Quadrulella symmetrica (Wallich 1864) Kosakyan, Lahr, Mulot, Meisterfeld, Mitchell and Lara
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1111/cla.12167 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5685109 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039E7023-9707-7C06-FF49-9F8C349CF9E9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Quadrulella symmetrica (Wallich 1864) Kosakyan, Lahr, Mulot, Meisterfeld, Mitchell and Lara |
| status |
|
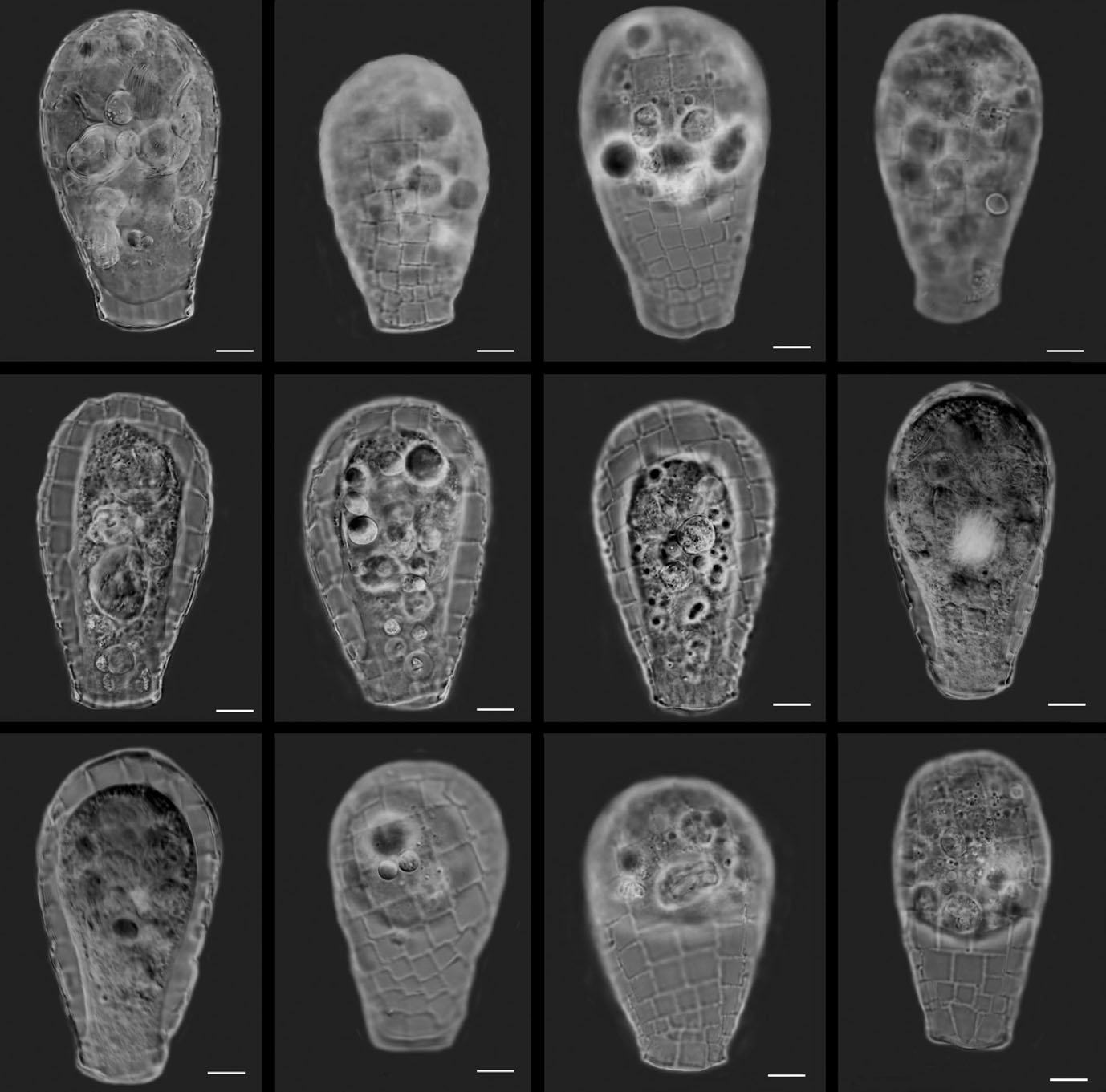
Quadrulella symmetrica (Wallich 1864) Kosakyan, Lahr, Mulot, Meisterfeld, Mitchell and Lara ( Fig. 3 View Fig. 3 )
1863 Difflugia proteiformis var. symmetrica Wallich, An. Mag. Nat. Hist. xii: 458.
1864 Difflugia pyriformis var. symmetrica Wallich, An. Mag. Nat. Hist. xiii: 232.
1864 Difflugia symmetrica Wallich, An. Mag. Nat. Hist. xiii: 245.
1871 Difflugia assulata Ehrenberg, Abh. Ak. Wis. Berlin: 249.
1871 Assulina assulata Ehrenberg, Abh. Ak. Wis. Berlin: 246.
1871 Difflugia carolensis Ehrenberg, Abh. Ak. Wis. Berlin: 250.
1871 Assulina leptolepis Ehrenberg, Abh. Ak. Wis. Berlin: 246, 274.
1875 Quadrula symmetrica Schulze, Arch. mik. Anat.: 329. (homonym)
Updated description. Test ovoid or pyriform, with a rounded posterior end, laterally compressed towards the pseudostome. Test colourless, composed of square plates, regularly arranged in rows. The plates are smaller near the aperture (4 – 5 µm), then gradually larger (reaching up to 10 – 12 µm) towards the posterior end of the test. Test length = 72 – 85 µm, breadth = 40 – 46 µm. Pseudostome 20 – 23 µm wide, often curved and bordered by a thin organic lip.
Differential diagnosis. Morphologically very similar to Q. variabilis , from which it differs by the dimension of the test and the size of scale plates (L = 72 – 85 µm, maximum plate size 10 – 12 µm in Q. symmetrica versus L = 66 – 69 µm, maximum scale size 7 – 9 µm). It can be discriminated from Q. madibai , which has plates of similar size, based on its less slender and elongated test (L/ B ratio is 2.0 – 2.3 in Q. madibai versus 1.7 – 1.9 in Q. symmetrica ). Moreover, the general outline of the test in Q. madibai is globally more tubular and does not present a distinct neck. Our molecular data clearly separate these two species (sequence divergence up to 10%).
Type. Fig. 16 in Wallich, 1863 An. Mag. Nat. Hist. XII.
Notes. Q. symmetrica is found in wet mosses ( Sphagnum or other), water streams, forest litter and soil, from all continents, except Antarctica. Detailed morphological and molecular observations are needed to clarify the true position of all described forms.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |