Deinopteroloma
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4196.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C029FBF5-EC33-4AF5-9487-3164662DFD73 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6071900 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AA535D-FFFC-FFFB-FF40-D38BFA09FCB8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Deinopteroloma |
| status |
|
Key to Deinopteroloma View in CoL species
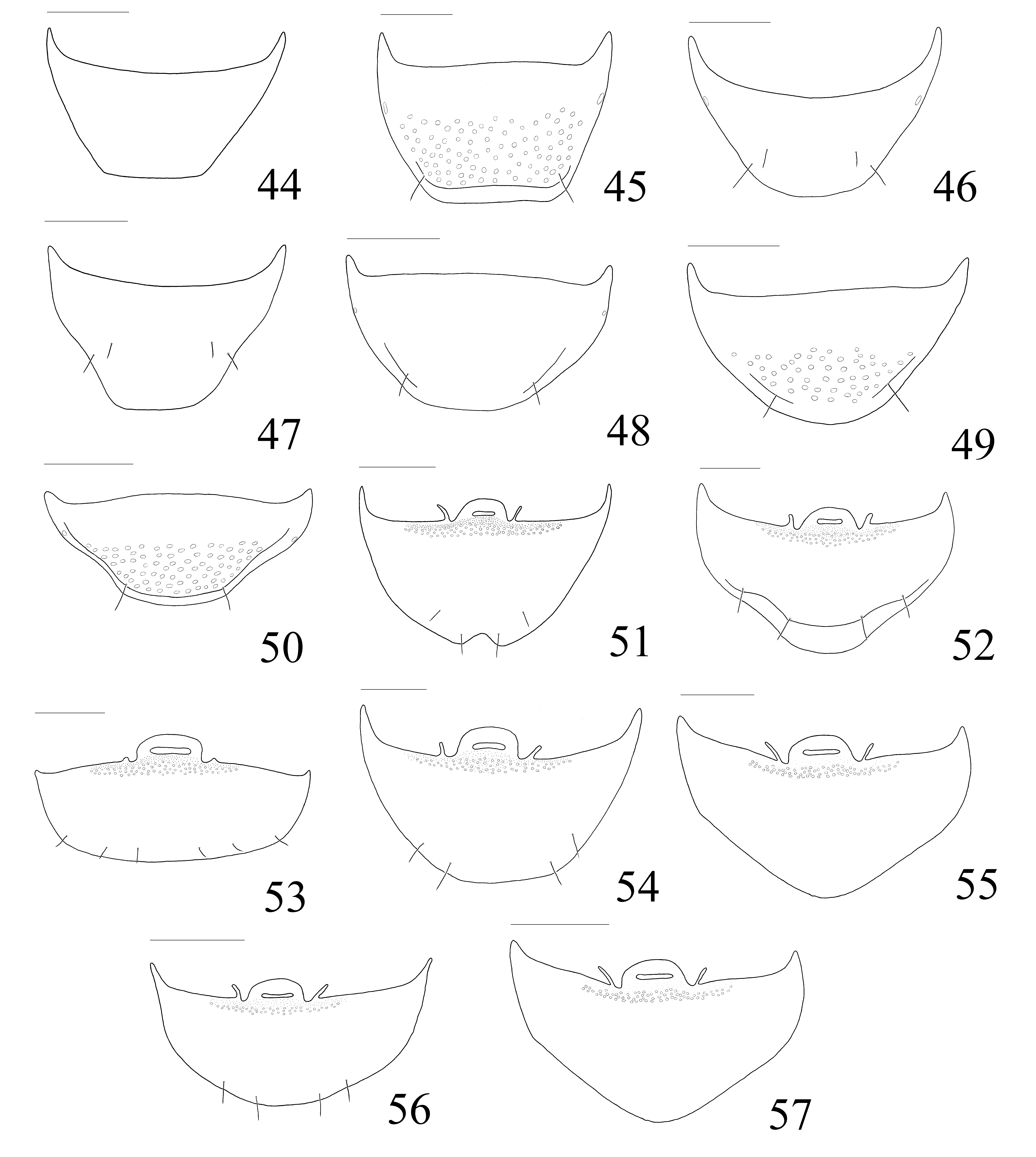
1 Pronotum noticeably wider than long; lateral margins crenate or crenulate......................................... 2
- Pronotum about as long as wide; lateral margins with strong and sharp spines. Aedeagus as in Smetana (1985a: Fig. 45 View FIGURES 44 – 57 ). Body length: 4.20 mm. North-eastern Burma............................................ D. diabolicum (Jansson, 1946) View in CoL
2 Lateral margins of pronotum with very fine, smooth crenulation. Elytra yellow brown to brown with dark brown very wide maculae in basal and apical portions. Pacific North American species........................................... 3
- Lateral margins of pronotum with uniform dense rounded crenulation or very coarsely crenate. Elytra yellow brown to piceous black, without very wide dark maculae in basal and apical portions.............................................. 4
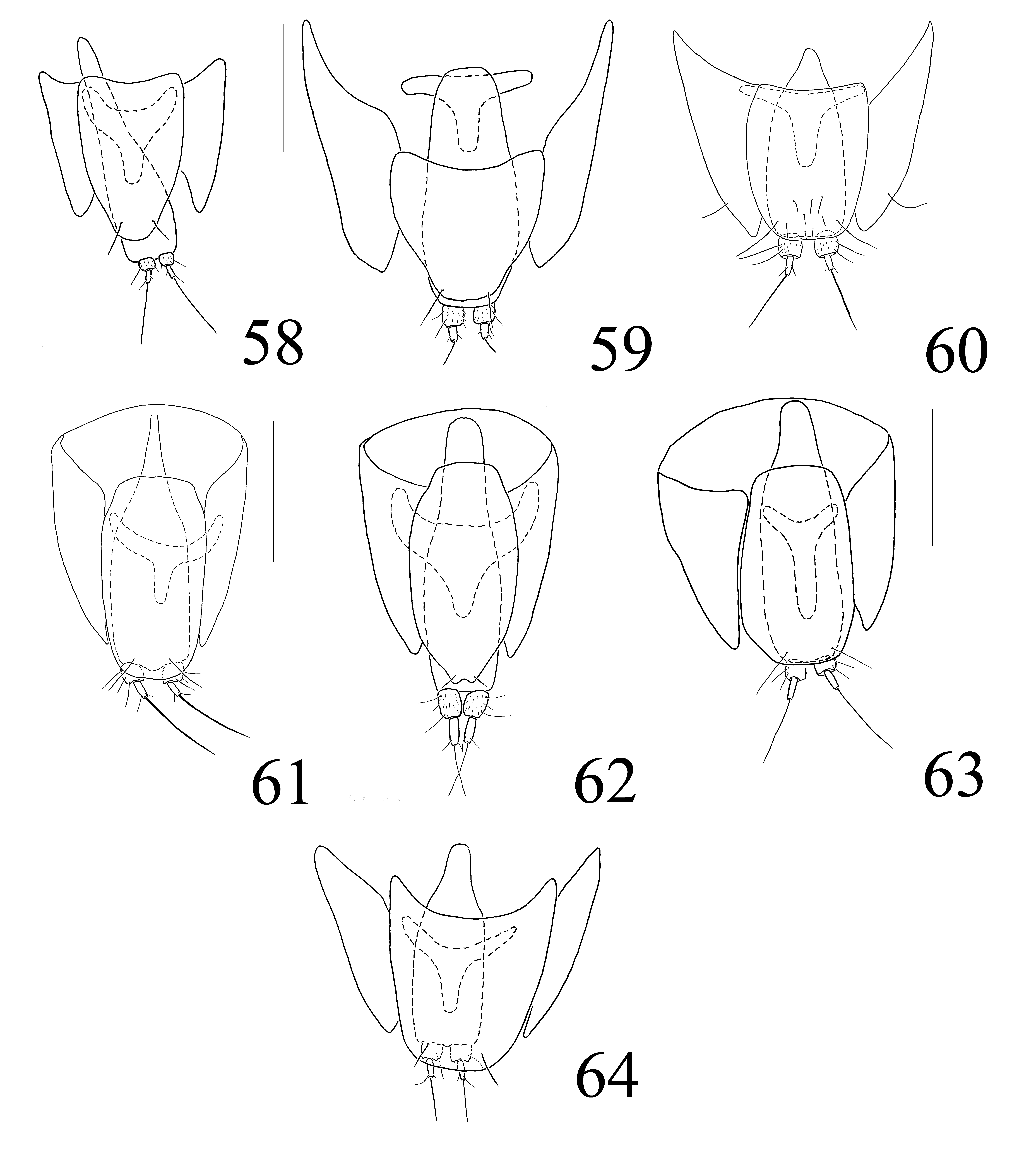
3 Groove between postocular ridge and margin of eye rugulose ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 46 View FIGURES 44 – 57 ); impressions posteriomediad of antocular indentation on head without appreciable microsculpture ( Smetana 1985a: Figs. 46−47 View FIGURES 44 – 57 ); lateral portions of pronotum dis- tinctly explanate ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 48 View FIGURES 44 – 57 ). Aedeagus as in Smetana (1985a: Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Body length: 4.00− 4.80 mm. Canada, USA....................................................................... D. subcostatum ( Mäklin, 1852)
- Groove between postocular ridge and margin of eye smooth ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 60 View FIGURES 58 – 64 ); impressions posteriomediad of antocular indentation on head with distict, coarse dense microsculpture ( Smetana 1985a: Figs. 60−61 View FIGURES 58 – 64 ); lateral portions of pronotum vaguely explanate ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 62 View FIGURES 58 – 64 ). Aedeagus as in Smetana (1985a: Fig. 14). Body length: 4.00− 4.50 mm. Canada, USA............................................................................ D. pictum (Fauvel, 1878)
4 Lateral margins of pronotum with dense, uniform crenulation without separate large teeth........................... 5
- Lateral margins of pronotum very coarsely crenate, with variable large teeth..................................... 11
5 Body small (2.13−2.67 mm), short ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Latero-apical portion of each elytron slightly explanate and reflexed. Elytra with variable brown U-shaped median and apical maculae. Aedeagus very narrow, with very long parameres ( Fig. 30 View FIGURES 30 – 35 ). China (Sichuan)..................................................................................... D. minor View in CoL sp.n.
- Body significantly larger, elongated. Latero-apical portion of each elytron without modifications. Elytra with variable whitish/ yellow to brown oblique maculae or spots. Aedeagus wider, parameres shorter.................................... 6
6 Each elytron with longitudinal protuberances in middle and apical third of elytra.................................. 7
- Each elytron without protuberances, with indistinct longitudinal elevations in basal third or without them............... 10
7 Antenna short, reaching shoulders of elytra when reclined. Each elytron with lateral margin distinctly concave in basal third. Each elytron with indistinct and irregular oblique brown spot in middle part and with indistinct, wide brown apical macula. Body length: 4.30 mm. Habitus as in Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6 – 9 . China (Sichuan)...................................... D. ruzickai View in CoL sp.n.
- Antenna longer, reaching anterior third of elytra when reclined. Each elytron with lateral margin not concave. Each elytron with or without spots.................................................................................. 8
8 Body piceous black with reddish brown lateral portions of pronotum, elytra without spots. Aedeagus as in Smetana (1985a: Fig. 28 View FIGURES 22 – 29 ). Body length: 3.80−4.00 mm. Eastern Nepal................................... D. crenatum Smetana, 1985 View in CoL
- Body red brown, head, middle portion of pronotum and variably located spots on elytra dark brown................... 9
9 Lateral margins of pronotum coarsely crenate. Aedeagus large and volumnious, distinctly longer than hind tibia, parameres not dilated medially in middle part and with obtusely triangular dorsal process apically, internal sac without strongly sclerotized structures ( Smetana 1986: Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Body length: 3.90 mm. Nepal.......................... D. cristatum Smetana, 1986 View in CoL
- Lateral margins of pronotum moderately coarsely crenate. Aedeagus small, about as long as hind tibia, parameres medially dilated in middle part and without obtusely triangular process apically, internal sac with single, strongly sclerotized structure ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 22 View FIGURES 22 – 29 ). Body length: 3.30−3.70 mm. Nepal, north-eastern India........... D. notabile ( Cameron, 1941) View in CoL
10 Pronotum markedly narrowed posteriad. Elytra slightly longer than width, without elevations. Body yellow brown, elytra brunneo-testaceous, each behind middle with oblique, whitish spot flanked by indefinite darker colour, and with two or three, mostly longitudinal, paler whitish-yellow spots in front of it. Aedeagus as in Watanabe (1991: Fig. 2−3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ), internal sac as in Smetana (2001: Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Body length: 3.50−3.6 mm. Taiwan............................... D. chiangi Smetana, 1990 View in CoL
- Pronotum gradually narrowed posteriad. Elytra distinctly longer than wide, with three very indistinct longitudinal median elevations in basal third. Body yellowish brown to reddish brown or brown; each elytron with yellow oblique spot in about apical third. Aedeagus as in Fig. 5. Body length: 2.97−3.80 mm. China (Sichuan).......................... D. emeicola View in CoL sp.n.
11 Elytral intervals without tubercles or longitudinal ridges. Head piceous-black; elytra testaceous with piceous-black apical macula covering about one fourth of elytral length on suture, but extended to almost half of elytral length laterally; each elytron with two additional, smaller darker spots at about middle. Body length 3.50 mm. North-eastern Burma............................................................................................... D. semiflavum (Jansson, 1946) View in CoL
- Elytral intervals with tubercles and longitudinal ridges.......................................................12
12 Each elytron with at least some, sometimes incospicuous, variably shaped obtuse or rounded protuberances, longitudinal ridges or small elongated tubercles....................................................................... 13
- Each elytron with numerous acute pyramidal tubercles and with two longitudinal irregular ridges with secondary tubercles near suture, one lower and less conspicuous at base and one higher and very conspicuous at about apical third........... 20
13 Subhumeral elytral elevation extended as fine ridge posteriad to almost apical third of elytral length................... 14
- Subhumeral elytral elevation, if present, not extended posteriad or short........................................ 15
14 Pronotum narrower (ratio 1.45), with less developed crenulation of lateral margins, with small latero-apical tooth. Elytra relatively narrow and elongate, appearing parallelsided. Each elytron with variable, brown oblique maculae about middle and with contrasting two or three longitudinal yellowish maculae. Aedeagus with moderately short asymmetrical parameres ( Smetana 2001: Figs. 2-3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Body length: 3.20−3.60 mm. China (Shaanxi)............................. D. gracile Smetana, 2001 View in CoL
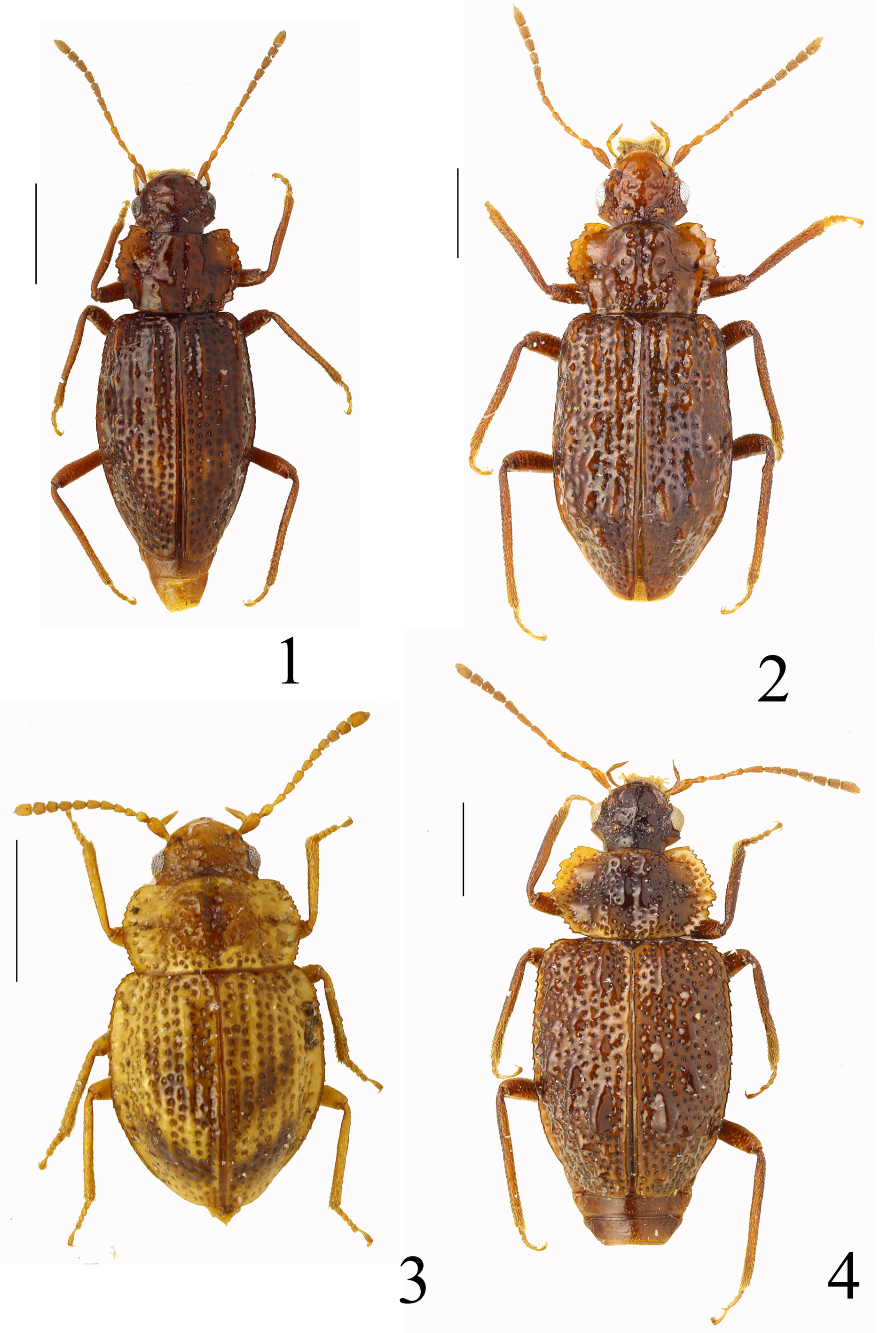
- Pronotum wider (ratio 1.7), with coarsely crenulate lateral margins, with sharp, distinctly protruding latero-apical tooth. Elytra wider, not parallelsided. Each elytron behind middle at suture with inconspicuous, irregular yellow-brown spots. Aedeagus with very long parameres ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 22 – 29 ). Body length: 3.15−4.32 mm. Habitus as in Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 4 . China (Sichuan).................................................................................................... D. bisbisinuatum View in CoL sp.n.
15 Surface of each elytron with small elongated tubercles....................................................... 16
- Surface of each elytron with indistinct to distinct narrow longitudinal ridges and sometimes with incospicuous medial and apical protuberances..................................................................................... 18
16 Body small (3.60 mm) and moderately wide. Elytra with series of yellow small spots on tubercles. Aedeagus as in Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36 – 43 . Habitus as in Fig. 8 View FIGURES 6 – 9 . Northern Vietnam..................................................... D. vesiculosum View in CoL sp.n.
- Body significantly larger, more elongated. Elytra bicoloured, yellow-brown with brown to black lateral and/or posterior third................................................................................................... 17
17 Base of each elytron with distinctly protruding shoulder, surface of elytra with series of distinct, convex tubercles. Elytra with brown lateral and posterior third portions. Body smaller, 4.25−4.31 mm. Habitus as in Fig. 9 View FIGURES 6 – 9 . China (Sichuan)................................................................................................... D. yinyang View in CoL sp.n.
- Base of each elytron with indistinctly protruding shoulder, surface of elytra with series of indistinct, slightly convex tubercles. Elytra with blackish posterior third portion. Aedeagus as in Assing (2015: Figs. 11, 19−20). Body larger, 5.00 mm. Northern Vietnam....................................................................... D. uncinatum Assing, 2015 View in CoL
18 Each elytron with indistinct longitudinal median ridges, without protuberances. Body yellowish brown to reddish brown, with yellow to yellow brown maculae, in about middle of elytra. Aedeagus as in Fig. 36 View FIGURES 36 – 43 . Body length: 4.25−4.92 mm. Habitus as in Fig. 7 View FIGURES 6 – 9 . China (Sichuan)............................................................. D. sextuberculatum View in CoL sp.n.
- Each elytron with indistinct one or two indistinct medial ridges, and with incospicuous protuberances distributed in basal and/ or apical portions of elytron. Body darker, red-brown to piceous-black........................................... 19
19 Body piceous to piceous-black, elytra paler medio-basally around suture, each elytron with small irregular, oblique yellowish stripes at about posterior third. Body smaller (3.70−3.90 mm). Apex of aedeagus broadly rounded, parameres abruptly curved mediad apically, each with apex hook-like ( Smetana 1996: Figs. 4−5 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). China (Fujian)......... D. hamatum Smetana, 1996 View in CoL
- Head dark red brown or some paler, pronotum red brown, elytra brown to red brown, each elytron with large piceous macula at about apical fourth. Body larger (4.30−4.60 mm). Apex of aedeagus subacute, apex of each paramere with acute ventro-lateral tooth ( Smetana 1996: Figs. 1, 3 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). China (Fujian).................................... D. tricuspidatum Smetana, 1996 View in CoL
20 Pronotum markedly constricted after middle, anterior part of lateral pronotal margin with very coarse crenulation. Body reddish brown. Body length: 4.90 mm. Habitus as in Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 . China (Sichuan).............................. D. draco View in CoL sp.n.
- Pronotum constricted just before posterior angles, lateral pronotal margin with moderately coarse crenulation........... 21
21 Elytra with less developed medial ridges and protuberances. Parameres of unequal length.......................... 22
- Elytra with very large and high longitudinal ridge in anterior third near suture or with very convex protuberances near suture in apical third. Parameres of about equal length.............................................................. 23
22 Lateral crenulation of pronotum slightly obtuse ( Assing 2015: Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Median protuberances in apical third of elytra well developed, as in Assing (2015: Fig. 5). Aedeagus as in Assing (2015: Figs. 14, 22). Body piceous black, except for rather narrowly brownish anterior three-fourths of lateral margins of pronotum. Body length: 5.40 mm. Northern Vietnam............................................................................................. D. dispar Assing, 2015 View in CoL
- Lateral crenulation of pronotum distinctly acute ( Assing 2015: Fig. 7 View FIGURES 6 – 9 ). Aedeagus as in Assing (2015: Fig. 25 View FIGURES 22 – 29 ). Median protuberances in apical third of elytra less developed, as in Assing (2015: Figs. 15). Aedeagus as in Assing (2015: Figs. 18, 25). Body dark brown, with dark yellowish lateral margins of pronotum. Body length: 4.80−5.40 mm. China (Gansu).......................................................................................... D. obtortum Assing, 2015 View in CoL
23 Parameres each with margin angulately dilated in about apical third ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 88). Body length: 4.60−4.90 mm. Eastern Nepal.................................................................. D. egregium Smetana, 1985 View in CoL
- Parameres each with lateral margin not angulately dilated in apical third........................................ 24
24 Body reddish brown with yellowish-brown lateral and apical portions of pronotum. Aedeagus as in Fig. 32 View FIGURES 30 – 35 . Body length: 4.75−5.20 mm. Habitus as in Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 . China (Yunnan)......................................... D. rougemonti View in CoL sp.n.
- Body piceous-black with brunneous lateral portions of pronotum, aedeagus different.............................. 25
25 Aedeagus short, moderately wide; parameres each with lateral margin distinctly emarginated just before apex, apex thus appearing hook-like ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36 – 43 ). Body length: 4.20−4.50 mm. Eastern Nepal...... D. insigne Smetana, 1985 View in CoL
- Aedeagus long and narrow; parameres each with lateral margin simple, not emarginated before apex ( Smetana 1985a: Fig. 34 View FIGURES 30 – 35 ). Body length: 4.60−4.80 mm. Nepal: Phulcoki........................................ D. spectabile Smetana, 1985 View in CoL
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Omaliinae |
|
Tribe |
Anthophagini |