevigatum in Australia ( South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria). These galls varied in size, ranging from 8–25 mm long and 6–12 mm thick. Young galls are usually closed and firm, but when old or parasitized, a longitudinal slit appears on one side that allows dispersal of the crawlers and (presumably) copulation. The second-instar males settle either on the exterior of the parent gall or nearby in the axil of a twig or bud scale ( Coles et al. 1988).
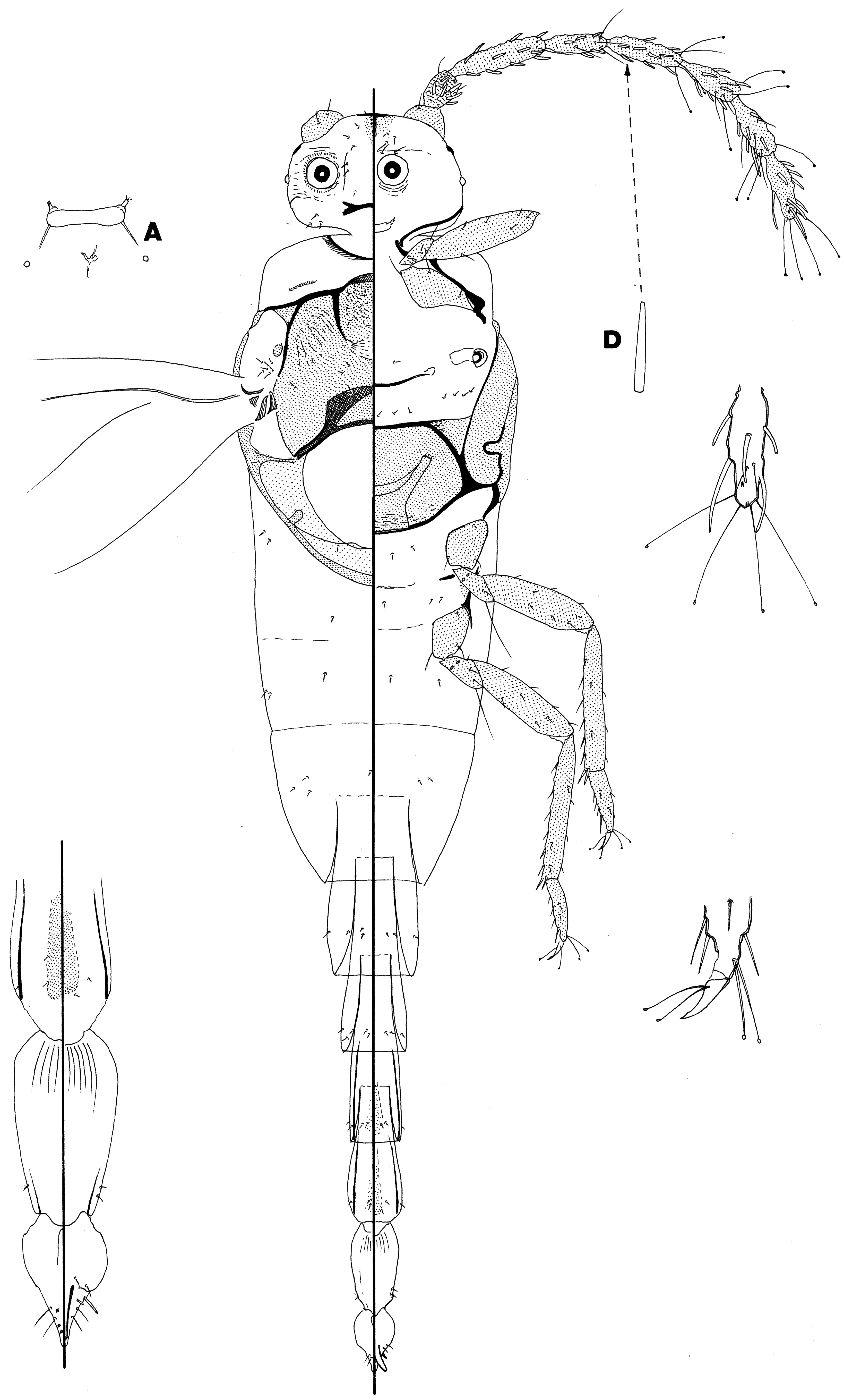
Generic diagnosis based on adult male morphology of C. leptospermi (described below) ( Fig. 26 View FIGURE 26 ) Body with abdomen attenuated and telescoping, narrowing gradually to style; body setae extremely few, almost all hs; loculate and simple pores absent. Head: dorsal mid-cranial ridge absent; postoccipital ridge well developed, with both anterior and posterior arms; genae with a few hs; ocular sclerite with very few concentric striations around simple eyes; antennae 8 segmented; flagellar segments with both hs and fs, latter rather short and stout; 1-4 capitate setae present on several antennal segments in addition to apical segment. Thorax: prosternal median ridge absent; prescutum without prescutal setae; scutal and scutellar setae present; postmesospiracular setae present; metasternum with few setae; metaprecoxal ridge present; hamulohalteres absent; alar lobe and alar setae absent; trochanter with campaniform sensilla in a line on each side; fs absent from tibia and tarsi; tarsi 1 segmented; claw digitules capitate; claws with a denticle. Abdomen: segments telescoping when not extended, but extremely elongate when extended; glandular pouches absent; abdominal segment IX with 2 pairs of short setae; style with hs and fs; style triangular and short, becoming sharply pointed posteriorly.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Callococcus Ferris 1918
| Hodgson, Chris 2020 |
S. newmanni
| Froggatt 1921 |
Callococcus
| Ferris 1918 |
Callococcus
| Ferris 1918 |
Callococcus
| Ferris 1918 |
Callococcus
| Ferris 1918 |
Callococcus
| Ferris 1918 |
S. leptospermi
| Maskell 1894 |
S. leptospermi
| Maskell 1894 |
C. leptospermi
| Maskell 1894 |
C. leptospermi
| Maskell 1894 |
S. acaciae
| Maskell 1893 |
S. acaciae
| Maskell 1893 |
Sphaerococcus
| Maskell 1892 |
Sphaerococcus
| Maskell 1892 |
S. casuarinae
| Maskell 1892 |
Sphaerococcus
| Maskell 1892 |