Molgula bouvetensis ( Michaelsen, 1904 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3920.1.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C6BB0C5A-3317-4119-9C41-02F0EC487A9E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6097440 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039E0352-FFBE-FF8C-33DD-FE62CA9A98EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Molgula bouvetensis ( Michaelsen, 1904 ) |
| status |
|
Molgula bouvetensis ( Michaelsen, 1904)
Bouvet Island, BIOMASS survey MD 24.
18/08/1980, 54°22’ S – 03° 15’ E, 150–218 m; 19/08/1980, 54°21’ S – 03°24’ E, 192–218 m; 20/08/1980, 54°28’ S – 03°21’ E, 195–203 m; 20/08/1980, 54°27’ S – 03°23’ E, 150–165 m; 21/08/1980, 54°25’S – 03°09’ E, 219– 305m.
Numerous specimens of very similar shape were collected by trawl. They are not very well fixed but in good enough condition to be compared with the 3 other groups of Antarctic Molgula with peduncle. Their general anatomy can hardly isolate them at first sight, only small differences can be pointed out but they may be sufficient to isolate and support the distinct species inhabiting a distant region. The description of Michaelsen (1904) is very detailed and corresponds to our observations.
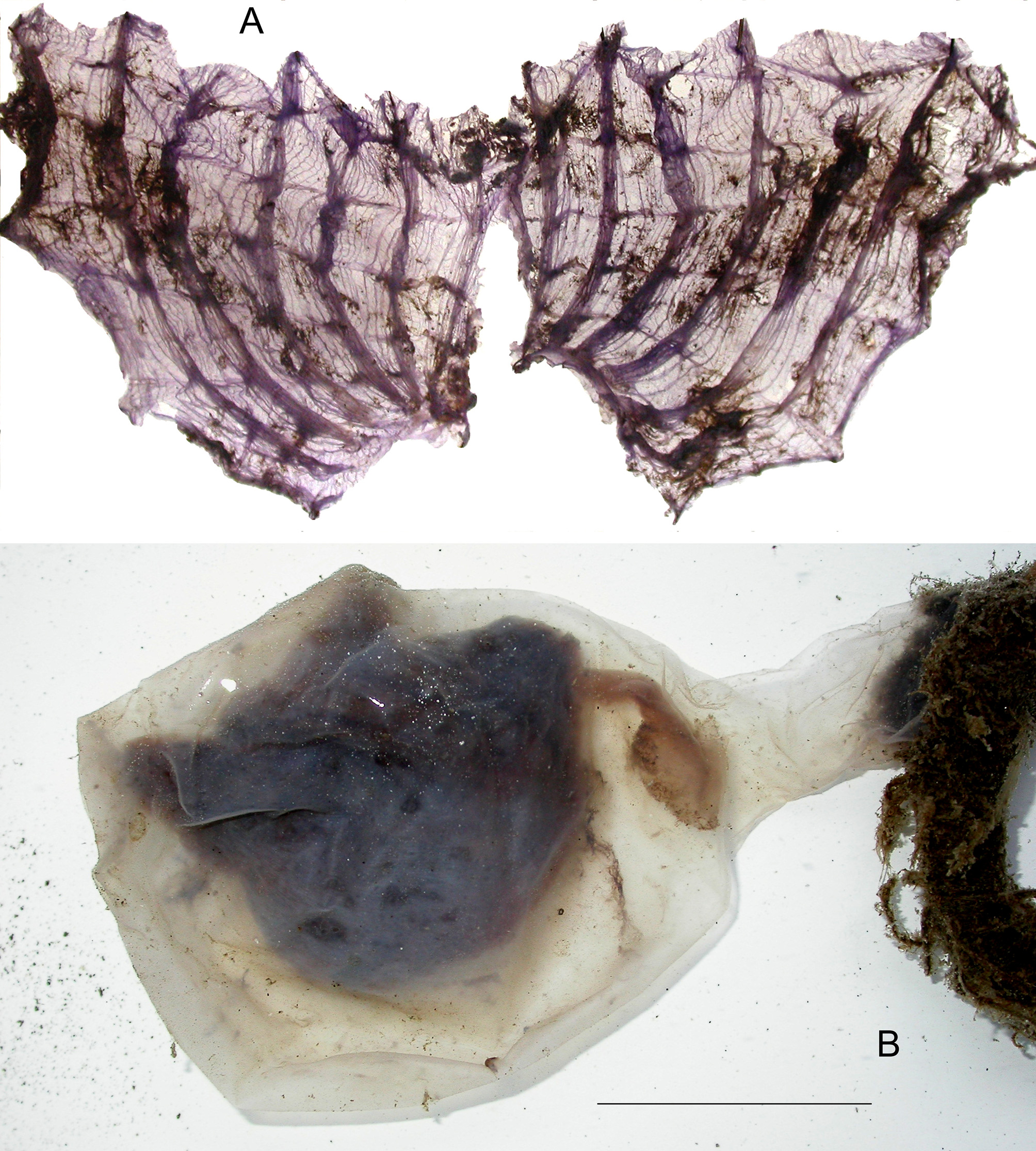
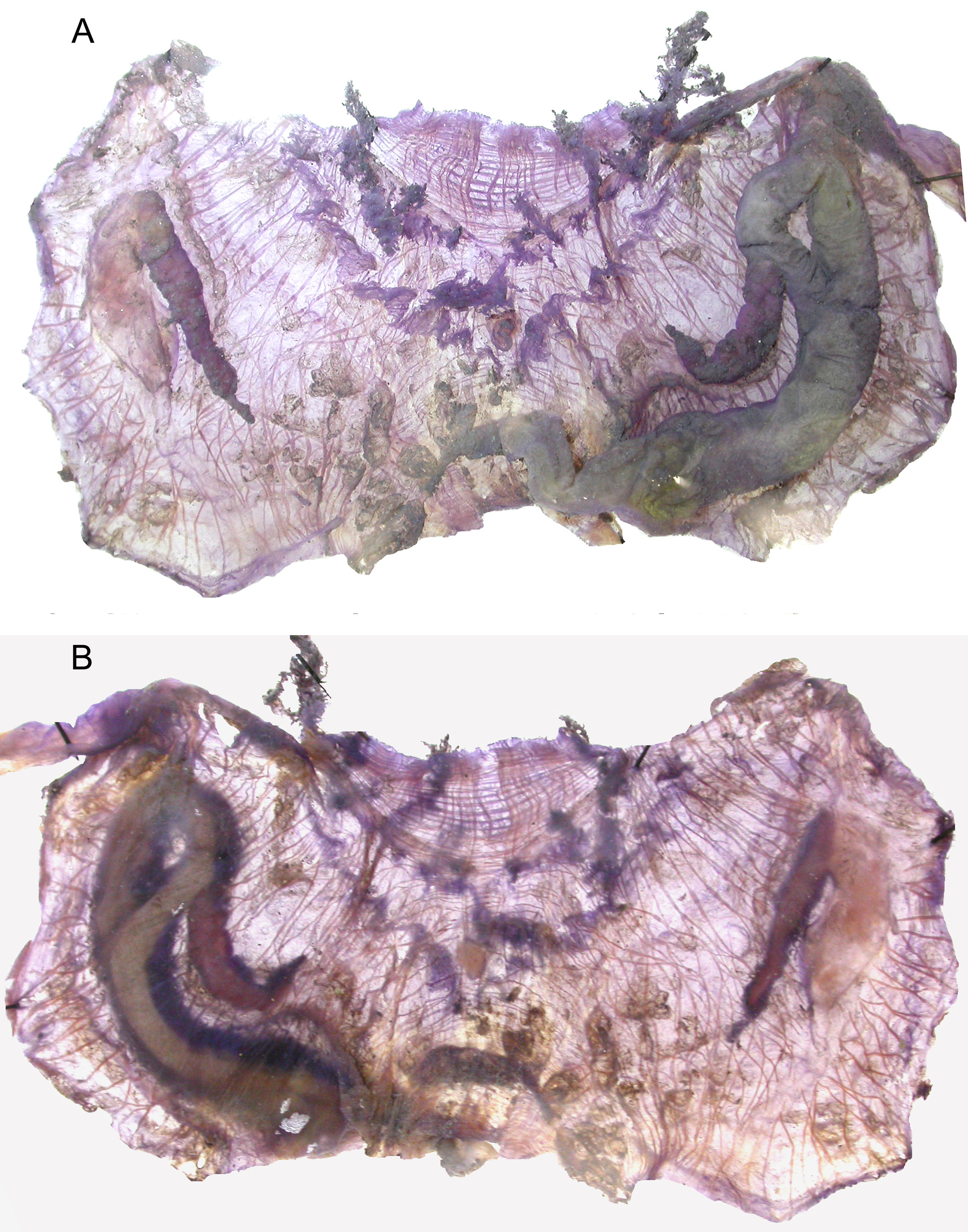
The specimens have an ovoid body 4 to 8 cm high, narrowing in a soft peduncle of variable size but not exceeding the body length. The peduncle ends in a tuft of filaments ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 B). The atrial siphon is apical, the oral siphon at 1/3 of the dorsal side. The tunic is thin, very resistant, granular at the surface and smooth on the internal side. It is often densely covered with various epibionts. The musculature of the body wall has the same bundles as in other Molgula groups, except a small difference in the middle of the body sides: the muscular ribbons are interrupted above the gonads only, but not over the kidney and the gut ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 B). There are 8 oral tentacles of irregular length, less bushy than in other groups ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 A). The dorsal tubercle has horns interiorly curved but not rolled; it opens on the left. The dorsal lamina is a high membrane with a smooth edge, prolonged on the left side of the oesophagus to join the base of the branchial folds where it forms large undulations. The branchial sac does not significantly differ from other close species. It has 7 high folds folded over the dorsal side ( Fig. 15 View FIGURE 15 A). The distribution of the longitudinal vessels is the common one, for example on a part of the tissue over the kidney in one specimen we found from the dorsal side:
….. (2 high vessels + 11 fold vessels + 5 thin vessels) +(3 high vessels + 11 folds vessels + 5 thin vessels)……There are 5 large transverse vessels on each side dorsally and an incomplete sixth at the base of the branchial sac, ventrally delimiting a seventh half row of stigmata, a structure common to all large specimens of pedunculate Molgula . The stigmata are longitudinal or irregular, cut in multiple pieces, slightly curved at the base of the folds and crossed by numerous parastigmatic vessels. The digestive loop is particularly long, curved, the two limbs closely linked except at the top of the loop ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 A,B). The oesophagus is short. The stomach is covered with the hepatic gland in two parts with flat papillae. The short rectum ends in a smooth edged anus. The rectum and the base of the branchial tissue are strongly attached to the atrial velum. The sausage –like gonads ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 A,B) are parallel to the kidney (left) or the gut loop (right) and are linked to these structures at their extremity as in Molgula pedunculata . The short sperm ducts are erect along the gonad. The oviduct is of medium length, but longer than a simple papilla.
In conclusion, specimens from Bouvet have characters in common with one or the other group from Terre Adélie and Kerguelen, but also differences that have to be taken into account as they are from a very distant region.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |