Eustigmaeus crassifolius Bizarro & Johann, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24349/acarologia/20204403 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CED8BACF-97B2-4280-BF32-35A181428A3E |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E20A82AA-CDA9-4950-BFFA-C128AE36178F |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:E20A82AA-CDA9-4950-BFFA-C128AE36178F |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Eustigmaeus crassifolius Bizarro & Johann |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Eustigmaeus crassifolius Bizarro & Johann n. sp.
Zoobank: E20A82AA-CDA9-4950-BFFA-C128AE36178F
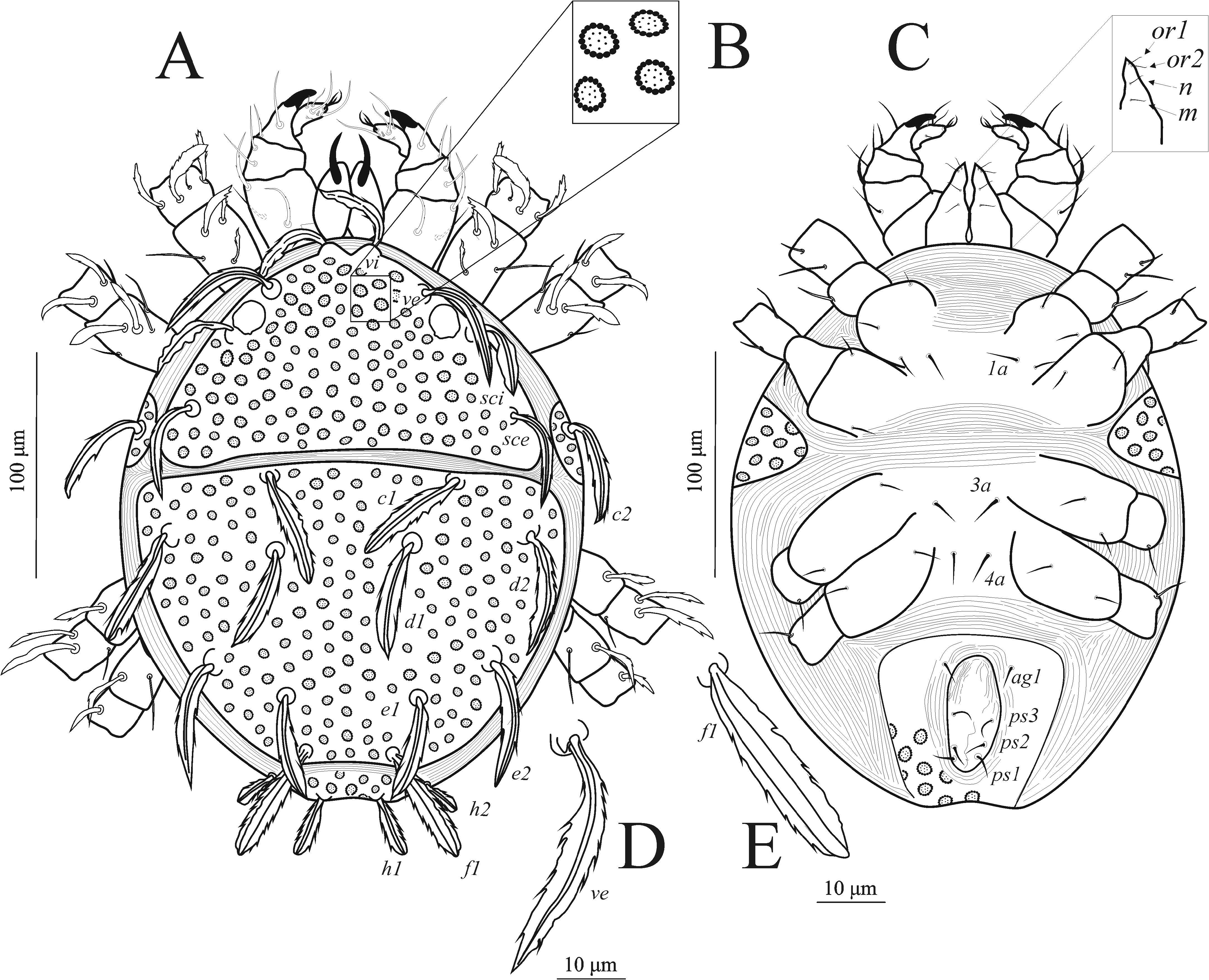
Description Female (n = 6) — Dorsum of idiosoma – ( Fig. 1A View Figure 1 ). Length of idiosoma 257 (245–262); width 213 (202–222); it is covered by two large shields, leaving exposed margin of unsclerotized cuticle around edges; shield ornamentation consists of asymmetrical oval dimples composed by small circles of equal sizes, dimples bearing vacuoles ( Fig. 1B View Figure 1 and Fig. 3 View Figure 3 ). Prodorsal shield triangular and bearing four pairs of feather-like setae vi, (ve ( Fig. 1D View Figure 1 ), sci and sce) and one pair of eyes between setae ve and sci. Humeral shields with bigger, irregular dimples and c2 inserted on it; hysterosomal shield with six pairs of feather-like setae c1 (, d1,
d2, e1, e2 and f1 ( Fig. 1E View Figure 1 )); dorsal body setae inserted on tubercles. Length of dorsal setae: vi 50 (47–53); ve 56 (50–60); sci 46 (44–50); sce 54 (52–59); c1 55 (49–55); c2 50 (47–52);
d1 57 (55–57); d2 56 (52–57); e1 53 (49–60); e2 57 (52–60); f1 53 (50–55); h1 31 (29–35);
h2 23 (23–24). Distances between dorsal setae: vi–vi 18 (14–19); ve–ve 62 (61–65); vi– ve
28 (23–31); ve–sci 28 (28–29); sci–sci 110 (108–113); sce–sce 144 (142–148); sci–sce 33
(32–36); c1–c1 70 (63–76); c1–d1 38 (36–40); c1–c2 66 (62–75); c1–d2 54 (53–58); c2–c2 189 (185–247); d1–d1 60 (57–67); d1–d2 52 (48–53); d1–e1 61 (61–67); d1–e2 62 (58–64); d2–d2
162 (154–162); d2– e2 59 (58–60); e1– e1 55 (52–56); e1– e2 40 (39–44); e2–e2 130 (122–131); e1–f1 43 (40–47); f1–f1 48 (44–51); h1–h1 21 (20–21); h2–h2 62 (58–66); h1–h2 20 (19-21). Venter of idiosoma – ( Fig. 1C View Figure 1 ). Endopodal plates, smooth, fused, separated by transverse striae between coxae II and III, bearing three pairs of setae 1 (a, 3a and 4a).
Anogenital area with unsclerotized smooth shield fused to the suranal shield; genital area with one pair of aggenital ag (1) and three pairs of pseudanal ps (1–ps3) setae, all slightly serrate to smooth; genital opening surrounded with striae. Suranal area unsclerotized, bearing irregular oval dimples equal to humeral shield situated dorsoventrally and bearing h1 and h2 setae. Measurements of setae: 1a 13 (12–14); 3a 11 (11–12); 4a 12 (11–16); ag1 12 (11–14); ps1 13 (13–15); ps2 12 (11–12); ps3 11 (10–12).
Gnathosoma – Length 77 (66–84); subcapitulum bearing smooth subcapitular setae m
9 (8–10) and n 8 (8–9) and adoral setae or1 8 (7-8) and or2 7 (7-8). Palp 66 (62–74) long
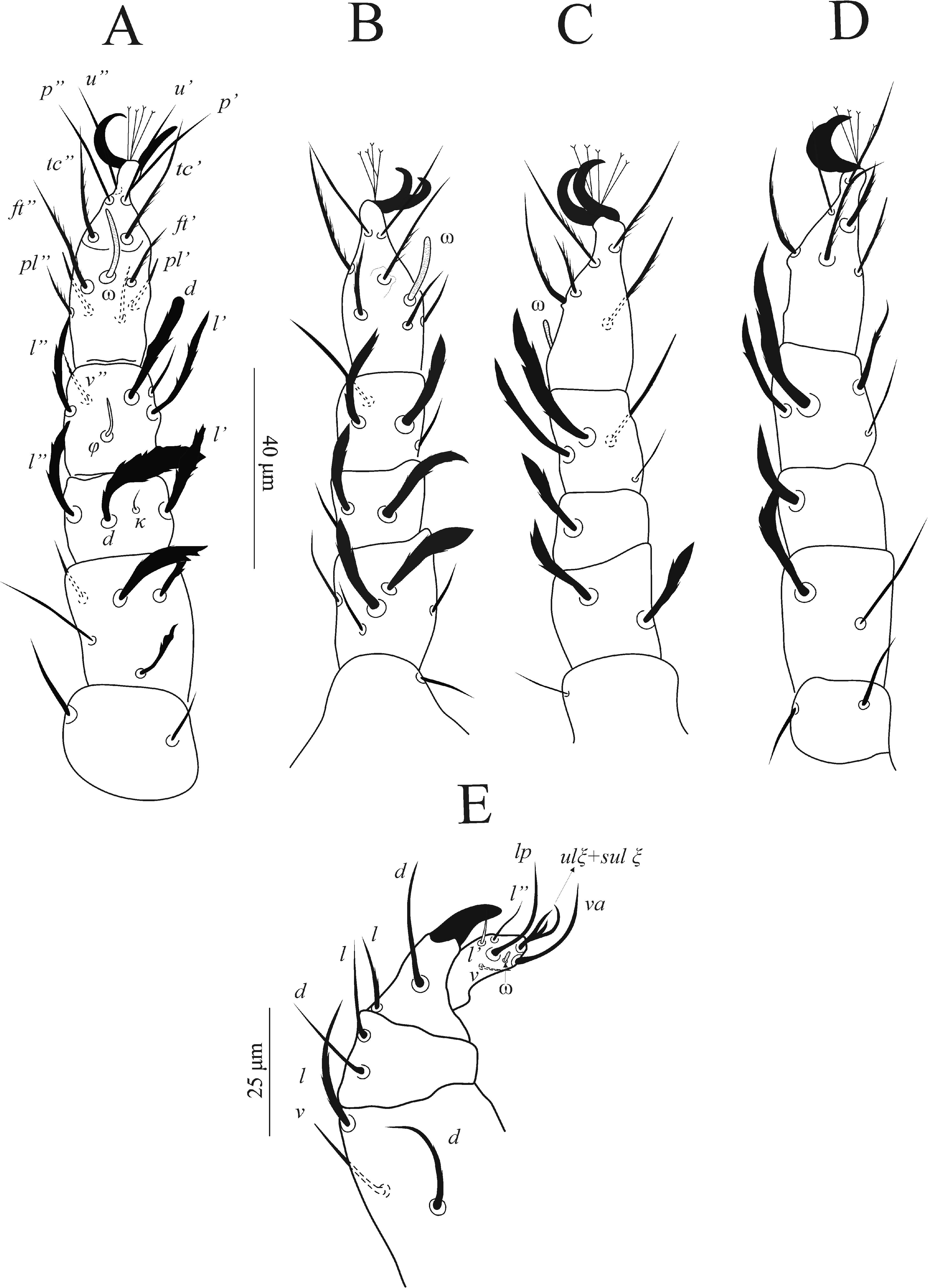
( Fig. 2E View Figure 2 ) five segmented; with thick smooth and serrate setae; palptrochanter without setae; palpfemur with three setae d (, v and l); palpgenu with two setae l (and d); palptibia with two setae (l and d) + one well-developed claw; palptarsus with five tactile setae l ′ (, l ″, v, lp and va)
view of idiosoma and subcapitulum; D – ve setae; E – f1 setae.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.